Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Dec;8(4):385-389. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.4.385.
Comparison of Component-Resolved Diagnosis by Using Allergen Microarray With the Conventional Tests in Allergic Rhinitis Patients: The First Using in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. rhinokim2002@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2128915
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.4.385
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to evaluate the component-resolved diagnosis using a microarray allergen chip (Immuno Solid-phase Allergen Chip, ImmunoCAP ISAC) and to compare this new diagnostic tool with the established ImmunoCAP methods for allergen-specific IgE detection in allergic rhinitis patients.
METHODS
One hundred sixty-eight allergic rhinitis patients were included in this study. All the patients were diagnosed with allergic rhinitis according to their clinical symptoms, physical examination and a positive skin prick test. We analyzed their specific IgEs for house dust mites (Dermatophagoides farine [DF] and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus [DP]), Alternaria alternata, birch, and mugwort using ImmunoCAP and ImmunoCAP ISAC in the same patient sample. We compared the sensitivity and correlation between the two tests.
RESULTS
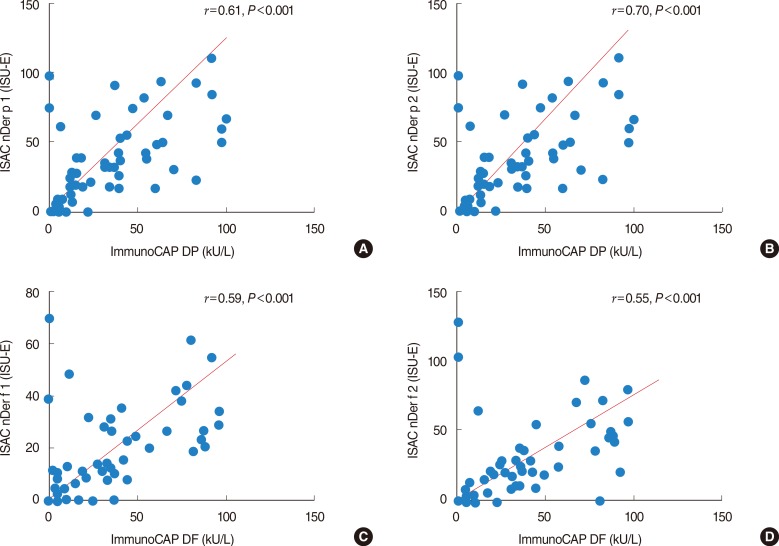
In cases of allergies to DP and DF, the sensitivity of the specific IgE was 80% and that of the allergen microarray was 78.9%. The correlation between the two tests was significant for both DP and DF (P<0.001). For the A. alternata, birch and mugwort allergens, the sensitivity of ImmunoCAP ISAC was slightly lower than that of ImmunoCAP.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that the allergen microarray chip method is a reliable new method to diagnose the components of an allergen in patients with allergic rhinitis sensitive to house dust mites. Further study about the utility of the allergen microarray is needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Patients’ Characteristics according to Allergic Sensitization in Chronic Rhinitis
Chung Man Sung, Hyung Chae Yang, Hyong-Ho Cho
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2018;61(2):85-90. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2017.00388.
Reference
-
1. Harwanegg C, Laffer S, Hiller R, Mueller MW, Kraft D, Spitzauer S, et al. Microarrayed recombinant allergens for diagnosis of allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003; 1. 33(1):7–13. PMID: 12534543.
Article2. Ferrer M, Sanz ML, Sastre J, Bartra J, del Cuvillo A, Montoro J, et al. Molecular diagnosis in allergology: application of the microarray technique. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2009; 19(Suppl 1):19–24.3. Mothes N, Valenta R, Spitzauer S. Allergy testing: the role of recombinant allergens. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2006; 44(2):125–132. PMID: 16475895.
Article4. Lidholm J, Ballmer-Weber BK, Mari A, Vieths S. Component-resolved diagnostics in food allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 6. 6(3):234–240. PMID: 16670520.
Article5. Ebo DG, Bridts CH, Verweij MM, De Knop KJ, Hagendorens MM, De Clerck LS, et al. Sensitization profiles in birch pollen-allergic patients with and without oral allergy syndrome to apple: lessons from multiplexed component-resolved allergy diagnosis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010; 2. 40(2):339–347. PMID: 19709127.
Article6. Shreffler WG. Microarrayed recombinant allergens for diagnostic testing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 4. 127(4):843–849. PMID: 21458654.
Article7. Vereda A, Andreae DA, Lin J, Shreffler WG, Ibanez MD, Cuesta-Herranz J, et al. Identification of IgE sequential epitopes of lentil (Len c 1) by means of peptide microarray immunoassay. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 9. 126(3):596–601.e1. PMID: 20816193.
Article8. Cerecedo I, Zamora J, Shreffler WG, Lin J, Bardina L, Dieguez MC, et al. Mapping of the IgE and IgG4 sequential epitopes of milk allergens with a peptide microarray-based immunoassay. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 9. 122(3):589–594. PMID: 18774394.
Article9. Ott H, Baron JM, Heise R, Ocklenburg C, Stanzel S, Merk HF, et al. Clinical usefulness of microarray-based IgE detection in children with suspected food allergy. Allergy. 2008; 11. 63(11):1521–1528. PMID: 18925888.
Article10. Lin J, Bardina L, Shreffler WG. Microarrayed allergen molecules for diagnostics of allergy. Methods Mol Biol. 2009; 2. 524:259–272. PMID: 19377951.
Article11. Wöhrl S. The potential of allergen biochips. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2008; 11. 2(3):186–190. PMID: 19076008.12. Jahn-Schmid B, Harwanegg C, Hiller R, Bohle B, Ebner C, Scheiner O, et al. Allergen microarray: comparison of microarray using recombinant allergens with conventional diagnostic methods to detect allergen-specific serum immunoglobulin E. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003; 10. 33(10):1443–1449. PMID: 14519153.
Article13. Canonica GW, Ansotegui IJ, Pawankar R, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, van Hage M, Baena-Cagnani CE, et al. A WAO - ARIA - GA2LEN consensus document on molecular-based allergy diagnostics. World Allergy Organ J. 2013; 10. 6(1):17. PMID: 24090398.14. Wohrl S, Vigl K, Zehetmayer S, Hiller R, Jarisch R, Prinz M, et al. The performance of a component-based allergen-microarray in clinical practice. Allergy. 2006; 5. 61(5):633–639. PMID: 16629796.
Article15. Cabrera-Freitag P, Goikoetxea MJ, Beorlegui C, Gamboa P, Gastaminza G, Fernandez-Benitez M, et al. Can component-based microarray replace fluorescent enzimoimmunoassay in the diagnosis of grass and cypress pollen allergy? Clin Exp Allergy. 2011; 10. 41(10):1440–1446. PMID: 21749500.
Article16. Gadisseur R, Chapelle JP, Cavalier E. A new tool in the field of in-vitro diagnosis of allergy: preliminary results in the comparison of ImmunoCAP© 250 with the ImmunoCAP© ISAC. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011; 2. 49(2):277–280. PMID: 21143018.
Article17. Bronnert M, Mancini J, Birnbaum J, Agabriel C, Liabeuf V, Porri F, et al. Component-resolved diagnosis with commercially available D. pteronyssinus Der p 1, Der p 2 and Der p 10: relevant markers for house dust mite allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 9. 42(9):1406–1415. PMID: 22747483.18. Wulfert F, Sanyasi G, Tongen L, Watanabe LA, Wang X, Renault NK, et al. Prediction of tolerance in children with IgE mediated cow's milk allergy by microarray profiling and chemometric approach. J Immunol Methods. 2012; 8. 382(1-2):48–57. PMID: 22580759.
Article19. Movérare R, Westritschnig K, Svensson M, Hayek B, Bende M, Pauli G, et al. Different IgE reactivity profiles in birch pollen-sensitive patients from six European populations revealed by recombinant allergens: an imprint of local sensitization. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002; 8. 128(4):325–335. PMID: 12218371.
Article20. Gadermaier G, Wopfner N, Wallner M, Egger M, Didierlaurent A, Regl G, et al. Array-based profiling of ragweed and mugwort pollen allergens. Allergy. 2008; 11. 63(11):1543–1549. PMID: 18925891.
Article21. Bousquet J, Michel FB. Specific immunotherapy in asthma. Allergy Proc. 1994; Nov-Dec. 15(6):329–333. PMID: 7721083.
Article22. Mellerup MT, Hahn GW, Poulsen LK, Malling H. Safety of allergen-specific immunotherapy. Relation between dosage regimen, allergen extract, disease and systemic side-effects during induction treatment. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000; 10. 30(10):1423–1429. PMID: 10998019.
Article23. Meyer CH, Bond JF, Chen MS, Kasaian MT. Comparison of the levels of the major allergens Der p I and Der p II in standardized extracts of the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994; 11. 24(11):1041–1048. PMID: 7874602.