Tuberc Respir Dis.
2011 Dec;71(6):470-475.
A Case of Interstitial Pneumonitis with Acute Live Injury Caused by Herbal Medicine Made from Golden Thread
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mp.chung@samsung.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- So far more than 350 drugs have been reported to be the cause for lung injury and the incidence tends to increase. Although infiltrative lung disease is the most common pattern of drug-induced lung injury, it can appear in the form of alveolar changes, vasculitis and other injury. Herbal medicine also has been known as a cause for interstitial pneumonitis, but it is difficult to identify the key herbal medicine because of the complex components of the contents. Till date, there is no report of pneumonitis caused by golden thread. Here we report a case of a 54-year-old male who developed interstitial pneumonitis with acute liver injury caused by herbal medicine made from golden thread.
MeSH Terms
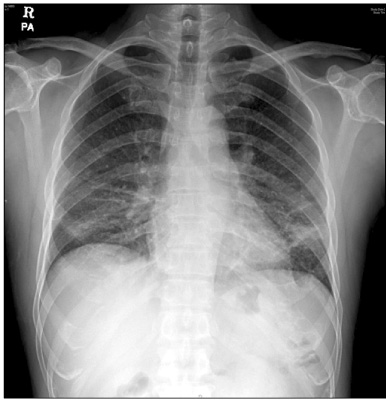
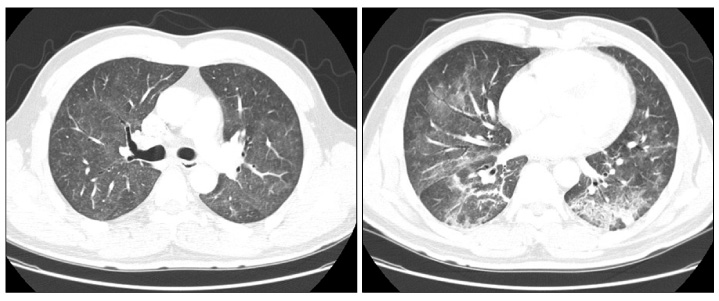
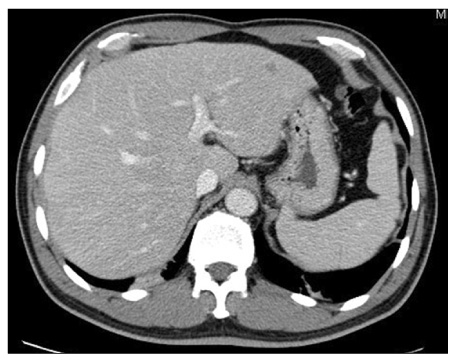
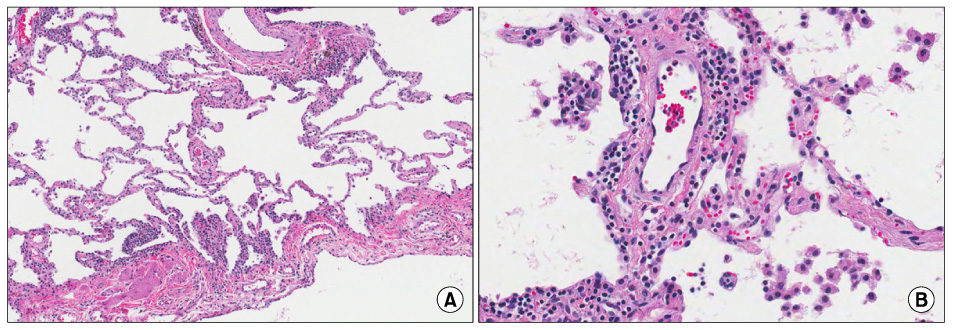
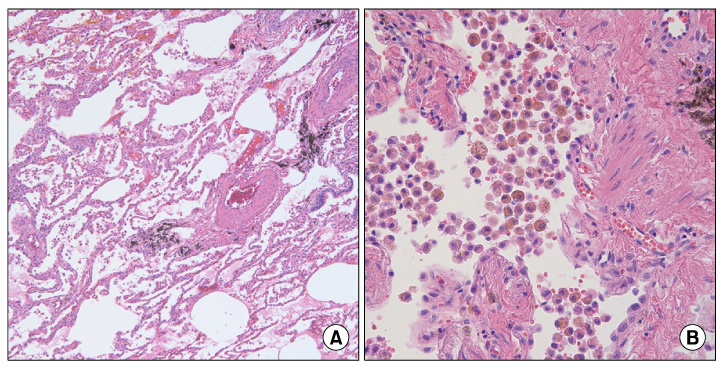
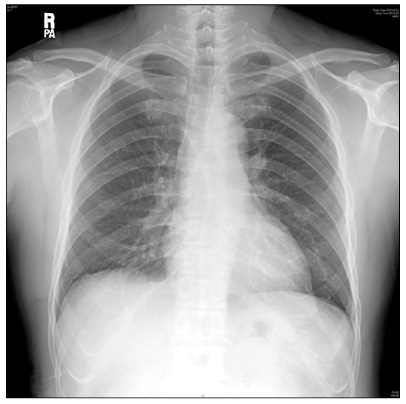
Figure
Reference
-
1. Camus P, Bonniaud P, Fanton A, Camus C, Baudaun N, Foucher P. Drug-induced and iatrogenic infiltrative lung disease. Clin Chest Med. 2004. 25:479–519.2. Tsukiyama K, Tasaka Y, Nakajima M, Hino J, Nakahama C, Okimoto N, et al. A case of pneumonitis due to sho-saiko-to. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1989. 27:1556–1561.3. Kim TG, Kim JS, Shin EA. Mixed herbal medicine induced diffuse infiltrative lung disease: the HRCT and histopathologic findings. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2010. 63:519–524.4. Takeshita K, Saisho Y, Kitamura K, Kaburagi N, Funabiki T, Inamura T, et al. Pneumonitis induced by ou-gon (scullcap). Intern Med. 2001. 40:764–768.5. Sakamoto O, Ichikado K, Kohrogi H, Suga M. Clinical and CT characteristics of Chinese medicine-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Respirology. 2003. 8:344–350.6. Shiota Y, Wilson JG, Matsumoto H, Munemasa M, Okamura M, Hiyama J, et al. Adult respiratory distress syndrome induced by a Chinese medicine, Kamisyoyosan. Intern Med. 1996. 35:494–496.7. Matsuno O, Okubo T, Hiroshige S, Takenaka R, Ono E, Ueno T, et al. Drug-induced lymphocyte stimulation test is not useful for the diagnosis of drug-induced pneumonia. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2007. 212:49–53.8. Yamawaki I, Katsura H, Taira M, Kadoriku C, Hashimoto I, Chiyotani A, et al. Six patients with pneumonitis related to blended Chinese traditional medicines. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. 34:1331–1336.9. Kang SH, Kim JI, Jeong KH, Ko KH, Ko PG, Hwang SW, et al. Clinical characteristics of 159 cases of acute toxic hepatitis. Korean J Hepatol. 2008. 14:483–492.10. Xie W, Zhao Y, Zhang Y. Traditional chinese medicines in treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. 2011:726723.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Recurrent Pneumonitis Caused by Bojungikgitang(Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang)
- A Case of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Complicated by Acute Pancreatitis and Interstitial Pneumonitis
- A Case of Life-Threatening Acute Kidney Injury with Toxic Encephalopathy Caused by Dioscorea quinqueloba
- A Case of Interstitial Pneumonitis after Interferon Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C
- A Case of Carbamazepine-Induced Acute Interstitial Nephritis