J Rheum Dis.
2014 Dec;21(6):282-288. 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.6.282.
Interstitial Lung Disease in Connective Tissue Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwsong@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2222931
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2014.21.6.282
Abstract
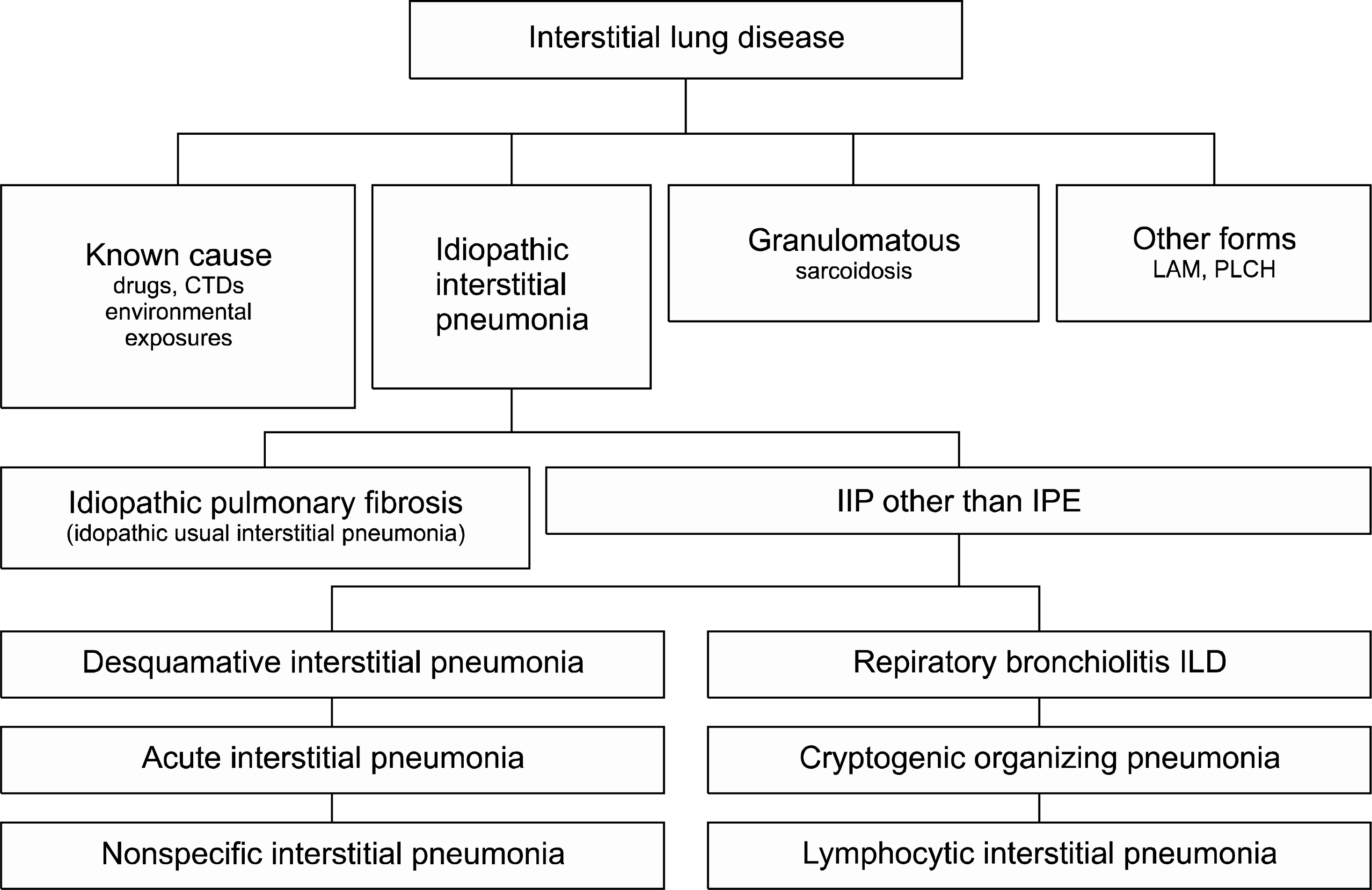
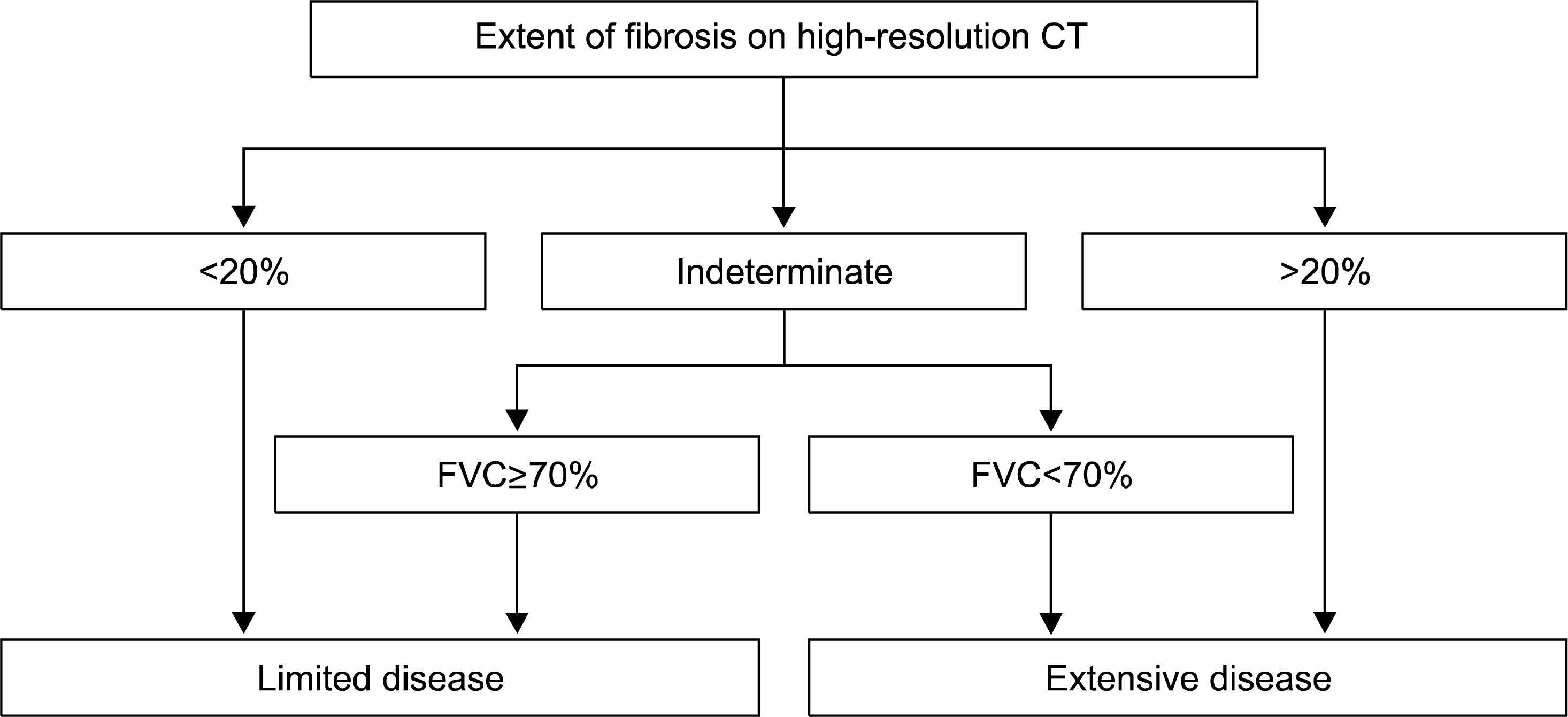
- Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is one of the most serious pulmonary complications of connective tissue diseases (CTDs), resulting in significant morbidity and mortality. ILD is frequently seen in CTDs, particularly systemic sclerosis, polymyositis/dermatomyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis; however, determining that ILD is associated with an established CTD requires the exclusion of alternative causes. Non-specific interstitial pneumonia is the most commonly observed histopathological pattern in CTD-associated ILD (CTD-ILD) except for rheumatoid arthritis, characterized by a higher frequency of usual interstitial pneumonia. Although CTD-ILD usually shows a stable or slowly progressive course, a subgroup exhibits a more severe and progressive course and requires pharmacologic intervention. Treatment strategies typically involve empirical use of immunosuppressive therapies, although a large, randomized study has examined the impact of immunosuppressive therapy for systemic sclerosis associated ILD and should also address comorbid conditions considering implementation of adjunctive therapeutic strategies. A subgroup of patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia who meet some, but not all, diagnostic criteria for CTDs were identified and well organized prospective studies are needed in to better determine whether evidence of autoimmunity in those plays a part in the evolution to well-defined CTDs or carries prognostic significance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Radiologic approach and progressive exploration of connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease: meeting the curiosity of rheumatologists
Hyeji Jeon, Bo Da Nam, Chong-Hyeon Yoon, Hyun-Sook Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2024;31(1):3-14. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2023.0042.
Reference
-
1. American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 165:277–304.2. Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, et al. ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Committee on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/ JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011; 183:788–824.3. Olson AL, Brown KK, Fischer A. Connective tissue disease-associated lung disease. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2012; 32:513–36.
Article4. Gochuico BR, Avila NA, Chow CK, Novero LJ, Wu HP, Ren P, et al. Progressive preclinical interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Intern Med. 2008; 168:159–66.
Article5. Launay D, Remy-Jardin M, Michon-Pasturel U, Mastora I, Hachulla E, Lambert M, et al. High resolution computed tomography in fibrosing alveolitis associated with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2006; 33:1789–801.6. Uffmann M, Kiener HP, Bankier AA, Baldt MM, Zontsich T, Herold CJ. Lung manifestation in asymptomatic patients with primary Sjö gren syndrome: assessment with high resolution CT and pulmonary function tests. J Thorac Imaging. 2001; 16:282–9.7. Dawson JK, Fewins HE, Desmond J, Lynch MP, Graham DR. Fibrosing alveolitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis as assessed by high resolution computed tomography, chest radiography, and pulmonary function tests. Thorax. 2001; 56:622–7.
Article8. Tzelepis GE, Toya SP, Moutsopoulos HM. Occult connective tissue diseases mimicking idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Eur Respir J. 2008; 31:11–20.
Article9. Fischer A. Interstitial lung disease: a rheumatologist's perspective. J Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 15:95–9.10. Vij R, Noth I, Strek ME. Autoimmune-featured interstitial lung disease: a distinct entity. Chest. 2011; 140:1292–9.11. Fischer A, West SG, Swigris JJ, Brown KK, du Bois RM. Connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: a call for clarification. Chest. 2010; 138:251–6.12. Park IN, Kim DS, Shim TS, Lim CM, Lee SD, Koh Y, et al. Acute exacerbation of interstitial pneumonia other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2007; 132:214–20.
Article13. Mittoo S, Gelber AC, Christopher-Stine L, Horton MR, Lechtzin N, Danoff SK. Ascertainment of collagen vascular disease in patients presenting with interstitial lung disease. Respir Med. 2009; 103:1152–8.
Article14. Wells AU. Pulmonary function tests in connective tissue disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 28:379–88.
Article15. Hwang JH, Misumi S, Sahin H, Brown KK, Newell JD, Lynch DA. Computed tomographic features of idiopathic fibrosing interstitial pneumonia: comparison with pulmonary fibrosis related to collagen vascular disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2009; 33:410–5.16. Assayag D, Elicker BM, Urbania TH, Colby TV, Kang BH, Ryu JH, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: radiologic identification of usual interstitial pneumonia pattern. Radiology. 2014; 270:583–8.
Article17. Park JH, Kim DS, Park IN, Jang SJ, Kitaichi M, Nicholson AG, et al. Prognosis of fibrotic interstitial pneumonia: idiopathic versus collagen vascular disease-related subtypes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 175:705–11.18. Lee HK, Kim DS, Yoo B, Seo JB, Rho JY, Colby TV, et al. Histopathologic pattern and clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Chest. 2005; 127:2019–27.
Article19. Kim EA, Lee KS, Johkoh T, Kim TS, Suh GY, Kwon OJ, et al. Interstitial lung diseases associated with collagen vascular diseases: radiologic and histopathologic findings. Radiographics. 2002; (22 Spec No):S151–65.
Article20. Won Huh J, Soon Kim D, Keun Lee C, Yoo B, Bum Seo J, Kitaichi M, et al. Two distinct clinical types of interstitial lung disease associated with polymyositis-dermatomyositis. Respir Med. 2007; 101:1761–9.
Article21. Ito I, Nagai S, Kitaichi M, Nicholson AG, Johkoh T, Noma S, et al. Pulmonary manifestations of primary Sjogren's syndrome: a clinical, radiologic, and pathologic study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:632–8.22. Leslie KO, Trahan S, Gruden J. Pulmonary pathology of the rheumatic diseases. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 28:369–78.
Article23. Song JW, Do KH, Kim MY, Jang SJ, Colby TV, Kim DS. Pathologic and radiologic differences between idiopathic and collagen vascular disease-related usual interstitial pneumonia. Chest. 2009; 136:23–30.
Article24. Bouros D, Wells AU, Nicholson AG, Colby TV, Polychronopoulos V, Pantelidis P, et al. Histopathologic subsets of fibrosing alveolitis in patients with systemic sclerosis and their relationship to outcome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 165:1581–6.
Article25. Kim EJ, Elicker BM, Maldonado F, Webb WR, Ryu JH, Van Uden JH, et al. Usual interstitial pneumonia in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2010; 35:1322–8.
Article26. Song JW, Lee HK, Lee CK, et al. Clinical course and outcome of rheumatoid arthritis-related usual interstitial pneumonia. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2013; 30:103–12.27. Goh NS, Desai SR, Veeraraghavan S, Hansell DM, Copley SJ, Maher TM, et al. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: a simple staging system. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 177:1248–54.28. Hant FN, Ludwicka-Bradley A, Wang HJ, Li N, Elashoff R, Tashkin DP, et al. Scleroderma Lung Study Research Group. Surfactant protein D and KL-6 as serum biomarkers of interstitial lung disease in patients with scleroderma. J Rheumatol. 2009; 36:773–80.
Article29. Kowal-Bielecka O, Kowal K, Highland KB, Silver RM. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in scleroderma interstitial lung disease: technical aspects and clinical correlations: review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 40:73–88.
Article30. Bonella F, Volpe A, Caramaschi P, Nava C, Ferrari P, Schenk K, et al. Surfactant protein D and KL-6 serum levels in systemic sclerosis: correlation with lung and systemic involvement. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2011; 28:27–33.31. Corte TJ, Copley SJ, Desai SR, Zappala CJ, Hansell DM, Nicholson AG, et al. Significance of connective tissue disease features in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2012; 39:661–8.
Article32. Hoyles RK, Ellis RW, Wellsbury J, Lees B, Newlands P, Goh NS, et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of corticosteroids and intravenous cyclophosphamide followed by oral azathioprine for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:3962–70.
Article33. Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ, Goldin J, Roth MD, Furst DE, et al. Scleroderma Lung Study Research Group. Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:2655–66.34. Ando K, Motojima S, Doi T, Nagaoka T, Kaneko N, Aoshima M, et al. Effect of glucocorticoid monotherapy on pulmonary function and survival in Japanese patients with scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease. Respir Investig. 2013; 51:69–75.
Article35. Horai Y, Isomoto E, Koga T, Okada A, Kawashiri SY, Tamai M, et al. Early diagnosis and treatment for remission of clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis complicated by rapid progress interstitial lung disease: a report of two cases. Mod Rheumatol. 2013; 23:190–4.
Article36. Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ, Roth MD, Furst DE, Silver RM, et al. Scleroderma Lung Study Research Group. Effects of 1-year treatment with cyclophosphamide on outcomes at 2 years in scleroderma lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 176:1026–34.
Article37. Yamasaki Y, Yamada H, Yamasaki M, Ohkubo M, Azuma K, Matsuoka S, et al. Intravenous cyclophosphamide therapy for progressive interstitial pneumonia in patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007; 46:124–30.
Article38. Wilkes MR, Sereika SM, Fertig N, Lucas MR, Oddis CV. Treatment of antisynthetase-associated interstitial lung disease with tacrolimus. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:2439–46.
Article39. Swigris JJ, Olson AL, Fischer A, Lynch DA, Cosgrove GP, Frankel SK, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil is safe, well tolerated, and preserves lung function in patients with connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease. Chest. 2006; 130:30–6.
Article40. Bérezné A, Ranque B, Valeyre D, Brauner M, Allanore Y, Launay D, et al. Therapeutic strategy combining intravenous cyclophosphamide followed by oral azathioprine to treat worsening interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis: a retrospective multicenter open-label study. J Rheumatol. 2008; 35:1064–72.41. Kotani T, Takeuchi T, Makino S, Hata K, Yoshida S, Nagai K, et al. Combination with corticosteroids and cyclosporin-A improves pulmonary function test results and chest HRCT findings in dermatomyositis patients with acute/subacute interstitial pneumonia. Clin Rheumatol. 2011; 30:1021–8.
Article42. Fischer A, Brown KK, Du Bois RM, Frankel SK, Cosgrove GP, Fernandez-Perez ER, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil improves lung function in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. 2013; 40:640–6.
Article43. Keir GJ, Maher TM, Ming D, Abdullah R, de Lauretis A, Wickremasinghe M, et al. Rituximab in severe, treatment-refractory interstitial lung disease. Respirology. 2014; 19:353–9.
Article44. Saggar R, Khanna D, Furst DE, Belperio JA, Park GS, Weigt SS, et al. Systemic sclerosis and bilateral lung transplantation: a single centre experience. Eur Respir J. 2010; 36:893–900.
Article45. Schachna L, Medsger TA Jr, Dauber JH, Wigley FM, Braunstein NA, White B, et al. Lung transplantation in scleroderma compared with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:3954–61.
Article46. Salhi B, Troosters T, Behaegel M, Joos G, Derom E. Effects of pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with restrictive lung diseases. Chest. 2010; 137:273–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Interstitial Lung Diseases: Respiratory Review of 2013
- Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease
- Impact of Rheumatologic Consultations on Detecting Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Connective Tissue Disease
- Pathological interpretation of connective tissue disease-associated lung diseases
- Interstitial Lung Diseases in Collagen Vascular Diseases