Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis.
2012 Mar;22(1):110-115.
Clinical Usefulness of Procalcitonin as Guideline of Antibiotic Treatment in Children with Respiratory Tract Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. immlee@cnu.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Procalcitonin (PCT), a precursor of calcitonin, has been described as a biomarker of bacterial infection and inflammation. This study was performed to evaluate the clinical usefulness of PCT levels and to reduce the unnecessary usage of antibiotics in children with lower respiratory tract infection (RTI).
METHODS
Eighty-eight children, with lower RTI, under the age of 5 years, who were admitted to Chungnam National University Hospital, between May 2010 and December 2010, were enrolled. White blood cell counts, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and PCT were measured. Blood and sputum cultures were performed to identify the causative bacteria and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction for the viruses. Clinical features were reviewed, retrospectively.
RESULTS
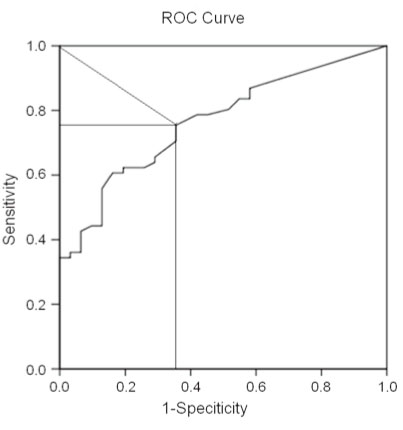
The mean participant age was 1.9+/-1.5 years. The cut-off value for serum PCT levels, which was derived from the receiver-operator characteristic curve, was 0.11 ng/mL. In 29 patients (33.0%) with low PCT levels (<0.11 ng/mL), antibiotic therapy showed no benefit for clinical and laboratory findings. However, in 59 patients (67.1%) with high PCT levels (> or =0.11 ng/mL), hospitalization (P=0.005) and fever (P=0.054) exhibited a shorter duration, after antibiotic therapy.
CONCLUSION
A single initial serum PCT levels (> or =0.11 ng/mL) may be clinically useful to give a guideline for antibiotic treatment in children with lower respiratory tract infection and to reduce the unnecessary usage of antibiotics.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Virkki R, Juven T, Rikalainen H, Svedström E, Mertsola J, Ruuskanen O. Differentiation of bacterial and viral pneumonia in children. Thorax. 2002. 57:438–441.
Article2. Nohynek H, Valkeila E, Leinonen M, Eskola J. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, white blood cell count and serum C-reactive protein in assessing etiologic diagnosis of acute lower respiratory infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995. 14:484–490.
Article3. Courtoy I, Lande AE, Turner RB. Accuracy of radiographic differentiation of bacterial from nonbacterial pneumonia. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1989. 28:261–264.
Article4. Deis JN, Creech CB, Estrada CM, Abramo TJ. Procalcitonin as a marker of severe bacterial infection in children in the emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2010. 26:51–60.
Article5. Becker KL, Snider R, Nylen ES. Procalcitonin assay in systemic inflammation, infection, and sepsis: clinical utility and limitations. Crit Care Med. 2008. 36:941–952.
Article6. Gendrel D, Raymond J, Assicot M, Moulin F, Iniguez JL, Lebon P, et al. Measurement of procalcitonin levels in children with bacterial or viral meningitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1997. 24:1240–1242.
Article7. Pecile P, Miorin E, Romanello C, Falleti E, Valent F, Giacomuzzi F, et al. Procalcitonin: a marker of severity of acute pyelonephritis among children. Pediatrics. 2004. 114:e249–e254.
Article8. Toikka P, Irjala K, Juvén T, Virkki R, Mertsola J, Leinonen M, et al. Serum procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 for distinguishing bacterial and viral pneumonia in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000. 19:598–602.
Article9. Don M, Valent F, Korppi M, Falleti E, De Candia A, Fasoli L, et al. Efficacy of serum procalcitonin in evaluating severity of community-acquired pneumonia in childhood. Scand J Infect Dis. 2007. 39:129–137.
Article10. Resch B, Gusenleitner W, Müller W. Procalcitonin, interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and leukocyte counts in infants with bronchiolitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 22:475–476.
Article11. Christ-Crain M, Müller B. Biomarkers in respiratory tract infections: diagnostic guides to antibiotic prescription, prognostic markers and mediators. Eur Respir J. 2007. 30:556–573.
Article12. Niederman MS. Biological markers to determine eligibility in trials for community-acquired pneumonia: a focus on procalcitonin. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 47:Suppl 3. S127–S132.
Article13. Gibot S, Cravoisy A, Levy B, Bene MC, Faure G, Bollaert PE. Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells and the diagnosis of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:451–458.
Article14. Simon L, Gauvin F, Amre DK, Saint-Louis P, Lacroix J. Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels as markers of bacterial infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 39:206–217.
Article15. Tang H, Huang T, Jing J, Shen H, Cui W. Effect of procalcitonin-guided treatment in patients with infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infection. 2009. 37:497–507.
Article16. Christ-Crain M, Stolz D, Bingisser R, Müller C, Miedinger D, Huber PR, et al. Procalcitonin guidance of antibiotic therapy in community-acquired pneumonia: a randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. 174:84–93.
Article17. Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Thomann R, Falconnier C, Wolbers M, Widmer I, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-based guidelines vs standard guidelines on antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections: the ProHOSP randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009. 302:1059–1066.
Article18. Kristoffersen KB, Søgaard OS, Wejse C, Black FT, Greve T, Tarp B, et al. Antibiotic treatment interruption of suspected lower respiratory tract infections based on a single procalcitonin measurement at hospital admission--a randomized trial. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009. 15:481–487.
Article19. Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Albrich W, Zimmerli W, Mueller B. ProHOSP Study Group. Guidance of antibiotic therapy with procalcitonin in lower respiratory tract infections: insights into the ProHOSP study. Virulence. 2010. 1:88–92.
Article20. Nascimento-Carvalho CM, Cardoso MR, Barral A, Araújo-Neto CA, Guerin S, Saukkoriipi A, et al. Procalcitonin is useful in identifying bacteraemia among children with pneumonia. Scand J Infect Dis. 2010. 42:644–649.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Utility of Procalcitonin on Antibiotic Stewardship: A Narrative Review
- Erratum: A Retrospective Analysis of Use in Hospitalized Children with Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
- Acute upper respiratory tract infection
- Current Status of Antibiotic Stewardship and the Role of Biomarkers in Antibiotic Stewardship Programs
- Antibiotic therapy decision and clinical outcome comparison based on serum procalcitonin in children with pneumonia