Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis.
2012 Sep;22(3):256-264.
Clinical Characteristics of Children with Lobar Pneumonia Caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. immlee@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was conducted to evaluate the prevalence, clinical characteristics and laboratory findings of lobar pneumonia in children caused by Mycoplasma pneumonia and to find a diagnostic tool for identifying M. pneumoniae infection in children.
METHODS
We analyzed medical records of 78 children between March 2010 and December 2011, who were admitted to our hospital and diagnosed with lobar pneumonia on the basis of chest X-rays. White blood cells (WBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), specific antibodies to M. pneuomoniae, and cold agglutinin (CA) were measured at the time of admission. Children were divided into 2 groups: those with M. pneuomoniae infection (group A) and those without infection (group B). Group A children were also subdivided into 2 categories: those with increased CA (group 1) and those without (group 2).
RESULTS
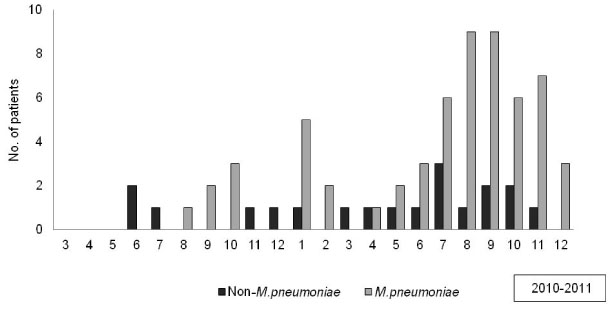
The prevalence of lobar pneumonia was higher in the year 2011 than in 2010. M. pneuomoniae infection usually occurs in summer and autumn. Group A children accounted for 75.6% (59/78) of all the cases. The onset ages was higher in group A than in group B (P=0.016). WBC counts and PCT values were higher in group B than in group A.(P=0.015 and P=0.011, respectively) Radiologic findings showed that the lower lobe was most commonly involved without predilection for either side and pleural effusion was present in 13.6% of all the cases. The duration of fever before admission was longer in group 1 than in group 2.(P=0.019)
CONCLUSION
It is concluded that lobar pneumonia caused by M. pneuomoniae can be more accurately diagnosed using serum PCT values than using CRP values.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim JW, Seo HK, Yoo EG, Park SJ, Yoon SH, Jung HY, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children, from 1979 to 2006-a meta-analysis. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:315–323.
Article2. Lee SH, Noh SM, Lee KY, Lee HS, Hong JH, Lee MH, et al. Clinico-epidemiologic study of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (1993 through 2003). Korean J Pediatr. 2005. 48:154–157.3. McIntosh K. Community-acquired pneumonia in children. N Engl J Med. 2002. 346:429–437.
Article4. Hsieh SC, Kuo YT, Chern MS, Chen CY, Chan WP, Yu C. Mycoplasma pneumonia: clinical and radiographic features in 39 children. Pediatr Int. 2007. 49:363–367.
Article5. John SD, Ramanathan J, Swischuk LE. Spectrum of clinical and radiographic findings in pediatric Mycoplasma pneumonia. Radiographics. 2001. 21:121–131.
Article6. Swischuk LE, Hayden CK Jr. Viral vs. bacterial pulmonary infections in children (is roentgenographic differentiation possible?). Pediatr Radiol. 1986. 16:278–284.
Article7. Lee YH, Shin YL, Suh WS, Shin MY, Park JO. A clinical study of lobar/lobular pneumonia in children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009. 19:271–281.8. Ahn YH, Park SH. Clinical considerations about mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in the young, between 2003 and 2006. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2007. 17:249–259.9. Putman CE, Curtis AM, Simeone JF, Jensen P. Mycoplasma pneumonia. Clinical and roentgenographic patterns. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975. 124:417–422.10. Long SS, Pickering LK, Prober CG. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 2009. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone;177–179.11. Waites KB. New concepts of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2003. 36:267–278.12. Ferwerda A, Moll HA, de Groot R. Respiratory tract infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children: a review of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. Eur J Pediatr. 2001. 160:483–491.
Article13. Finnegan OC, Fowles SJ, White RJ. Radiographic appearances of mycoplasma pneumonia. Thorax. 1981. 36:469–472.
Article14. Hong JY, Nah SY, Nam SG, Choi EH, Park JY, Lee HJ. Occurrence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Seoul, Korea, from 1986 to 1995. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1997. 40:607–613.15. Park HY, Woo CW, Choung JT, Son CS, Tockgo YC. Trend of the mycoplasma pneumonia - during recent 9 years period. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 1995. 5:49–59.16. Kim JH, Chae SA, Lee DK. Clinical findings of Mycoplasma pneumonia in children, from 1998 to 2003. Korean J Pediatr. 2005. 48:969–975.17. Kim JT. Laboratory diagnosis of Mycoplasma infection. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2006. 16:23–25.18. Waris ME, Toikka P, Saarinen T, Nikkari S, Meurman O, Vainionpaa R, et al. Diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. 36:3155–3159.
Article19. Jacobs E, Bennewitz A, Bredt W. Reaction pattern of human anti-Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and immunoblotting. J Clin Microbiol. 1986. 23:517–522.
Article20. Levine DP, Lerner AM. The clinical spectrum of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. Med Clin North Am. 1978. 62:961–978.
Article21. Wall RA, Corrah PT, Mabey DC, Greenwood BM. The etiology of lobar pneumonia in the Gambia. Bull World Health Organ. 1986. 64:553–558.22. Michelow IC, Olsen K, Lozano J, Rollins NK, Duffy LB, Ziegler T, et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children. Pediatrics. 2004. 113:701–707.
Article23. Morozumi M, Takahashi T, Ubukata K. Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: characteristics of isolates and clinical aspects of community-acquired pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 2010. 16:78–86.
Article24. Byun SY, Bae YJ, Yoo JH, Jung JA. Comparison of clinical characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia according to the pleural effusion. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2006. 16:327–334.25. Cassell GH, Cole BC. Mycoplasmas as agents of human disease. N Engl J Med. 1981. 304:80–89.
Article26. Hedlund J, Hansson LO. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels in community-acquired pneumonia: correlation with etiology and prognosis. Infection. 2000. 28:68–73.
Article27. Virkki R, Juven T, Rikalainen H, Svedstrom E, Mertsola J, Ruuskanen O. Differentiation of bacterial and viral pneumonia in children. Thorax. 2002. 57:438–441.
Article28. Simon L, Gauvin F, Amre DK, Saint-Louis P, Lacroix J. Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels as markers of bacterial infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 39:206–217.
Article29. Jereb M, Kotar T. Usefulness of procalcitonin to differentiate typical from atypical community-acquired pneumonia. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2006. 118:170–174.
Article30. Gendrel D, Raymond J, Coste J, Moulin F, Lorrot M, Guerin S, et al. Comparison of procalcitonin with C-reactive protein, interleukin 6 and interferon-alpha for differentiation of bacterial vs. viral infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999. 18:875–881.
Article31. Prat C, Dominguez J, Rodrigo C, Gimenez M, Azuara M, Jimenez O, et al. Procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and leukocyte count in children with lower respiratory tract infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 22:963–968.
Article32. Dandona P, Nix D, Wilson MF, Aljada A, Love J, Assicot M, et al. Procalcitonin increase after endotoxin injection in normal subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994. 79:1605–1608.
Article33. Hatherill M, Tibby SM, Sykes K, Turner C, Murdoch IA. Diagnostic markers of infection: comparison of procalcitonin with C reactive protein and leucocyte count. Arch Dis Child. 1999. 81:417–421.
Article34. Lee JY, Hwang SJ, Shim JW, Jung HL, Park MS, Woo HY, et al. Clinical significance of serum procalcitonin in patients with community-acquired lobar Pneumonia. Korean J Lab Med. 2010. 30:406–413.
Article35. Hansson LO, Axelsson G, Linne T, Aurelius E, Lindquist L. Serum C-reactive protein in the differential diagnosis of acute meningitis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1993. 25:625–630.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Consideration on Pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Children
- A clinical study of mycoplasma pneumonia in children during recent 5 years
- Mycoplasma Pneumoniae-Associated Necrotizing Pneumonia in Children: a case-report
- Clinical differences according to radiological patterns in childhood Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Clinical Observation on Pneumonia due to Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Children