Tuberc Respir Dis.
2009 Nov;67(5):436-444.
Utility of Micro CT in a Murine Model of Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. gyjin@jbnu.ac.kr
- 2Research Center for Pulmonary Disorders, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. leeyc@jbnu.ac.kr
- 3Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 5Department of Pathology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiology, Iksan Hospital, Iksan, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Micro computed tomography (CT) is rapidly developing as an imaging tool, especially for mice, which have become the experimental animal of choice for many pulmonary disease studies. We evaluated the usefulness of micro CT for evaluating lung fibrosis in the murine model of bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis.
METHODS
The control mice (n=10) were treated with saline. The murine model of lung fibrosis (n=60) was established by administering bleomycin intra-tracheally. Among the 70 mice, only 20 mice had successful imaging analyses. We analyzed the micro CT and pathological findings and examined the correlation between imaging scoring in micro CT and histological scoring of pulmonary inflammation or fibrosis.
RESULTS
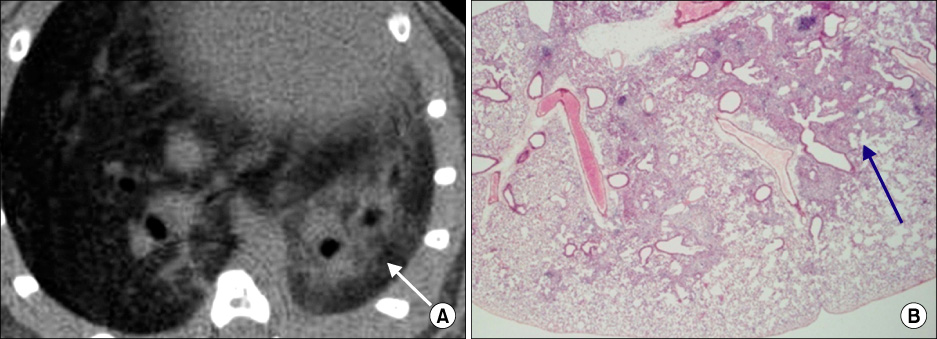
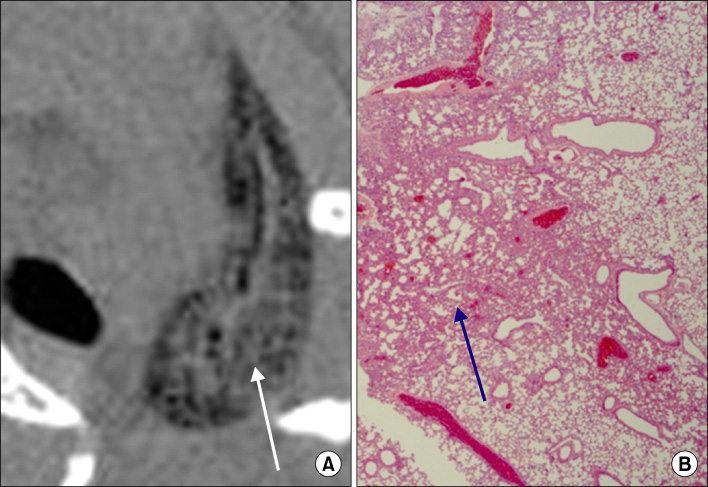
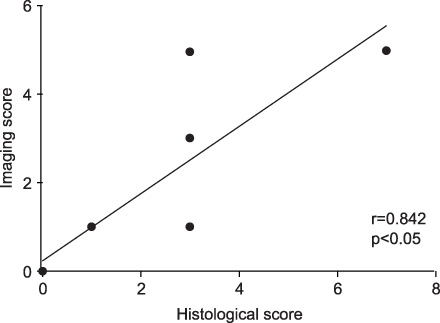
The control group showed normal findings on micro CT. The abnormal findings on micro CT performed at 3 weeks after the administration of bleomycin were ground-glass opacity (GGO) and consolidation. At 6 weeks after bleomycin administration, micro CT showed various patterns such as GGO, consolidation, bronchiectasis, small nodules, and reticular opacity. GGO (r=0.84) and consolidation (r=0.69) on micro CT were significantly correlated with histological scoring that reflected pulmonary inflammation (p<0.05). In addition, bronchiectasis (r=0.63) and reticular opacity (r=0.83) on micro CT shown at 6 weeks after bleomycin administration correlated with histological scoring that reflected lung fibrosis (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that micro CT findings from a murine model of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis reflect pathologic findings, and micro CT may be useful for predicting bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gross TJ, Hunninghake GW. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2001. 345:517–525.2. Moeller A, Ask K, Warburton D, Gauldie J, Kolb M. The bleomycin animal model: a useful tool to investigate treatment options for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. 40:362–382.3. Sleijfer S. Bleomycin-induced pneumonitis. Chest. 2001. 120:617–624.4. Ritman EL. Micro-computed tomography of the lungs and pulmonary-vascular system. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005. 2:477–480. 5015. Ritman EL. Micro-computed tomography-current status and developments. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2004. 6:185–208.6. Johnson KA. Imaging techniques for small animal imaging models of pulmonary disease: micro-CT. Toxicol Pathol. 2007. 35:59–64.7. Lee HJ, Goo JM, Kim NR, Kim MA, Chung DH, Son KR, et al. Semiquantitative measurement of murine bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in in vivo and postmortem conditions using microcomputed tomography: correlation with pathologic scores--initial results. Invest Radiol. 2008. 43:453–460.8. Cavanaugh D, Travis EL, Price RE, Gladish G, White RA, Wang M, et al. Quantification of bleomycin-induced murine lung damage in vivo with micro-computed tomography. Acad Radiol. 2006. 13:1505–1512.9. Genovese T, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R, Mazzon E, Mastruzzo C, Catalano P, et al. Effect of rosiglitazone and 15-deoxy-Delta12, 14-prostaglandin J2 on bleomycin-induced lung injury. Eur Respir J. 2005. 25:225–234.10. Ashcroft T, Simpson JM, Timbrell V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J Clin Pathol. 1988. 41:467–470.11. Langheinrich AC, Leithäuser B, Greschus S, Von Gerlach S, Breithecker A, Matthias FR, et al. Acute rat lung injury: feasibility of assessment with micro-CT. Radiology. 2004. 233:165–171.12. Ford NL, Wheatley AR, Holdsworth DW, Drangova M. Optimization of a retrospective technique for respiratory-gated high speed micro-CT of free-breathing rodents. Phys Med Biol. 2007. 52:5749–5769.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serial Micro-CT Assessment of the Therapeutic Effects of Rosiglitazone in a Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis Mouse Model
- Deficiency of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 2 (S1Pâ‚‚) Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
- HRCT Findings of Bleomycin-Related Lung Toxicity: A Report of 2 Case
- Dietary Flavonoid Apigenin is not Effective in Preventing Development of a Bleomycin-Induced Murine Model of Scleroderma
- Induction of Animal Model of Scleroderma with Repeated Injection of Bleomycin