Lab Anim Res.
2010 Jun;26(2):153-164. 10.5625/lar.2010.26.2.153.
Reference Data of the Main Physiological Parameters in Control Sprague-Dawley Rats from Pre-clinical Toxicity Studies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Preclinical Research Center, ChemOn Inc., Yongin, Korea. swansong@chemon.co.kr
- KMID: 2312061
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2010.26.2.153
Abstract
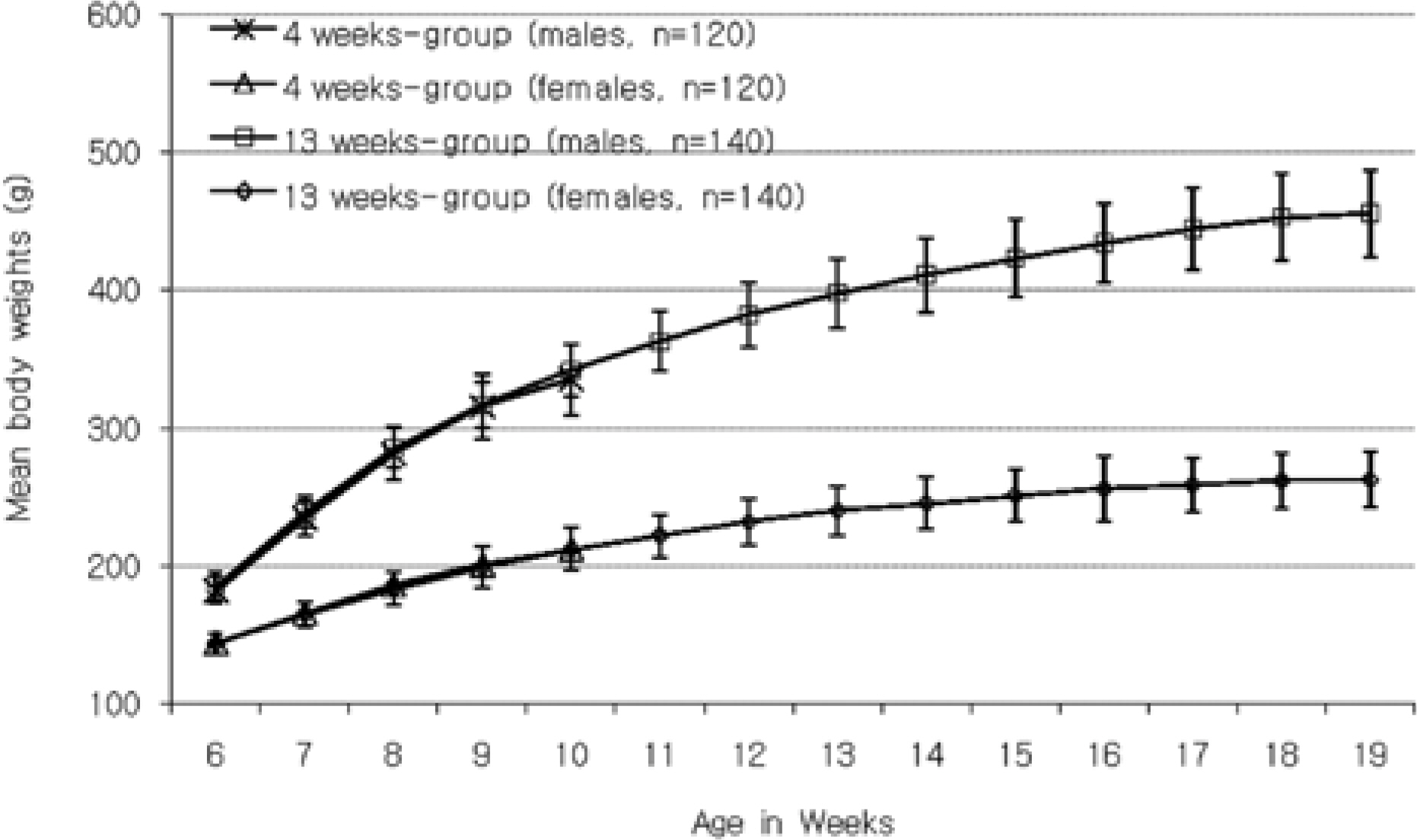
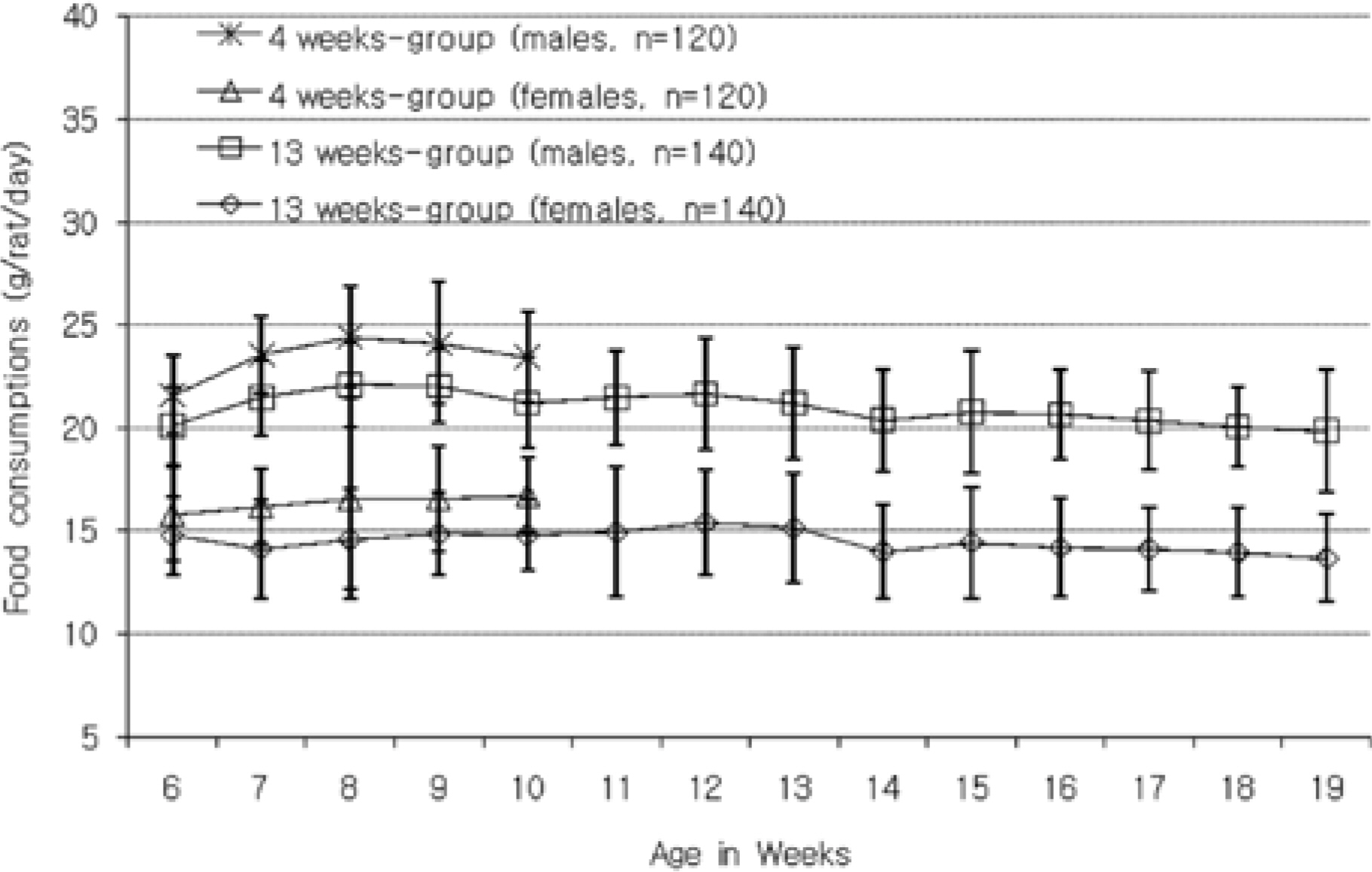
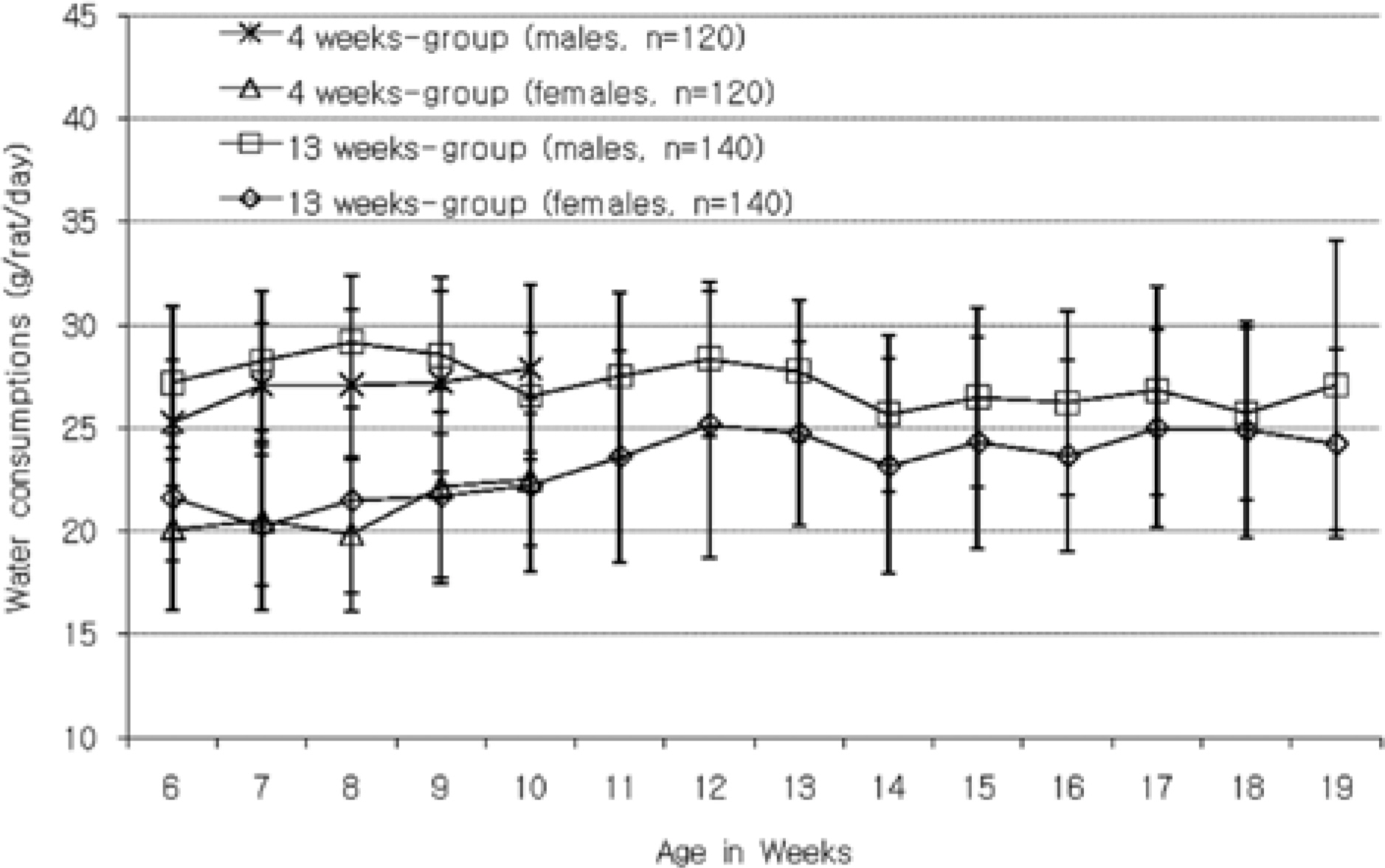
- The purpose of this paper is to provide reference data related to the body weight, food & water consumptions, urinalysis, hematology and serum biochemistry parameters and absolute & relative organ weights obtained from control Sprague-Dawley rats, used in the 4-week and 13-week repeated-dose toxicity studies conducted in our laboratory between 2005 and 2008. The mean, standard deviation, minimum and maximum range values for hematology and serum biochemistry parameters, data of absolute & relative organ weights, and the difference between sexes and study duration of week 4 versus 13 week are presented. The studies were conducted according to "the standards of Toxicity Study for Medicinal Products" (2005) and The KFDA Notification No. 2000-63 'Good Laboratory Practice (GLP)' (2000) issued by KFDA. These data could be used as reference material of Sprague-Dawley rats by conducting the studies to evaluate the toxicological profile of pre-clinical toxicity studies.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Acute toxicity and cytotoxicity evaluation of
Dendrobium moniliforme aqueous extractin vivo andin vitro
Mu-Jin Lee, Ho-Kyung Jung, Min-Suk Kim, Ji-Hun Jang, Mi-Ok Sim, Tea-Mook Kim, Ho Park, Byung-Kwan Ahn, Hyun-Woo Cho, Jung-Hee Cho, Won-Seok Jung, Jong-Choon Kim
Lab Anim Res. 2016;32(3):144-150. doi: 10.5625/lar.2016.32.3.144.
Reference
-
Abrass C.K.2000. The nature of chronic progressive nephropathy in aging rats. Adv. Ren. Replace. Ther. 7(1):4–10.
ArticleAlemán C.L.., Más R.M.., Rodeiro I.., Noa M.., Hernández C.., Menéndez R.., Gámez R.1998. Reference database of the main physiological parameters in Sprague Dawley rats from 6 to 32 months. Lab. Anim. 32(4):457–66.Alemán C.L.., Noa M.., Más R.., Rodeiro I.., Mesa R.., Menéndez R.., Gámez R.., Hernández C.2000. Reference data for the principal physiological indicators in three species of laboratory animals. Lab. Anim. 34(4):379–385.
ArticleAlt J.M.., Deerberg F.., Hackbarth H.J.., Stolte H.1980. The study of urinary protein excretion in male rats as compared with human proteinuria. Contrib. Nephrol. 19:1979–1987.Ando R.., Nakamura A.., Nagatani M.., Yamakawa S.., Ohira T.., Takagi M.., Matsushima K.., Aoki A.., Fujita Y.., Tamura K.2008. Comparison of Past and Recent Historical Control Data in Relation to Spontaneous Tumors During Carcinogenicity Testing in Fischer 344 Rats. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 21:53–60.
ArticleBauck L.., Stefkovic G.1986. Searching the records for clues about kidney disease in guineapigs. Vet. Med. 81, 1127– 1130.Baylis C.2005. Changes in renal hemodynamics and structure in the aging kidney; sexual dimorphism and the nitric oxide system. Exp. Gerontol. 40(4):271–278.
ArticleBolton W.K.., Benton F.R.., Maclay J.G.., Sturgill B.C.1976. Spontaneous glomerular sclerosis in aging Sprague-Dawley rats. I. Lesions associated with mesangial IgM deposits. Am. J. Pathol. 85(2):277–302.Bounous D.., Bourdeaux M.K.., Hoskins J.D.1995. Hematology of normal dogs and cats and responses to diseases. pp. 337-353, WB Saunders Co, Philadelphia.Braun J.P.., Aktas M.., Lefebvre H.., Rico A.G.., Toutain P.L.1993. Clinical enzymology for the assessment of organ damage: interspecific differences. Comp. Haematol. Int. 3:27–32.
ArticleDodds W.J.1980. Hemostasis and coagulation. p. 671–718. Academic Press;New York:Elcüman E.A.., Akay M.T.1998. Age-Dependent Immuno-localization of Fibronectin and Histological Changes in the Thymus of Rats. Vet. Res. Comm. 22(8):525–532.Elmore S.A.2006. Enhanced Histopathology of the Thymus. Toxicol. Pathol. 34(5):656–665.
ArticleGonder J.C.., Laber K.2007. A renewed look at laboratory rodent housing and management. ILAR J. 48(1):29–36.
ArticleIwata H.., Hagiwara T.., Katoh M.., Yamamoto S.., Yamakawa S.., Shiga A.., Hirouchi Y.., Kobayashi K.., Inoue H.., Enomoto M.1993. Historical control data of organ weight and gross findings in F344/DuCrj rats and B6C3F1 mice. Jikken Dobutsu. 42(3):383–396.Kaneko J.J.1997. Serum proteins and the dysproteinemias. pp. 117–138, Academic Press, London, New York.Kang B.H.., Kim Y.B.., Lee H.S.., Kim Y.H.., Im W.J.., Ha H.S.2004. Background Data on Hematology, Blood Biochemistry and Organ Weights for 2 Weeks and 4 Weeks Repeated-Dose Toxicity Studies Using Sprague-Dawley (SD) Rats. Korean J. of Lab. Anim. Sci. 20(2):134–140.Kang B.H.., Son, H.Y. Ha C.S.., Lee H.S.., Song S.W.1995. Reference values of hematology and serum chemistry in Ktc: Sprague-Dawley rats. Korean J. of Lab. Anim. Sci. 11(2):141–145.Kitagaki M.., Yamaguchi M.., Nakamura M.., Sakurada K.., Suwa T.., Sasa H.2005. Age-related changes in haematology and serum chemistry of Weiser-Maples guineapigs (Cavia porcellus). Lab. Anim. 39(3):321–330.
ArticleKohn D.F.., Clifford C.B.2002. Laboratory animal medicine. pp. 121-165, Academic Press, Amsterdam.Leonard R.., Ruben Z.1986. Hematology reference values for peripheral blood of laboratory rats. Lab. Anim. Sci. 36(3):Lipman N.S.., Perkins S.E.2002. Laboratory animal medicine, pp. 1143-1184, Academic Press, Amsterdam.Loeb W.F.., Carakostas M.C.1992. Pathobiology of the Aging Rat. pp. 7-13, ILSI Press, Washington.Loeb W.F.., Das S.R.., Harbour L.S.., Turturro A.., Bucci T.J.., Clifford C.B.1996. Pathobiology of the Aging Mouse. pp. 3-20, ILSI Press, Washington.Loria A.., Reverte V.., Salazar F.., Saez F.., Llinas M.T.., Salazar F.J.2007. Sex and age differences of renal function in rats with reduced Ang II activity during the nephrogenic period. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 293(2):506–510.
ArticleMatsuzawa T.., Nomura M.., Yonezawa H.., Unno T.1995. Selection of appropriate parameters, use of a quality control concept, and suitable statistical analyses for clinical pathology examination of animals in toxicity studies: results of a current survey by the Japanese Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association. Comp. Haematol. Int. 5:196–200.
ArticleOwen R.A.., Haywood R.1986. Age-related variations in renal structure and function in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol. Pathol. 14:158–167.
ArticlePetterino C.., Argentino-Storino A.2006. Clinical chemistry and haematology historical data in control Sprague-Dawley rats from pre-clinical toxicity studies. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 57(3):213–219.
ArticleRagan H.A.., Weller R.E.1999. The Clinical Chemistry of Laboratory Animals, 2nd ed., pp. 519-548, Taylor & Francis Inc, Philadelphia.Roe F.J.C.1991. Biological Effects of Dietary Restriction. pp 287-Roe, F.J.C. (1993) Experimental Toxicology. pp. 28, Surrey, Bibra.Sauer M.B.., Dulac H.., Clark S.., Moffitt K.M.., Price J.., Dambach D.., Mosher H.., Bounous D.., Keller L.2006. Clinical pathology laboratory values of rats housed in wire-bottom cages compared with those of rats housed in solid-bottom cages. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 45(1):30–35.Seki M.., Hirashima K.., Kobayashi K.1981. Hematology of experimental animals. pp. 334335, Soft Science, Inc., Tokyo.Sharp J.., Zammit T.., Azar T.., Lawson D.2003. Stress-like responses to common procedures in individually and group-housed female rats. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 42(1):9–18.Snell K.C.1967. Pathology of laboratory rats and mice. pp. 104-145, Blackwell, Oxford.Song C.W.., Hwang H.S.., Han S.S.1990. Studies on the Basic data of Ktc: SD Rats with Age-Body weight, Hematology, Serum Chemistry and Urinalysis. Korean J. of Lab. Anim. Sci. 6(1):33–43.Song C.W.., Hwang H.S.., Han S.S.1992. Studies on the Basic data of Ktc: Wistar Rats with Age-Body weight, Organ Weight, Hematology, Serum Chemistry and Urinalysis. Korean J. of Lab. Anim. Sci. 8(1):13–22.Stevens K.R.., Gallo M.A.1989. Principles and Methods of Toxicology. 3rd ed., pp. 237-250. Raven Press, New York.Tanimoto Y.1988. Laboratory animals [in Japanese] pp. 91, Soft Science, Inc., Tokyo, Japan.Uchida K.., Chikai T.., Takase H.., Nomura Y.., Seo S.., Nakao H.., Takeuchi N.1990. Age-Related Changes of Bile Acid Metabolism in Rats. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 10(1):37–48.
ArticleVerhagen A.M.., Attia D.M.., Koomans H.A.., Joles J.A.2000. Male gender increases sensitivity to proteinuria induced by mild NOS inhibition in rats: role of sex hormones. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 279(4):664–670.
ArticleWeingand K.W.., Bloom J.., Carakostas M.., Hall R.., Helfrich M.., Latimer K.., Levine B.., Neptun D.., Rebar A.., Stitzel K.., Troup C.1992. Clinical pathology testing recommendations for nonclinical toxicity and safety studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 20:539–543.
ArticleWilliams G.M.., Weirburger J.H.1991. Chemical carcinogenesis. pp. 127-200, Pergamon Press, New York.Wolford S.T.., Schroer R.A.., Gohs F.X.., Gallo P.P.., Brodeck M.., Falk H.B.., Ruhren F.R.1986. Reference range data base for serum chemistry and hematology values in laboratory animals. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. 18(2):161–188.
ArticleWolford S.T.., Schorer R.A.., Gallo P.P.., Gohs F.X.., Brodeck M.., Falk H.B.., Ruhren R.1987. Age-related changes in serum chemistry and hematology values in normal Sprague-Dawley rats. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 8(1):80–88.
ArticleYamada J.1989. Biochemical Reference Data Book on Experimental Animals. Soft Science. Inc. Tokyo, Japan.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A 6-Week Oral Toxicity Study of Oral Cholera Vaccine in Sprague-Dawley Rats
- Historical control data from 13-week repeated toxicity studies in Crj:CD (SD) rats
- Single- and repeated-dose toxicities of aloe fermentation products in rats
- Subacute Oral Toxicity Study of Korean Red Ginseng Extract in Sprague-Dawley Rats
- Effect of Agglomeration on the Toxicity of Nano-sized Carbon Black in Sprague-Dawley Rats