Tuberc Respir Dis.
2008 Nov;65(5):416-420.
A Case of Recurrent Pneumonitis Caused by Bojungikgitang(Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. choisj@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- Many classes of drug, such as antineoplastic drugs and antiarrhythmic drugs, have potential to induce interstitial lung disease. Herbal medicines are also believed to have the potential to induce pneumonitis. However, to our knowledge, there are no reports of pneumonitis caused by herbal medications in the Korean medical database. We report a case of recurrent pneumonitis caused by a self rechallenge of the Herbal medicine Bojungikgitang (Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang : Hochu-ekki-to).
MeSH Terms
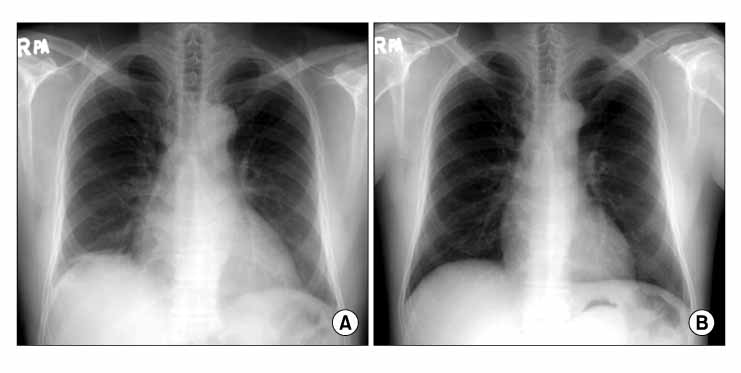
Figure
Reference
-
1. Murray JF, Nadel JA, Mason RJ, Broaddus VC. Textbook of respiratory medicine. 2005. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders.2. Tsukiyama K, Tasaka Y, Nakajima M, Hino J, Nakahama C, Okimoto N, et al. A case of pneumonitis due to sho-saiko-to. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1989. 27:1556–1561.3. Maruyama Y, Maruyama M, Takada T, Haraguchi M, Uno K. A case of pneumonitis due to Rikkunshi-to. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1994. 32:84–89.4. Temaru R, Yamashita N, Matsui S, Ohta T, Kawasaki A, Kobayashi M. A case of drug induced pneumonitis caused by saiboku-To. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1994. 32:485–490.5. Takeshita K, Saisho Y, Kitamura K, Kaburagi N, Funabiki T, Inamura T, et al. Pneumonitis induced by ou-gon (scullcap). Intern Med. 2001. 40:764–768.6. Katayama H, Hamada H, Yokoyama A, Kadowaki T, Ito R, Higaki J. A case of interstitial pneumonia caused by gosha-jinki-gan. Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2004. 41:675–678.7. Hata Y, Uehara H. A case where herbal medicine sho-seiryu-to induced interstitial pneumonitis. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2005. 43:23–31.8. Toyoshima M, Chida K, Suda T, Harada M. A case of pneumonitis caused by Seisin-renshi-in, herbal medicine. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2008. 46:31–34.9. Kawasaki A, Mizushima Y, Kunitani H, Kitagawa M, Kobayashi M. A useful diagnostic method for drug-induced pneumonitis: a case report. Am J Chin Med. 1994. 22:329–336.10. Yum HK, Han SH, Kim HG, Lee HK, Jeon WK, Lee YW, et al. A case of gold induced hypersensitivity pneumonitis diagnosed by lymphocyte stimulation test with gold. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1994. 41:546–551.11. Matsuno O, Okubo T, Hiroshige S, Takenaka R, Ono E, Ueno T, et al. Drug-induced lymphocyte stimulation test is not useful for the diagnosis of drug-induced pneumonia. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2007. 212:49–53.12. Shiota Y, Wilson JG, Matsumoto H, Munemasa M, Okamura M, Hiyama J, et al. Adult respiratory distress syndrome induced by a Chinese medicine, Kamisyoyosan. Intern Med. 1996. 35:494–496.13. Ikegami F, Sumino M, Fujii Y, Akiba T, Satoh T. Pharmacology and toxicology of Bupleurum root-containing Kampo medicines in clinical use. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2006. 25:481–494.14. Inoue T, Tanaka E, Sakuramoto M, Minakuchi M, Maeda Y, Tanizawa K, et al. A case of drug-induced pleuritis, possibly due to Hochuekkito. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2007. 45:258–261.15. Akira M, Ishikawa H, Yamamoto S. Drug-induced pneumonitis: thin-section CT findings in 60 patients. Radiology. 2002. 224:852–860.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of QI Activity Evaluation Framework Based on PDCA and Case Study on Quality Improvement Activities
- A Case Study on Quality Improvement of the Food Services for Staff : Focused on Food Waste Reducing
- Quality Improvement in Neonatal Intensive Care Units
- Quality improvement in pediatric care
- Foreign Body Granuloma Following Hwangryunhaedok-tang Pharmacopuncture for Postherpetic Neuralgia