Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2017 Jul;5(4):200-204. 10.4168/aard.2017.5.4.200.
Clinical characteristics of total IgE in pediatric allergic disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. bschoi@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2387647
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2017.5.4.200
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Serum total and specific IgE levels have been widely used to diagnose allergic disease. However, it has recently been suggested that serum total IgE does not properly reflect specific IgE. Therefore, we evaluated the clinical significance of serum total IgE in pediatric allergic disease.
METHODS
This study included 633 patients who visited Kyungpook National University Children's Hospital between March 2013 and April 2015. We used immunoCAP, an inhalant multiple allergen simultaneous test (MAST), and food MAST to measure specific IgE. We used a skin prick test in some patients and measured serum total IgE, eosinophil count, and serum eosinophil cationic protein in all patients.
RESULTS
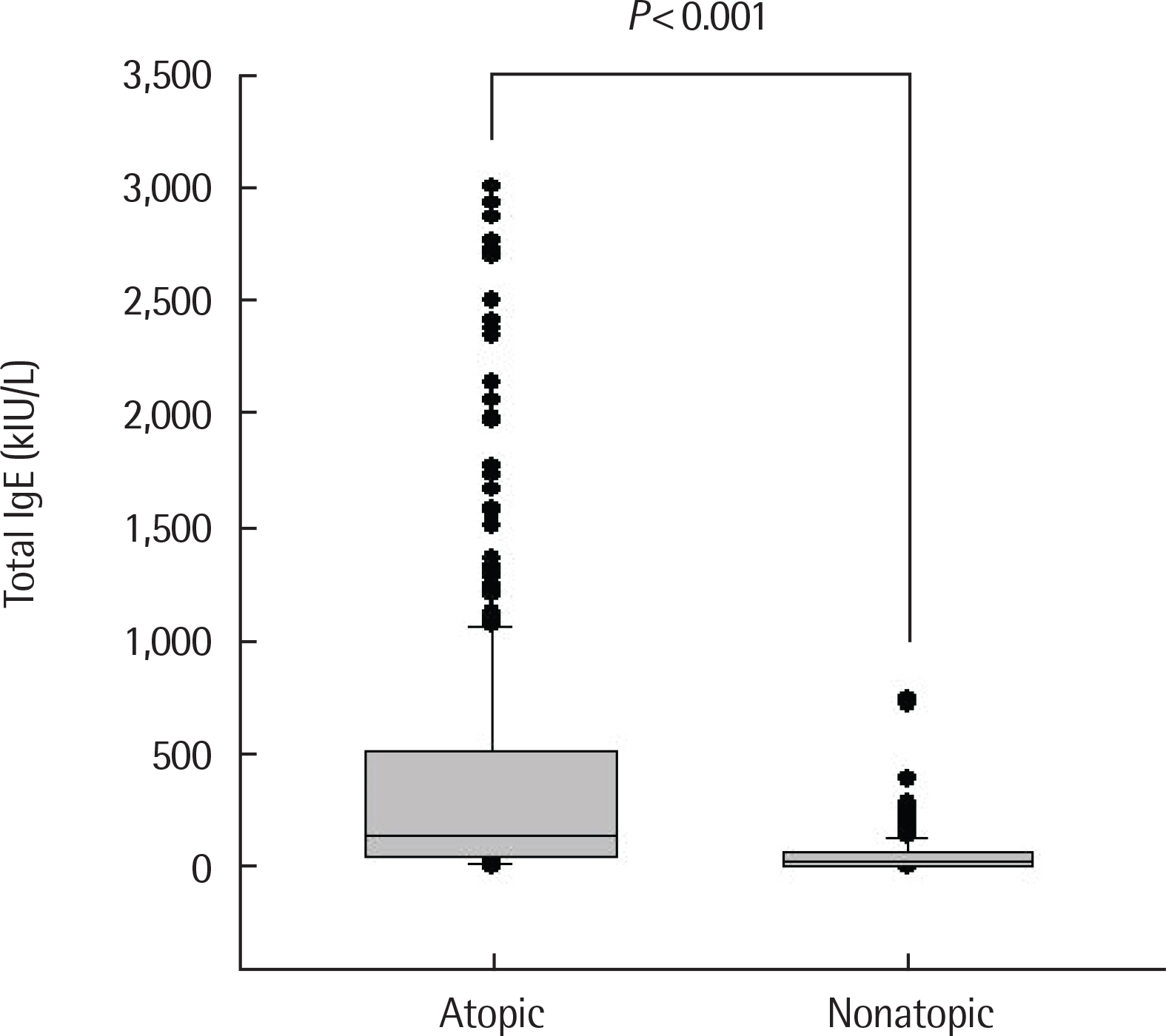
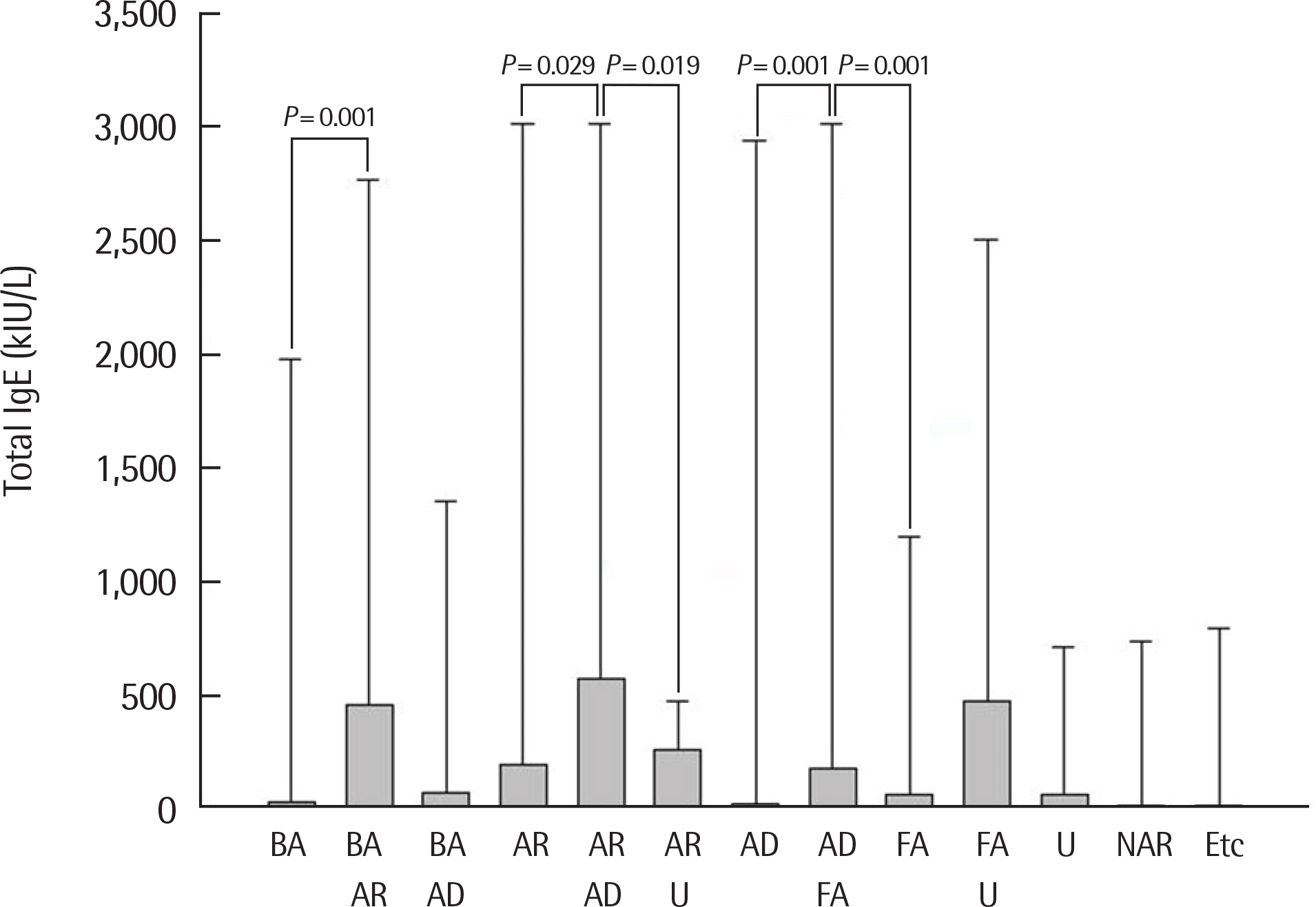
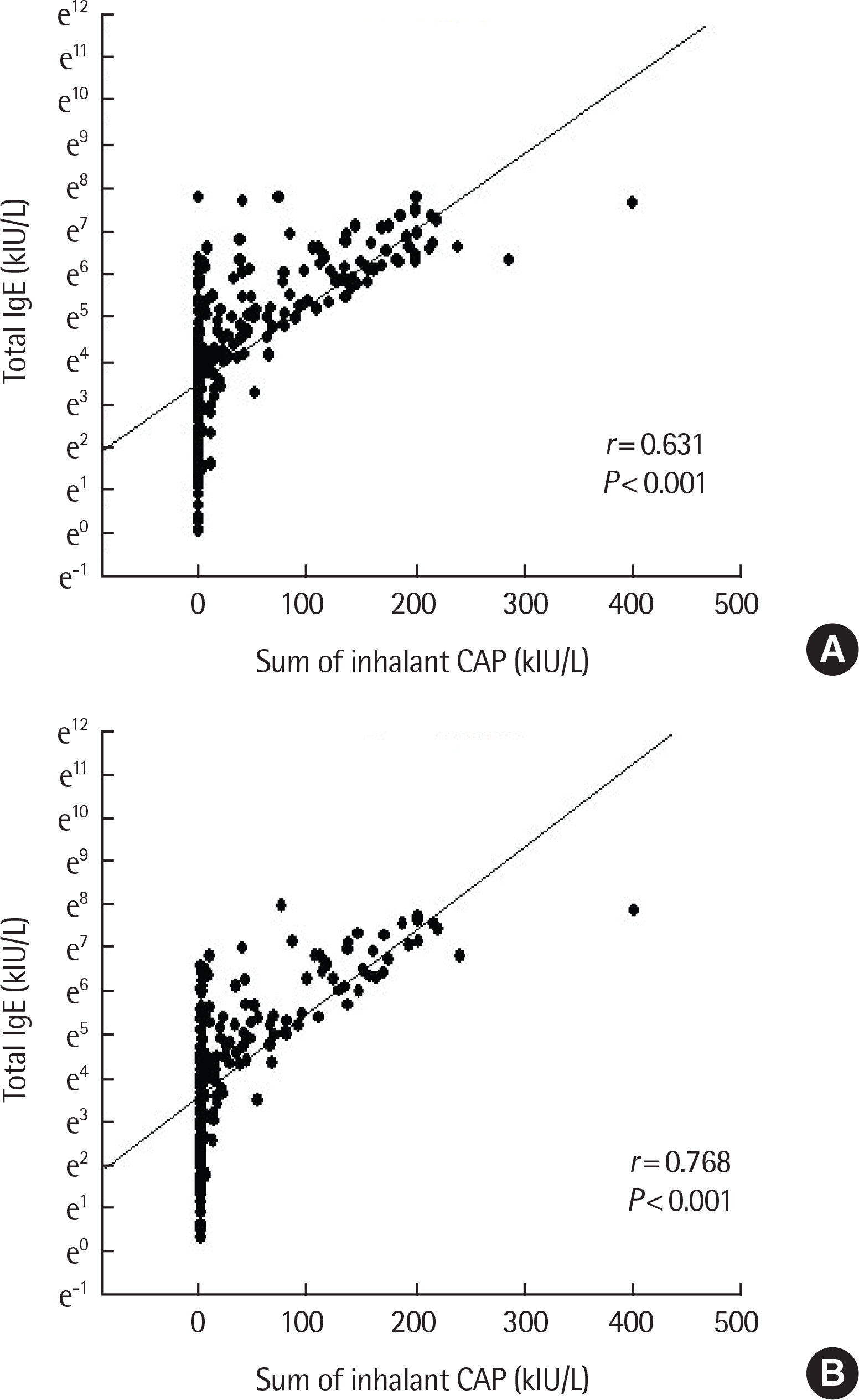
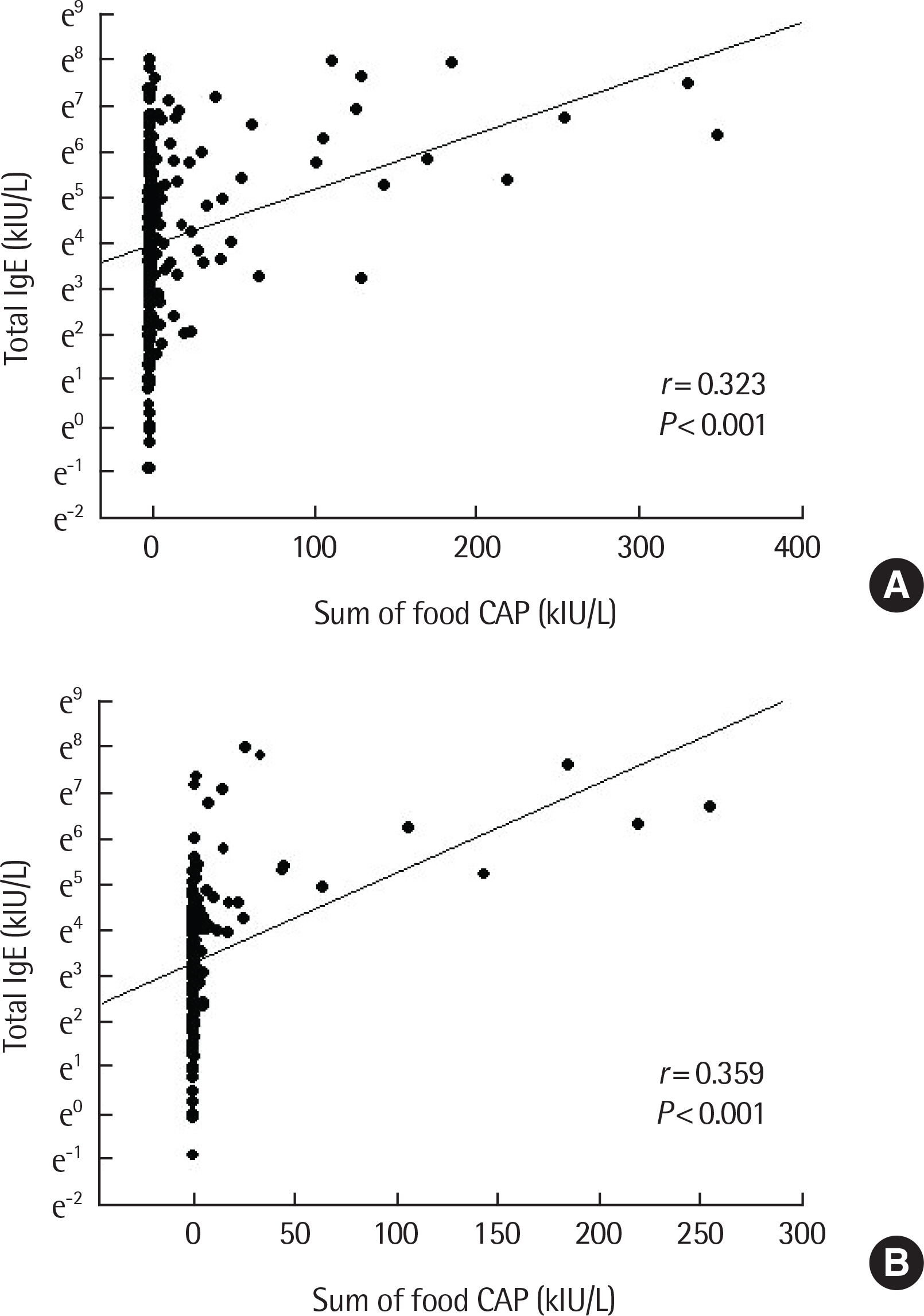
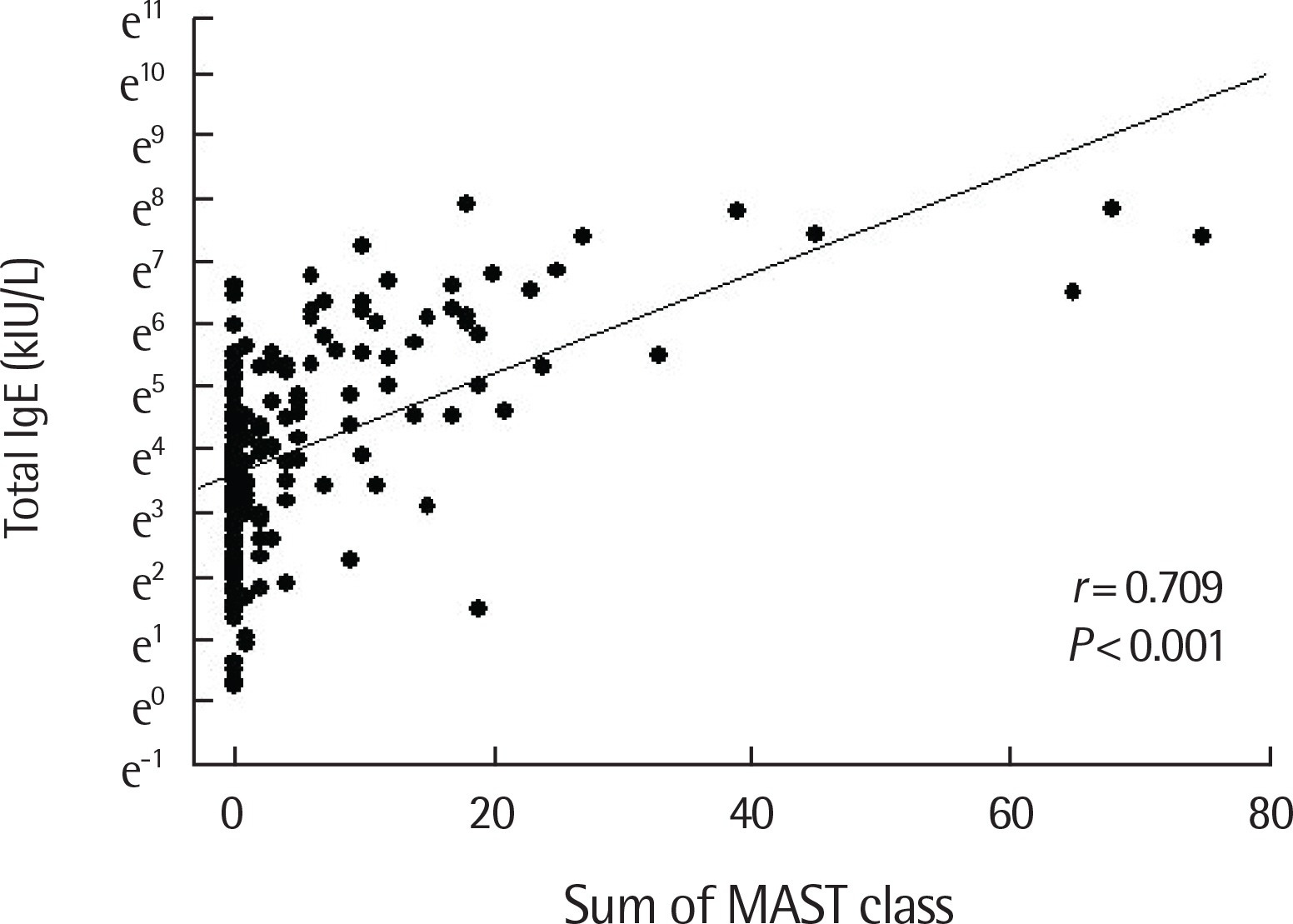
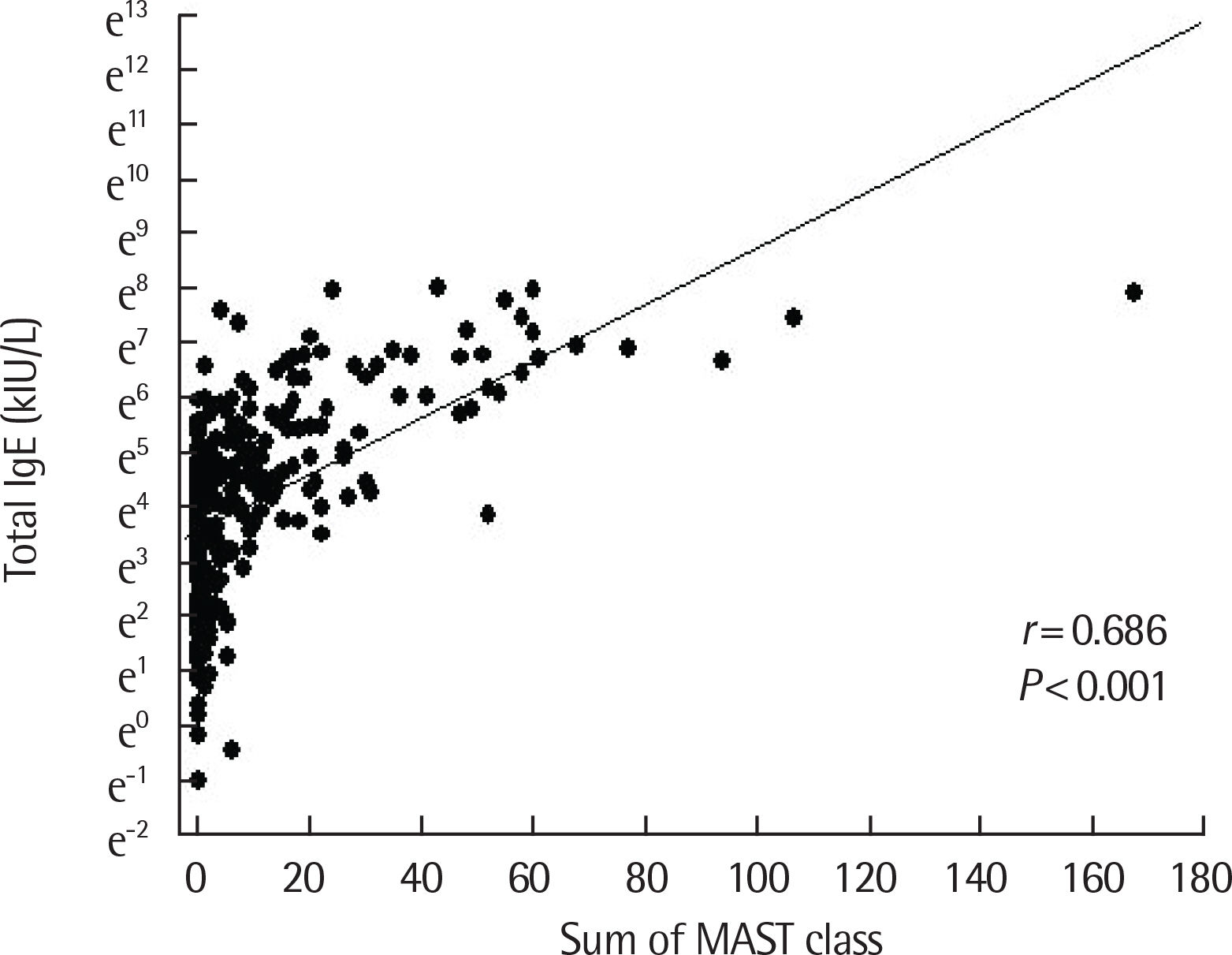
There was a positive correlation between serum total IgE and antigen level in the inhalant immunoCAP test. Specifically, the sum of immunoCAP levels was highly correlated with serum total IgE (r=0.631, P<0.001). Moreover, there was a positive correlation between serum total IgE and the sum of food immunoCAP levels (r=0.323, P<0.001). Among the food immunoCAP antigens, milk was highly correlated with serum total IgE (r=0.558, P<0.001). There was a positive correlation between serum total IgE and the sum of class levels of inhalant/food MAST tests (r=0.709, P<0.001 and r=0.686, P<0.001, respectively). There was also a positive correlation between serum total IgE and the number of positive skin prick tests (r=0.445, P<0.001).
CONCLUSION
Serum total IgE may reflect the sum of serum specific IgE levels in pediatric allergic disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Klink M, Cline MG, Halonen M, Burrows B. Problems in defining normal limits for serum IgE. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990; 85:440–4.
Article2. Chung HL. Clinical significance of serum IgE. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:416–21.
Article3. Orgel HA. Genetic and developmental aspects of IgE. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1975; 22:17–32.4. Ahmed I, Nasreen S. Frequency of raised serum IgE level in childhood atopic dermatitis. J Pak Med Assoc. 2007; 57:431–4.5. Sunyer J, Antó JM, Castellsagué J, Soriano JB, Roca J. Total serum IgE is associated with asthma independently of specific IgE levels. The Spanish Group of the European Study of Asthma. Eur Respir J. 1996; 9:1880–4.6. Koh HS, Lee KS, Han DH, Rha YH, Choi SH. Relationship between serum total IgE, specific IgE, and peripheral blood eosinophil count according to specific allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:123–8.
Article7. Jung SW, Oh EJ, Lee J, Kim Y, Kim SY, Kim Y, et al. Usefulness of total IgE in predicting positive allergen specific IgE Tests in Korean subjects. Korean J Lab Med. 2010; 30:660–7.
Article8. Woo SI, Lim JS, Hahn YS. Relationship of indoor aeroallergen specific IgE with total IgE and airway hyperresponsiveness in children with atopic asthma. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009; 19:47–55.9. Erwin EA, Rönmark E, Wickens K, Perzanowski MS, Barry D, Lundbäck B, et al. Contribution of dust mite and cat specific IgE to total IgE: relevance to asthma prevalence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:359–65.10. Sinclair D, Peters SA. The predictive value of total serum IgE for a positive allergen specific IgE result. J Clin Pathol. 2004; 57:956–9.
Article11. Chang ML, Cui C, Liu YH, Pei LC, Shao B. Analysis of total immunoglobulin E and specific immunoglobulin E of 3,721 patients with allergic disease. Biomed Rep. 2015; 3:573–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical significance of serum IgE
- Immunoglobulin E in health and disease
- Relationship between serum total IgE, specific IgE, and peripheral blood eosinophil count according to specific allergic diseases
- Usefulness of the MAST in Allergic Skin Diseases
- Clinical Characteristics of Allergic Asthmatics with Normal Total Serum IgE Levels