J Rheum Dis.
2011 Dec;18(4):292-296. 10.4078/jrd.2011.18.4.292.
A Case of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Complicated by Acute Pancreatitis and Interstitial Pneumonitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Busan Medical Center, Busan, Korea. jiny0122a@daum.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Busan Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2223133
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2011.18.4.292
Abstract
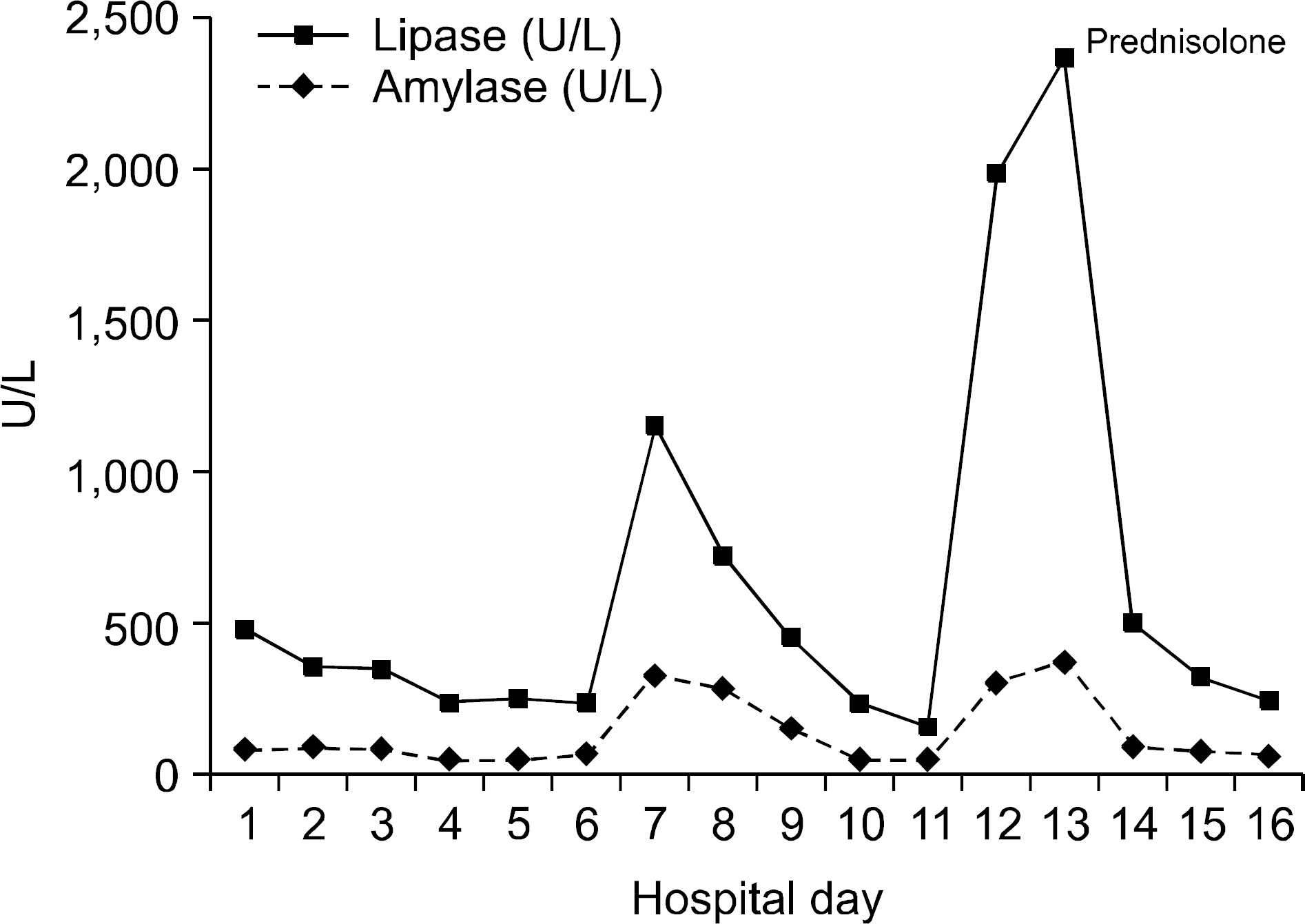
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP) is a systemic vasculitis involving the skin, gut, joint and kidney that is characterized by immunoglobulin A (IgA)-dominant immune deposits in target organs. Gastrointestinal involvement is known to be relatively common, but acute pancreatitis and pulmonary involvement are rare in Henoch-Schonlein purpura. We experienced a case of a 46-year-old man who developed adult-onset HSP complicated by acute pancreatitis and interstitial pneumonitis. The patient received corticosteroid therapy at a dosage of 0.5 mg/kg. After corticosteroid therapy, patient's symptoms improved. We report here the first case of HSP complicated by acute pancreatitis and interstitial pneumonitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
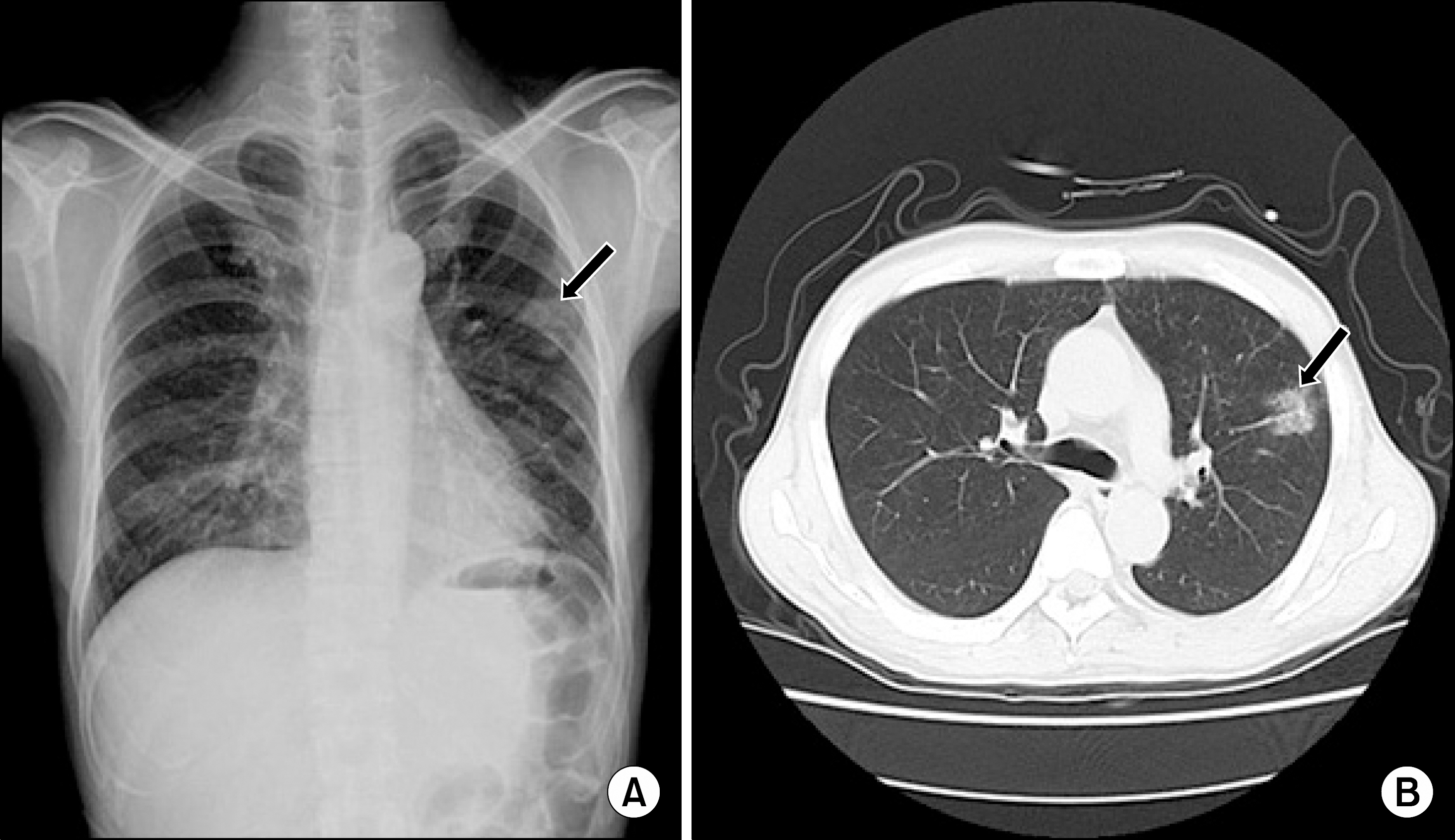
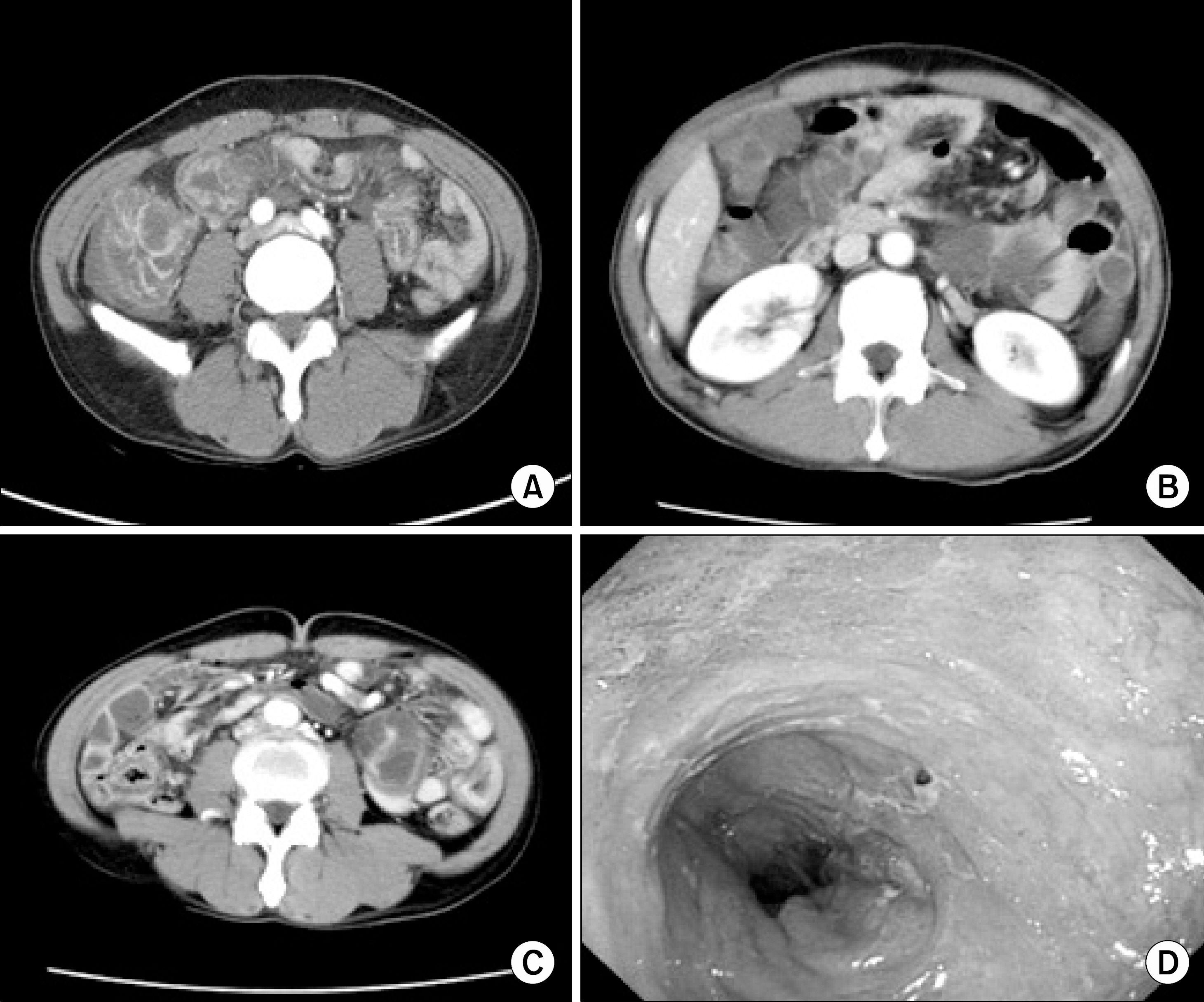
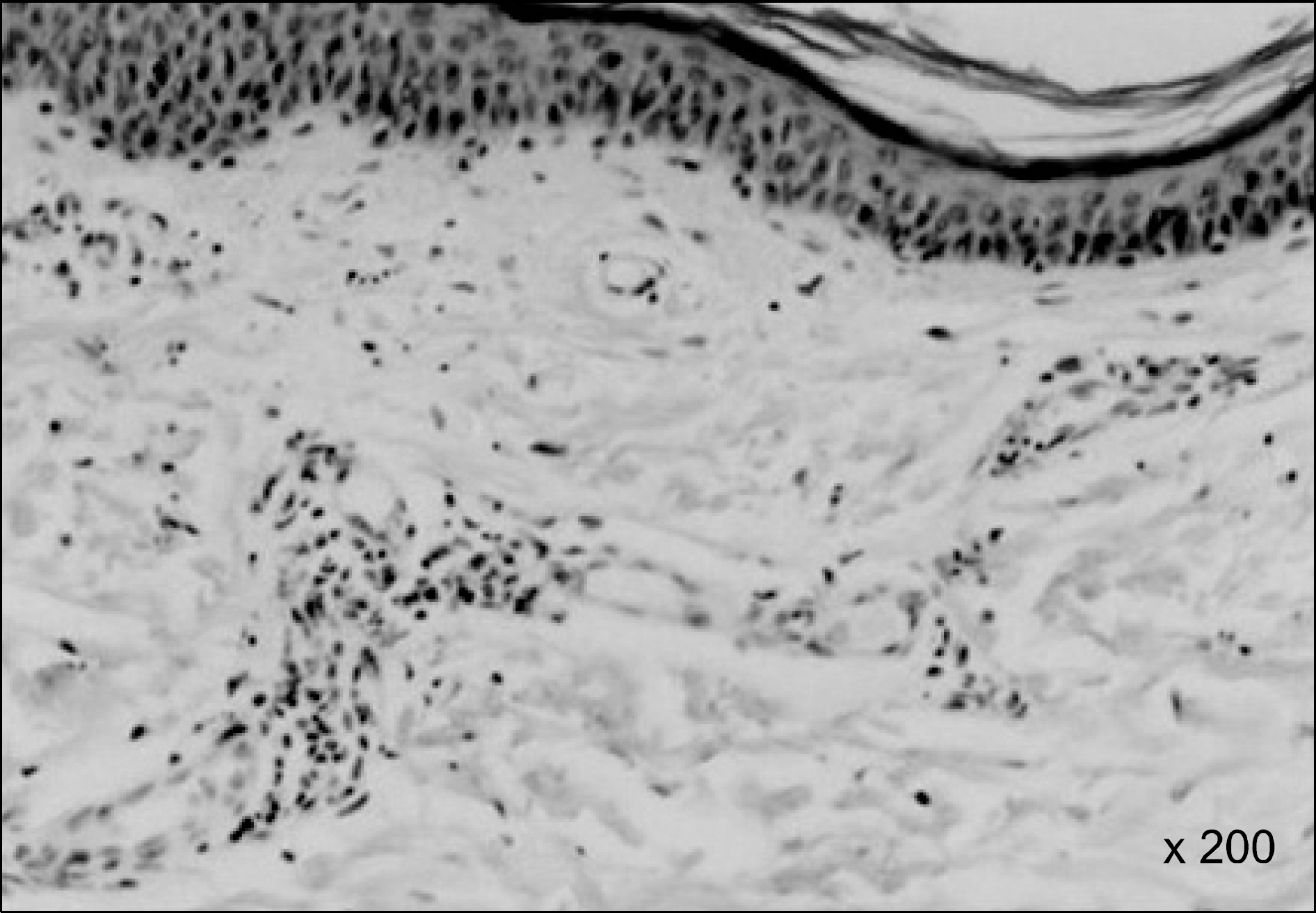
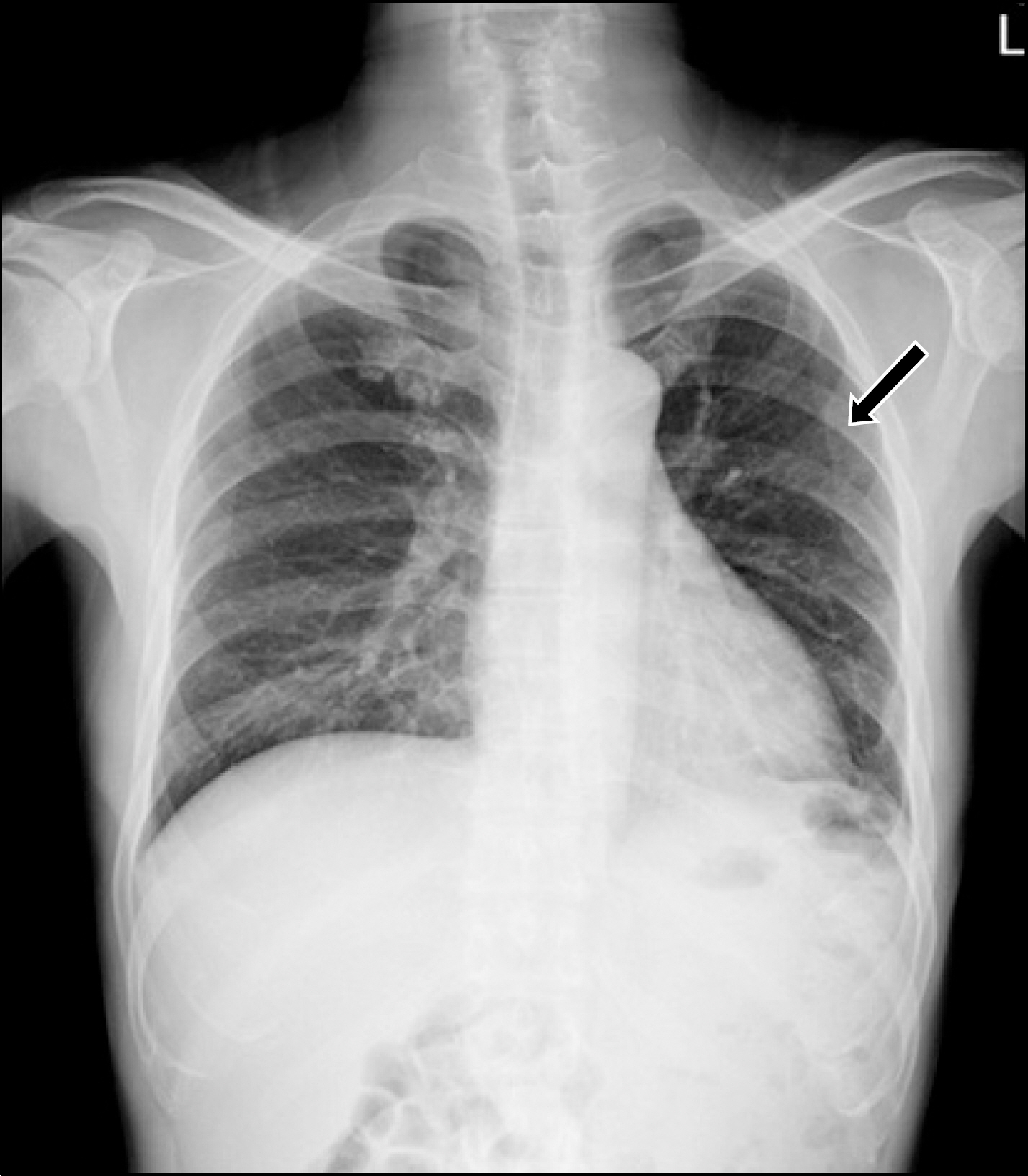
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Saulsbury FT. Henoch-Schö nlein purpura. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001; 13:35–40.2. Saulsbury FT. Heavy and light chain composition of serum IgA and IgA rheumatoid factor in Henoch-Schö nlein purpura. Arthritis Rheum. 1992; 35:1377–80.3. Choong CK, Beasley SW. Intra-abdominal manifestations of Henoch-Schö nlein purpura. J Paediatr Child Health. 1998; 34:405–9.4. Cheung KM, Mok F, Lam P, Chan KH. Pancreatitis associated with Henoch-Schonlein purpura. J Paediatr Child Health. 2001; 37:311–3.
Article5. Frigui M, Lehiani D, Koubaa M, Bouaziz Z, Abid B, Beyrouti I, et al. Acute pancreatitis as initial manifestation of adult Henoch-Schö nlein purpura: report of a case and review of literature. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 23:189–92.6. Nadrous HF, Yu AC, Specks U, Ryu JH. Pulmonary involvement in Henoch-Schö nlein purpura. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004; 79:1151–7.7. Sohagia AB, Gunturu SG, Tong TR, Hertan HI. Henoch-schonlein purpura-a case report and review of the literature. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2010; 2010; 597648.
Article8. Kang Y, Ha YJ, Lee KH, Jung SY, Lee SW, Lee SK, et al. Clinical manifestations of Korean adult patients with Henoch-schö nlein purpura. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2010; 17:133–42.9. Chen SY, Kong MS. Gastrointestinal manifestations and complications of Henoch-Schö nlein purpura. Chang Gung Med J. 2004; 27:175–81.10. Toskin KD. Syndrome of hemorrhagic pancreatitis as a manifestation of Schö nlein-Henoch disease. Klin Khir. 1965; 11:65–7.11. Rai A, Nast C, Adler S. Henoch-Schö nlein purpura nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10:2637–44.12. Saulsbury FT. Henoch-Schö nlein purpura. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010; 22:598–602.13. Lim YS, Ryu JK, Lee HC, Kim YT, Yoon YB, Kim CY. Comparison of etiological and prognostic factors in acute nexrotizing pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1997; 29:667–76.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Allergic Purpura
- Acute Pancreatitis as a Complication of Adult Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
- Clinical Study on Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
- A Case of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Complicated by Hemorrhagic Ascites and Multiple Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- A Case of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura with Acute Pancreatitis and Hypovolemic Acute Renal Failure