Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Sep;75(3):111-115.
Multiple Cancers in a Patient with Systemic Sclerosis and Aggravated Interstitial Lung Disease by Chemotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ckpaul@catholic.ac.kr
Abstract
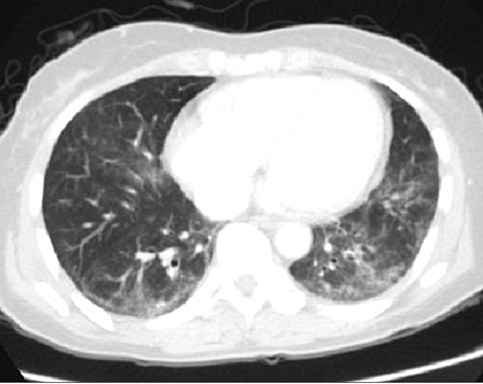
- Although the relationship between malignancy risk with systemic sclerosis (SSc) has been inconclusive, there are some previous studies for a positive correlation. Most patients with SSc have some degree of lung parenchymal involvement in the form of interstitial thickening and fibrosis. Interstitial lung disease is the most common pulmonary manifestation of SSc. Interstitial lung disease following chemotherapy (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin [FOLFOX]) is an uncommon life-threatening complication and it is induced by oxaliplatin. We report a case of multiple cancers in a patient with SSc and aggravated interstitial lung disease by chemotherapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hassoun PM. Lung involvement in systemic sclerosis. Presse Med. 2011; 40(1 Pt 2):e3–e17.2. Rosenthal AK, McLaughlin JK, Gridley G, Nyren O. Incidence of cancer among patients with systemic sclerosis. Cancer. 1995; 76:910–914.3. Kang KY, Yim HW, Kim IJ, Yoon JU, Ju JH, Kim HY, et al. Incidence of cancer among patients with systemic sclerosis in Korea: results from a single centre. Scand J Rheumatol. 2009; 38:299–303.4. Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2343–2351.5. Jeon HJ, Woo JH, Lee HY, Park KJ, Choi HJ. Adjuvant chemotherapy using the FOLFOX regimen in colon cancer. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2011; 27:140–146.6. Shimura T, Fuse N, Yoshino T, Minashi K, Tahara M, Doi T, et al. Clinical features of interstitial lung disease induced by standard chemotherapy (FOLFOX or FOLFIRI) for colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2010; 21:2005–2010.7. Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, et al. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 18th ed. New York: McGrow Hill;2012.8. Steen VD, Medsger TA Jr. Severe organ involvement in systemic sclerosis with diffuse scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:2437–2444.9. Lazarus MN, Robinson D, Mak V, Moller H, Isenberg DA. Incidence of cancer in a cohort of patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006; 45:1012–1015.10. Pearson JE, Silman AJ. Risk of cancer in patients with scleroderma. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003; 62:697–699.11. Siau K, Laversuch CJ, Creamer P, O'Rourke KP. Malignancy in scleroderma patients from south west England: a population-based cohort study. Rheumatol Int. 2011; 31:641–645.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spinal anesthesia for cesarean section in a patient with systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease: a case report
- Effect of Cyclophospharmide Pulse and Combined with Per Oral Low Dose Glucorticoid on Pulmonary Fibrosis in Patient with Sistemic Sclerosis
- A Case of Systemic Sclerosis Sine Scleroderma Presenting as Pulmonary Interstitial Fibrosis
- Interstitial Lung Disease in Connective Tissue Disease
- Short-Term Lung Function Changes and Predictors of Progressive Systemic Sclerosis–Related Interstitial Lung Disease