Lab Med Online.
2014 Jan;4(1):43-50.
Performance Comparison of ImmunoCAP and HYTEC 288 in the Quantitative Tests of Allergen-specific IgE
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. yaong97@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine and Molecular Genetics, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In vitro measurement of allergen-specific IgE has become an important part of allergy diagnoses. HYTEC 288 system (Hycor Biomedical Inc., USA), which was recently introduced in Korea, is a fully automated immunoassay for quantitative measurements of allergen-specific IgE. In this study, we compared the clinical utility of this in vitro allergy test with that of ImmunoCAP assay (ImmunoDiagnostics, Sweden).
METHODS
To evaluate the reproducibility of HYTEC 288 system, 50 serum samples were tested in duplicate each for Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (d1) and D. farinae (d2) specific IgE. To assess the agreement between ImmunoCAP and HYTEC 288 assays, 56 serum samples were tested for the other 21 allergen-specific IgE.
RESULTS
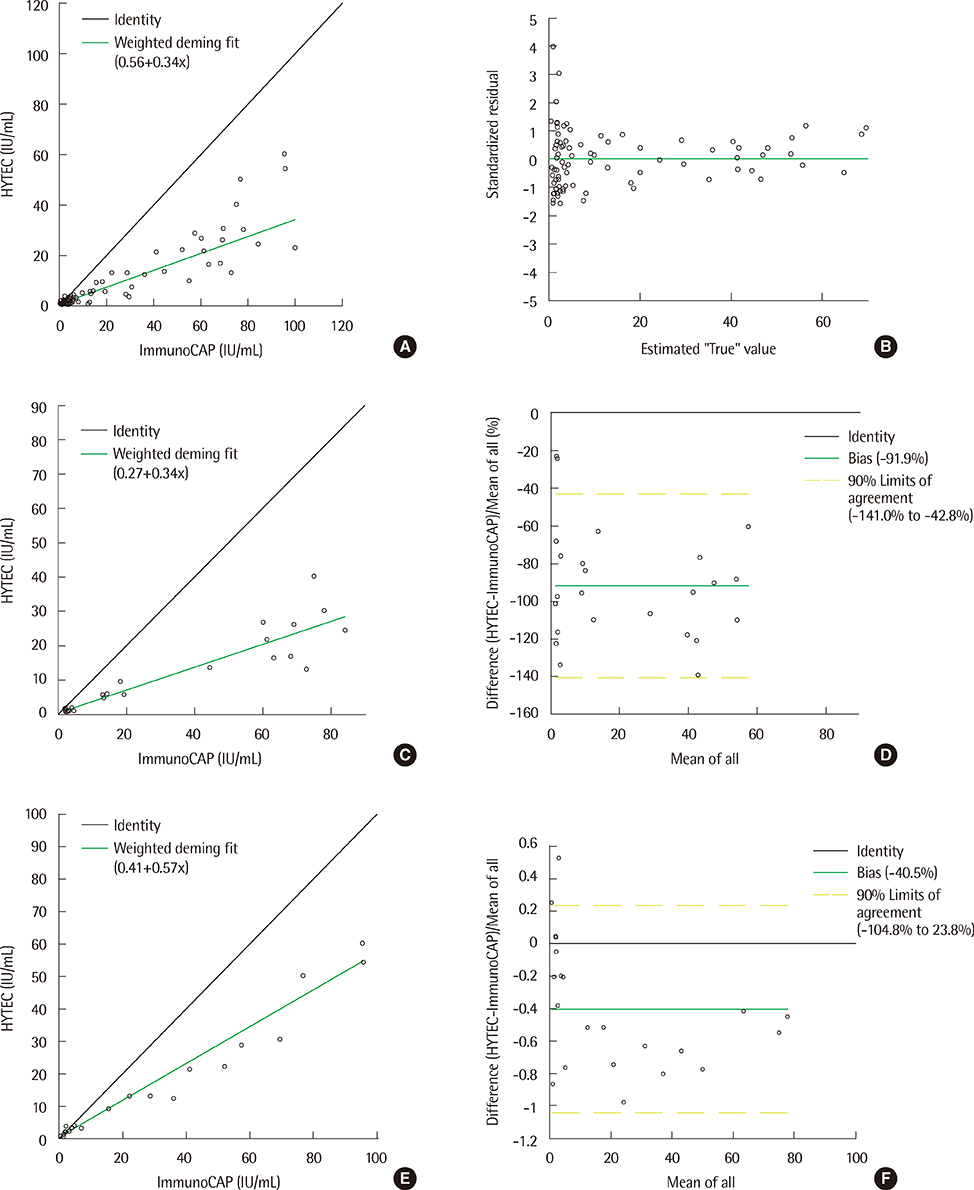
No significant differences within the range of quantitative analysis were observed between HYTEC 288 and ImmunoCAP assays for d1 and d2 (P=0.65 and 0.55, respectively). The agreements of HYTEC allergen-specific IgE assay with ImmunoCAP within +/-1 class grade were 80% and 100% for d1 and d2, respectively. The correlation coefficients between HYTEC 288 and ImmunoCAP results within the range of quantitative analysis were overally 0.90, regardless of allergen, for d1 and d2 specific IgE, 0.91 and 0.98, respectively. Running times for the HYTEC 288 and Phardia 100 were 5.5 and 4.6 min per test, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Hycor HYTEC 288 showed a favorable agreement with ImmunoCAP and can be used for fully automated quantitative measurements of allergen-specific IgE in the clinical laboratory.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bernstein IL, Li JT, Bernstein DI, Hamilton R, Spector SL, Tan R, et al. Allergy diagnostic testing: an updated practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100(3 Suppl 3):S1–S148.
Article2. Douglass JA, O'Hehir RE. 1.Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of allergic disease: the basics. Med J Aust. 2006; 185:228–233.3. Cox L, Williams B, Sicherer S, Oppenheimer J, Sher L, Hamilton R, et al. Pearls and pitfalls of allergy diagnostic testing: report from the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Specific IgE Test Task Force. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 101:580–592.
Article4. Lim HS, Yoon JK, Lee HH. Allergen patterns using MAST cla test in Korean pediatric patients. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2001; 21:292–297.5. Han M, Shin S, Park H, Park KU, Park MH, Song EY. Comparison of three multiple allergen simultaneous tests: RIDA allergy screen, MAST optigen, and polycheck allergy. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:340513.
Article6. Wang J, Godbold JH, Sampson HA. Correlation of serum allergy (IgE) tests performed by different assay systems. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:1219–1224.
Article7. Ewan PW, Coote D. Evaluation of a capsulated hydrophilic carrier polymer (the ImmunoCAP) for measurement of specific IgE antibodies. Allergy. 1990; 45:22–29.
Article8. Nolte H, DuBuske LM. Performance characteristics of a new automated enzyme immunoassay for the measurement of allergen-specific IgE. Summary of the probability outcomes comparing results of allergen skin testing to results obtained with the HYTEC system and CAP system. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997; 79:27–34.
Article9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; approved guideline-second edition. CLSI document EP5-A2. Wayne PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2004.10. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; approved guideline-second edition. CLSI document EP9-A2. Wayne PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2002.11. Lee SI, Shin MH, Lee HB, Lee JS, Son BK, Koh YY, et al. Prevalences of symptoms of asthma and other allergic diseases in korean children: a nationwide questionnaire survey. J Korean Med Sci. 2001; 16:155–164.
Article12. Lee SY, Kwon JW, Seo JH, Song YH, Kim BJ, Yu J, et al. Prevalence of atopy and allergic diseases in Korean children: associations with a farming environment and rural lifestyle. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012; 158:168–174.
Article13. Maloney JM, Rudengren M, Ahlstedt S, Bock SA, Sampson HA. The use of serum-specific IgE measurements for the diagnosis of peanut, tree nut, and seed allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122:145–151.
Article14. Hamilton RG. Proficiency survey-based evaluation of clinical total and allergen-specific IgE assay performance. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010; 134:975–982.
Article15. Corey JP, Mamikoglu B, Akbar I, Houser SM, Gungor A. ImmunoCAP and HY*TEC enzyme immunoassays in the detection of allergen-specific IgE compared with serial skin end-point titration by receiver operating characteristic analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000; 122:64–70.
Article16. Kontis KJ, Chen A, Wang J, Nayak N, Li TM. Performance of a fully automated in vitro allergy testing system. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 1997; 25:63–66.17. Wang J, Godbold JH, Sampson HA. Correlation of serum allergy (IgE) tests performed by different assay systems. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:1219–1224.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Component-Resolved Diagnosis by Using Allergen Microarray With the Conventional Tests in Allergic Rhinitis Patients: The First Using in Korea
- Allergen Microarrays for In Vitro Diagnostics of Allergies: Comparison with ImmunoCAP and AdvanSure
- Clinical characteristics of total IgE in pediatric allergic disease
- Detection of Allergen Specific IgE by AdvanSure Allergy Screen Test
- Comparison of skin prick test and serum specific IgE measured by ImmunoCAP system for various inhalant allergens