J Rheum Dis.
2012 Feb;19(1):43-46. 10.4078/jrd.2012.19.1.43.
Acute Pancreatitis as a Complication of Adult Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. byoo@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2223119
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.1.43
Abstract
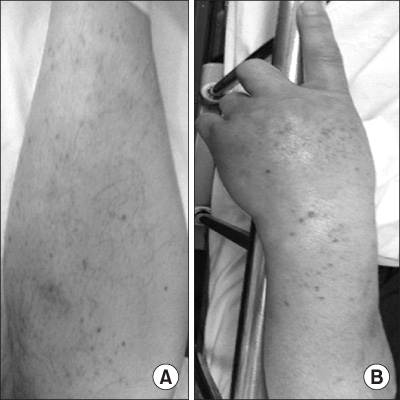
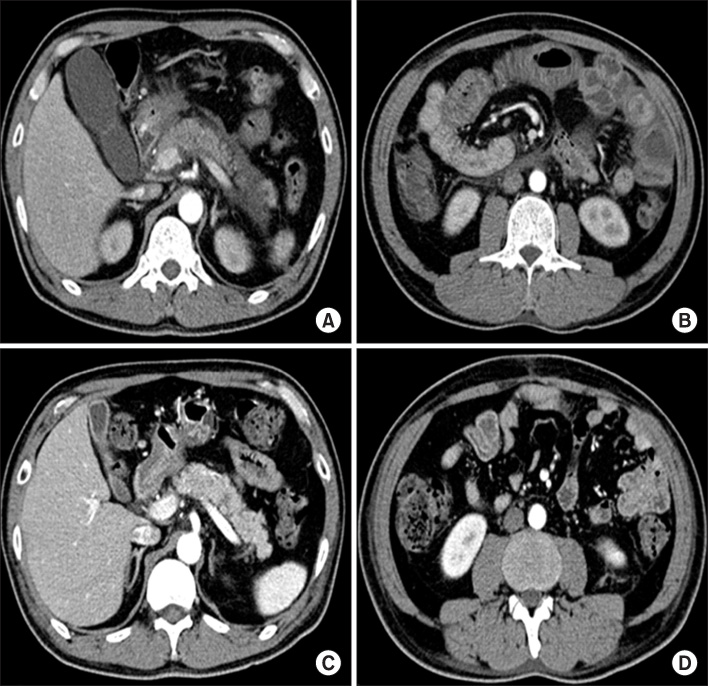
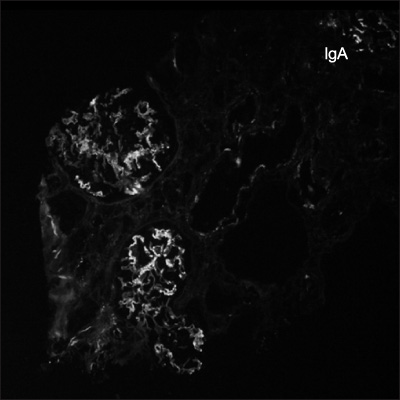
- Pancreatitis is a rare manifestation of adult Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP). We describe here a 53-year-old man who presented with acute pancreatitis as a complication of adult HSP. Pancreatic involvement in HSP is self-limiting and benign. Prompt resolution can be achieved by treatment with steroids. Elevated serum amylase and lipase concentrations may be early diagnostic indicators of HSP pancreatitis. Patients with HSP who have abdominal pain should be evaluated for pancreatitis by measuring serum amylase and lipase concentrations and by abdominal computed tomography scan, to plan specific treatment and avoid unnecessary surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chang WL, Yang YH, Lin YT, Chiang BL. Gastrointestinal manifestations in Henoch-Schönlein purpura: a review of 261 patients. Acta Paediatr. 2004. 93:1427–1431.2. Choong CK, Beasley SW. Intra-abdominal manifestations of Henoch-Schönlein purpura. J Paediatr Child Health. 1998. 34:405–409.3. Diaz CF. Schonlein-Henoch purpura and pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1995. 40:750–751.4. Lévy-Weil FE, Sigal M, Renard P, Pouliquen X, Gaulier A, Moulonguet Doleris L, et al. Acute pancreatitis in rheumatoid purpura. Apropos of 2 cases. Rev Med Interne. 1997. 18:54–58.5. Garner JA. Acute pancreatitis as a complication of anaphylactoid (Henoch-Schönlein) purpura. Arch Dis Child. 1977. 52:971–972.6. Branski D, Gross V, Gross-Kieselstein E, Roll D, Abrahamov A. Pancreatitis as a complication of Henoch--Schonlein purpura. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1982. 1:275–276.7. Puppala AR, Cheng JC, Steinheber FU. Pancreatitis--a rare complication of Schönlein-Henoch purpura. Am J Gastroenterol. 1978. 69:101–104.8. El Alami S, Azar C, Bheane M, Derumier J. Acute pancreatitis: a rare initial clinical manifestation of Henoch-Schönlein disease. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1994. 57:264–265.9. Frigui M, Lehiani D, Koubaa M, Bouaziz Z, Abid B, Beyrouti I, et al. Acute pancreatitis as initial manifestation of adult Henoch-Schönlein purpura: report of a case and review of literature. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. 23:189–192.10. Cheung KM, Mok F, Lam P, Chan KH. Pancreatitis associated with Henoch-Schönlein purpura. J Paediatr Child Health. 2001. 37:311–313.11. Soyer T, Egritas O, Atmaca E, Akman H, Oztürk H, Tezic T. Acute pancreatitis: a rare presenting feature of Henoch Schönlein purpura. J Paediatr Child Health. 2008. 44:152–153.12. Dinler G, Bek K, Açikgöz Y, Kalayci AG. Acute pancreatitis as a presenting feature of Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Turk J Pediatr. 2010. 52:191–193.13. Toskin KD. Syndrome of hemorrhagic pancreatitis as a manifestation of Schönlein-Henoch disease. Klin Khir. 1965. 11:65–67.14. Russo M, Texier P, Brun P, Huault G. Acute pancreatitis in rheumatoid purpura. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1987. 44:474.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Allergic Purpura
- A Case of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Complicated by Acute Pancreatitis and Interstitial Pneumonitis
- Small Intestinal Perforation as a Complication of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
- Clinical Study on Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
- A Case of Henoch-Schonlein Purpura with Acute Pancreatitis and Hypovolemic Acute Renal Failure