Tuberc Respir Dis.
2011 Dec;71(6):459-463.
A Case of Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Hematology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. skysong3@hanmail.net
Abstract
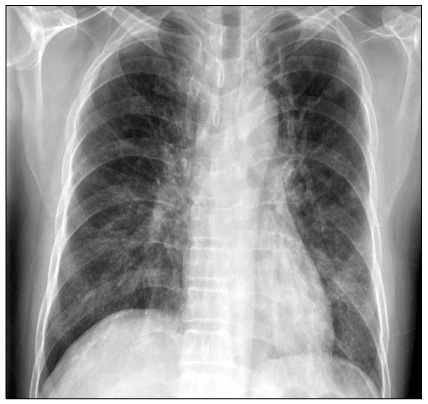
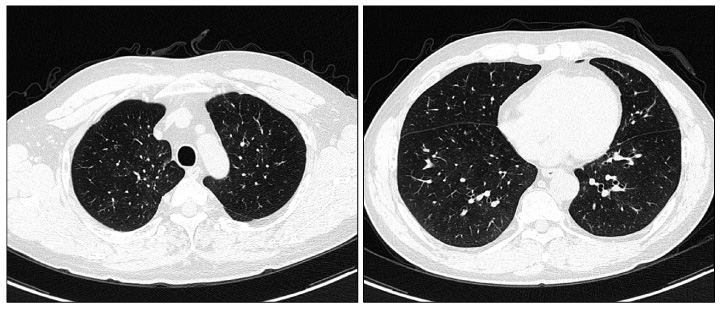
- Pulmonary complications occur in 40~60% of patients who receive hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and are a source of substantial morbidity and mortality. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia (AEP) is an uncommon, non-infectious pulmonary complication occurring in HSCT recipients. We now report the case of a 52-year-old man with AEP who was treated with allogenic HSCT due to acute myeloid leukemia. He complained of fever, cough and dyspnea 390 days after allogenic HSCT. He also had skin and hepatic graft versus host disease (GVHD). Hypoxemia, diffuse pulmonary infiltrates on a chest x-ray and eosinophilia in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were also noted in several tests. His symptoms, pulmonary infiltrates, hepatic dysfunction and skin lesions rapidly improved after treatment with corticosteroid therapy. Our case supports the idea that AEP is a late phase non-infectious pulmonary complication and one of the manifestations of chronic GVHD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chan CK, Hyland RH, Hutcheon MA. Pulmonary complications following bone marrow transplantation. Clin Chest Med. 1990. 11:323–332.2. Jules-Elysee K, Stover DE, Yahalom J, White DA, Gulati SC. Pulmonary complications in lymphoma patients treated with high-dose therapy autologous bone marrow transplantation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992. 146:485–491.3. Bensinger WI, Martin PJ, Storer B, Clift R, Forman SJ, Negrin R, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow as compared with peripheral-blood cells from HLA-identical relatives in patients with hematologic cancers. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:175–181.4. Afessa B, Litzow MR, Tefferi A. Bronchiolitis obliterans and other late onset non-infectious pulmonary complications in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001. 28:425–434.5. Sakaida E, Nakaseko C, Harima A, Yokota A, Cho R, Saito Y, et al. Late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications after allogeneic stem cell transplantation are significantly associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease and with the graft-versus-leukemia effect. Blood. 2003. 102:4236–4242.6. Yoshimi M, Nannya Y, Watanabe T, Asai T, Ichikawa M, Yamamoto G, et al. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia is a non-infectious lung complication after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2009. 89:244–248.7. Wagner T, Dhedin N, Philippe B, Rivaud E, Vernant JP, Couderc LJ. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol. 2006. 85:202–203.8. Choi YK, Kim SY, Yoon HK, Kim HJ, Lee JW, Min WS, et al. A case of acute eosinophilic pneumonia after unrelated bone marrow transplantation. Korean J Med. 2005. 68:453–456.9. Sullivan KM, Agura E, Anasetti C, Appelbaum F, Badger C, Bearman S, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease and other late complications of bone marrow transplantation. Semin Hematol. 1991. 28:250–259.10. Allen J. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. 27:142–147.11. Akhtari M, Langston AA, Waller EK, Gal AA. Eosinophilic pulmonary syndrome as a manifestation of GVHD following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in three patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009. 43:155–158.12. Arslan O, Akan H, Koç H, Beksaç M, Ilhan O, Ozcan M, et al. Eosinophilia after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation using busulfan and cyclophosphamide conditioning regimen. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996. 18:261.13. Pope-Harman AL, Davis WB, Allen ED, Christoforidis AJ, Allen JN. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia. A summary of 15 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996. 75:334–342.14. Shiota Y, Kawai T, Matsumoto H, Hiyama J, Tokuda Y, Marukawa M, et al. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia following cigarette smoking. Intern Med. 2000. 39:830–833.15. Duncker C, Dohr D, Harsdorf S, Duyster J, Stefanic M, Martini C, et al. Non-infectious lung complications are closely associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease: a single center study of incidence, risk factors and outcome. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000. 25:1263–1268.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of acute eosinophilic pneumonia after unrelated bone marrow transplantation
- Opening the era of in vivo xenotransplantation model for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- A case of pneumomediastinum combined with chronic graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Inborn Error of Metabolism