J Korean Acad Nurs Adm.
2015 Jan;21(1):32-42. 10.11111/jkana.2015.21.1.32.
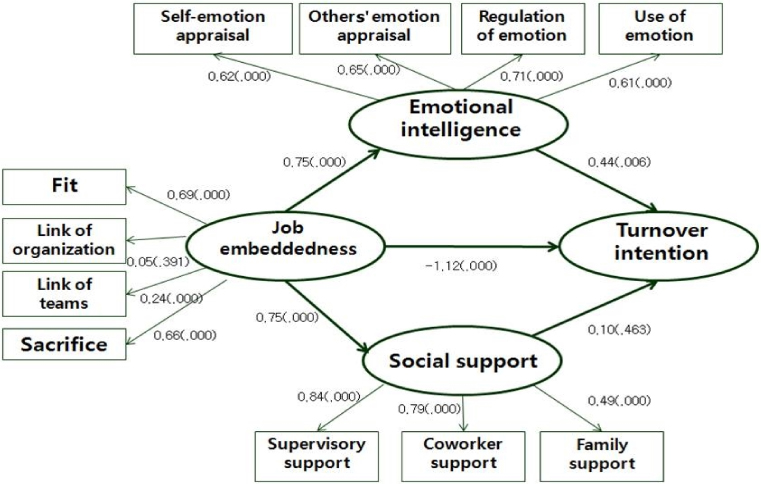
Structural Relationships among Job Embeddedness, Emotional Intelligence, Social Support and Turnover Intention of Nurses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Chung-Ang University Hospital, Korea. vikyhj@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2321277
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2015.21.1.32
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was done to elicit basic data for effective human resource management by identifying the relationships among job embeddedness, emotional intelligence, social support, and the turnover intention of Nurses.
METHODS
Research design was to build a hypothetical causal model between variables and to verify its fitness. The sample for this study was 283 nurses with careers of more than 6 months in one hospital of more than 800 beds located in Seoul. They agreed in writing and this study was approved by the Institutional Review Board. Data were analyzed using SPSS 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 program.
RESULTS
Differences in general characteristics for the variables were significant for age, marital status, education, work experience, job title, income, and department. Job embeddedness, emotional intelligence and social support were significantly correlated to turnover intention. Job embeddedness to emotional intelligence and social support showed positive effects and a negative effect to turnover intention. Emotional intelligence to turnover intention showed a positive effect, but social support was not significant.
CONCLUSION
Organizations should provide ways to minimize voluntary turnover of a competent workforce and demonstrate their competency. Also it should develop training and management programs to effectively utilize emotional intelligence.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Influence of Resilience and Job Embeddedness on Turnover Intention in General Hospital Nurses
Kyoung Ja Ko, Soo-Kyoung Lee
J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2019;25(4):362-372. doi: 10.11111/jkana.2019.25.4.362.Influence of Emotional Intelligence and Empathy on the Facilitative Communication Ability of Psychiatric Nurses
Eun-jung Oh, Myung Ha Lee, Sung Hee Ko
J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2016;25(4):283-293. doi: 10.12934/jkpmhn.2016.25.4.283.
Reference
-
1. Jones CB. The costs of nurse turnover. Part 1. An economic perspective. J Nurs Adm. 2004; 3:562–570. DOI: 10.1097/00005110-200412000-00006.2. Curry JP, Wakefield DS, Price JL, Mueller CW, McCloskey JC. Determinants of turnover among nursing department employees. Res Nurs Health. 1985; 8(4):397–411. DOI: 10.1002/nur.4770080413.3. Mobley WH. Intermediate linkages in the relationship between job satisfaction and employee turnover. J Appl Psychol. 1977; 62(2):237–240. DOI: 10.1037/0021-9010.62.2.237.4. Griffeth RW, Hom PW, Gaertner S. A meta analysis of antecedents and correlates of employee turnover: Update, moderator tests, and research implications for the millennium. J Manage. 2000; 26:463–488. DOI: 10.1016/S0149-2063(00)00043-X.5. Mitchell TR, Holtom BC, Lee TW, Erez M. Why people stay: Using job embeddedness to predict voluntary turnover. Acad Manage J. 2001; 44:1102–1121. DOI: 10.2307/3069391.6. Wong C, Law KS. The effects of leader and follower emotional intelligence of performance and attitude: An exploratory study. Leadersh Q. 2002; 13(3):243–274. DOI: 10.1016/S1048-9843(02)00099-1.7. Goleman D. Emotional intelligence. New York: Bantam Books;1995.8. Cherniss C, Adler M. Promoting emotional intelligence in organization. Alexandria. VA: American Society for Training & Development;2000.9. Ashforth BE, Humphrey RH. Emotional labor in service roles: The influence of identity. Acad Manage Rev. 1993; 18(1):88–115. DOI: 10.2307/258824.10. Han SJ. Influence of clinical nurses' emotional intelligence on their career commitment and turnover intention: Moderating role of career commitment. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2011; 11(7):418–425. DOI: 10.5392/JKCA.2011.11.7.418.11. Cohen A. An examination of the relationships between work commitment and nonwork domains. Hum Relat. 1995; 48:239–263. DOI: 10.1177/001872679504800302.12. Simons RL, Beaman J, Conger R, Chao W. Stress, support, and antisocial behavior trait as determinants of emotional well-being and parenting practices among single mothers. J Marriage Fam. 1993; 55(2):385–398. DOI: 10.2307/352809.13. Kim IS. The role of self-efficacy and social support in the relationship between emotional labor and burn out, turn over intention among hospital nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2009; 15:515–526.14. Kim HS, Yim HW, Jeong SH, Jo SJ. An association among verbal abuse, social support and turnover intention for special unit nurses in a hospital. Korean J Occup Environ Med. 2009; 21(4):388–395.15. Kim EA. The study on the relationship between job embeddedness and turnover intention. J Employ Career. 2013; 3(1):27–47.16. Park KK, Lee KE. A study on the relationship between job embeddedness and turnover intention in Korea. Korean Manag Rev. 2004; 33(5):1423–1440.17. Ko JS. A study on the moderating effect of emotional intelligence and turnover intention by job embeddedness. J Ind Econ Bus. 2012; 25(2):1789–1810.18. Kim YM, Kang YS. The relationship among career plateau, self-efficacy, job embeddedness and turnover intention of nurses in small and medium sized hospitals. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2013; 14(10):5078–5090. DOI: 10.5762/KAIS.2013.14.10.5078.19. Kang MS, Kang YS. Empowerment moderating effect between job embeddedness and intention to transfer in service industry employee. J Bus Educ. 2011; 25(3):195–214.20. Song BS, Kang MS, Kim HC. Emotional intelligence moderating effect between job embeddedness and intentional transfer. Journal of Business Education. 2010; 24(1):419–437.21. Sung TJ. Easy statistical analysis for SPSS/AMOS users. Seoul: Hakjisa;2007. p. 339–388.22. Jo KJ. A study on work-family conflict and its consequences among sales persons [dissertation]. Chungju: Chungbuk National University;2008.23. Mobley WH. Employee turnover: Cause, consequences, and control. MA: Addision-Wesley;1982.24. Moon SJ. Structural model of nurses' intentions of changing work places [dissertation]. Seoul: Kyung Hee University;2010.25. Kim JH. The effects of job embeddedness on turnover intention and organizational citizenship behavior in hospital employees: focusing on moderating effect of personality traits [dissertation]. Busan: Kyungsung University;2010.26. Chung KY, Kim WD. The effect of emotional intelligence on organizational citizenship behavior and turnover intention of hotel employees: Moderating role of leader-member exchange. J Foodserv Manage. 2008; 11(4):419–444.27. Lee MS, Jung DJ. The effects of social support on job embeddedness of hotel employee. J Tourism Leis Res. 2013; 25(8):95–112.28. Sung YH, Hwang MS, Kim KS, Chun NM. Influence of clinical nurse specialists' emotional intelligence on their organizational commitment and turnover intention. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2010; 16(3):259–266. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2010.16.3.259.29. Jeon JH, Yom YH. Roles of empowerment and emotional intelligence in the relationship between job embeddedness and turnover intension among general hospital nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2014; 20(3):302–312. DOI: 10.11111/jkana.2014.20.3.302.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Structural Model of Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention: Focusing on Organizational Characteristics, Job Satisfaction, and Job Embeddedness
- Roles of Empowerment and Emotional Intelligence in the Relationship between Job Embeddedness and Turnover Intension among General Hospital Nurses
- Effects of Self-efficacy, Career Plateau, Job Embeddedness, and Organizational Commitment on the Turnover Intention of Nurses
- Effect of Job Embeddedness and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Intention in Nurses
- Mediation Effect of Organizational Citizenship Behavior between Job Embeddedness and Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses