Kosin Med J.
2019 Jun;34(1):57-64. 10.7180/kmj.2019.34.1.57.
Mycoplasma Pneumoniae-Associated Necrotizing Pneumonia in Children: a case-report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Busan St. Mary's Hospital, Busan, Korea. hyh190@naver.com
- KMID: 2451777
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2019.34.1.57
Abstract
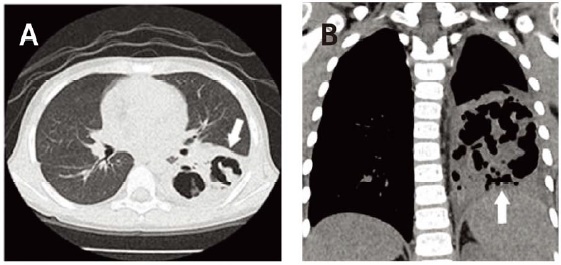
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae is the most common bacterial strain causing atypical pneumonia in children and adolencents. Although it is known to cause mild symptoms, it can also cause severe pulmonary or extrapulmonary complications in rare cases. Necrotizing pneumonia (NP) is often reported as a complication of Streptococcus pneumoniae and is very rarely caused by M. pneumoniae. We report a case in which a 5-year-old boy was diagnosed with lobar pneumonia with symptoms that aggravated even with macrolide antibiotic treatment. Anti-mycoplasma pneumoniae Ig-M test yielded high values, and direct polymerase chain reaction results were also positive. NP caused by M. pneumoniae was confirmed on computed tomography. After treatment involving tosufloxacin and systemic steroid, the lesion decreased in size and improved gradually when followed-up for more than 1 year. The patient did not have any predisposing or risk factors for NP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ferwerda A, Moll HA, de Groot R. Respiratory tract infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children: a review of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. Eur J Pediatr. 2001; 160:483–491.
Article2. Lee NY, Hur TH, Song SW, Lee HK, Lee KY, Lee HS, et al. Clinical Aspects of Necrotizing Pneumonitis Resulting from Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection in Children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2007; 17:183–195.3. Hacimustafaoglu M, Celebi S, Sarimehmet H, Gurpinar A, Ercan I. Necrotizing pneumonia in children. Acta Paediatr. 2004; 93:1172–1177.
Article4. Kawai Y, Miyashita N, Kubo M, Akaike H, Kato A, Nishizawa Y, et al. Nationwide surveillance of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in pediatric patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013; 57:4046–4049.
Article5. Kim JH, Kim EJ, Kwon JH, Seo WH, Yoo Y, Choung JT, Song DJ. Clinical characteristics of respiratory viral coinfection in pediatric Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017; 5:15–20.
Article6. Committee for the Guidelines in Management of Respiratory Infectious Diseases in Children. Ouchi K, Kurosaki T, Okada K, editors. Guidelines for the management of respiratory infectious diseases in children in Japan. Japanese Society of Pediatric Pulmonology;Japanese Society for Pediatric Infectious Diseases;2011.7. Tamura A, Matsubara K, Tanaka T, Nigami H, Yura K, Fukaya T. Methylprednisolone pulse therapy for refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. J Infect. 2008; 57:223–228.
Article8. Morozumi M, Takahashi T, Ubukata K. Macrolideresistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: characteristics of isolates and clinical aspects of community-acquired pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 2010; 16:78–86.
Article9. Klement E, Talkington DF, Wasserzug O, Kayout R, Davidovitch N, Dumke R, et al. Identification of risk factors for infection in an outbreak of Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory tract disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 43:1239–1245.
Article10. Chiu CY, Chiang LM, Chen TP. Mycoplasma pneumonia infections complicated by necrotizing pneumonitis with massive pleural effusion. Eur J Pediatr. 2006; 165:275–277.
Article11. Ma YJ, Wang SM, Cho YH, Shen CF, Liu CC, Chi H, et al. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics in children with community-acquired mycoplasma pneumonia in Taiwan: A nationwide surveillance. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2015; 48:632–638.
Article12. Sawicki GS, Lu FL, Valim C, Cleveland RH, Colin AA. Necrotising pneumonia is an increasingly detected complication of pneumonia in children. The European respiratory journal. 2008; 31:1285–1291.
Article13. Maroushek SR. Principles of antimycobacterial therapy. In : Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2105. p. 1439–1444.14. Wy HH, Min DH, Kim DS, Park MS, Shim JW, Jung HL, et al. Clinical characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children during the recent 3 epidemics. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017; 5:8–14.
Article15. Miyashita N, Kawai Y, Inamura N, Tanaka T, Akaike H, Teranishi H, et al. Setting a standard for the initiation of steroid therapy in refractory or severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in adolescents and adults. J Infect Chemother. 2015; 21:153–160.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A clinical study of mycoplasma pneumonia in children during recent 5 years
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children
- Clinical Observation on Pneumonia due to Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Children
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Complicated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia
- Clinical Consideration on Pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Children