Lab Anim Res.
2012 Jun;28(2):115-121. 10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.115.
Historical control data from 13-week repeated toxicity studies in Crj:CD (SD) rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Biotoxtech Co., Ltd, Ochang Scientific Industrial Complex, Cheongwon-gun, Korea.
- 2Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Namseoul University, Cheonan, Korea. kang@nsu.ac.kr
- 3Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. jkkang@cbu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1436707
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.115
Abstract
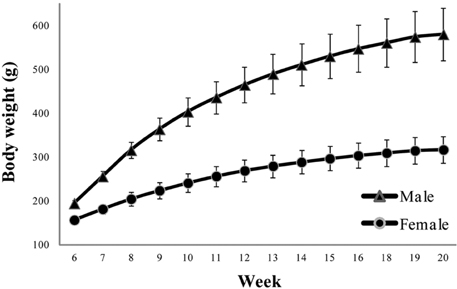
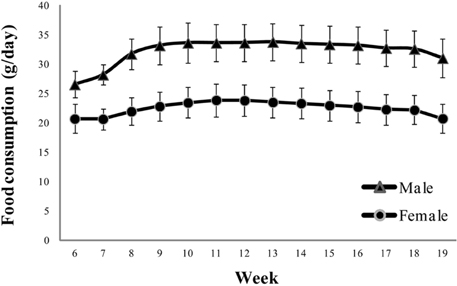
- Reference ranges of standard experimental parameters are useful for comparisons in toxicology. The aim of this study was to collect data from 13-week repeated toxicity studies in Crl:CD (SD) rats, a strain widely used for toxicity and efficacy research, for establishing domestic reference values. Data on body weight, food consumption; urinalysis, hematological, and blood biochemical parameters; and organ weights were collected from 11 toxicity studies in 220 Crl:CD (SD) rats (110 males and 110 females). The studies had been performed at a single testing facility over the last 5 years and involved animals sourced from a single breeder. The findings were collated as means, standard deviations, percentages, and ranges. Urine volume, uterus weight, eosinophil, and basophil counts, and triglyceride, total bilirubin, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase levels showed standard deviations of 30% or more. These historical control data would help to interpret the effects of test substances in routine toxicity and efficacy studies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Acute toxicity and cytotoxicity evaluation of
Dendrobium moniliforme aqueous extractin vivo andin vitro
Mu-Jin Lee, Ho-Kyung Jung, Min-Suk Kim, Ji-Hun Jang, Mi-Ok Sim, Tea-Mook Kim, Ho Park, Byung-Kwan Ahn, Hyun-Woo Cho, Jung-Hee Cho, Won-Seok Jung, Jong-Choon Kim
Lab Anim Res. 2016;32(3):144-150. doi: 10.5625/lar.2016.32.3.144.
Reference
-
1. Kang BH, Kim IH, Kim YB, Kim YH, Lee HS, Ha CS. Reference Values of Organ Weights in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Korean J Vet Pathol. 2001. 5:39–42.2. Cho JH, Jeong SH, Ku HO, Kang HG, Park JM, Yun HI, Lee YS. Improved Novel Method of Blood Sample Collection via Jugular Vein in Unanesthetized Rats. Lab Anim Res. 1997. 13:117–120.3. Kang BH, Kim YB, Lee HS, Kim YH, Im WJ, Ha CS. Background Data on Hematology, Blood Chemistry and Organ Weights for 2 Weeks and 4 Weeks Repeated-Dose Toxicity Studies Using Sprague-Dawley (SD) Rats. Lab Anim Res. 2004. 20:134–140.4. Ha CS, Son HY, Kang BY, Cha SW, Park JI, Han SS. A Study of Hematology and Serum Chemistry in Beagle Dogs. Lab Anim Res. 1995. 11:153–158.5. Song CW, Cho KH, Han HS, Han SS. The Effects of Fasting Time on Haematological and Blood Biochemical Parameters in SD Rats. Lab Anim Res. 1994. 10:73–80.6. Stockham SL, Scott MA. Fundamentals of Veterinary Clinical Pathology. 2002. Wiley-Blackwell;32–34.7. Hirata M, Nomura G, Tanimoto Y. Stability of Serum Components in Monkey, Dog and Rat. Exp Anim. 1979. 28:401–404.8. Song CW, Hwang HS, Han SS. Studies on the Basic Data of Ktc:SD Rats with Age-Body Weight, Hematology, Serum Chemistry and Urinalysis. Lab Anim Res. 1990. 6:33–43.9. Kang BH, Son HY, Ha CS, Lee HS, Song SW. Reference Values of Hematology and Serum Chemistry in Ktc:Sprague-Dawley Rats. Lab Anim Res. 1995. 11:141–145.10. Gwon YI, Kang SC, Kang JS, Gwon JK, Park WD, Shin JH, Won R, Lee JS, Choi WC, Hwang SY. Clinical Pathology of Laboratory Animal. 2009. Academya;84–85.11. Yamada H. Evaluation methods for nephrotoxicity. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2009. 133(3):154–157.12. Hayes AW. Principles and Methods of Toxicology. 2001. 4th ed. CRC/Taylor & Francis;1032–1033.13. Meyer DJ, Harvey JW. Veterinary Laboratory Medicine: Interpretation & Diagnosis. 1998. 2nd ed. WB Saunders;223–224.14. Verhagen AM, Attia DM, Koomans HA, Joles JA. Male gender increases sensitivity to proteinuria induced by mild NOS inhibition in rats: role of sex hormones. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000. 279(4):F664–F670.15. Swenberg JA. Alpha 2u-globulin nephropathy: review of the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved and their implications for human risk assessment. Environ Health Perspect. 1993. 101:Suppl 6. 39–44.16. Gad SC. Animal Models in Toxicology. 2008. 2nd ed. CRC/Taylor & Francis;814–815.17. Hamamura M, Hirose A, Kamata E, Katoku K, Kuwasaki E, Oshikata T, Nakahara Y, Ema M, Hasegawa R. Semi-quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of male rat-specific alpha2u-globulin accumulation for chemical toxicity evaluation. J Toxicol Sci. 2006. 31(1):35–47.18. Kim JS, Hwang SY, Chu SK, Kim IT. The Effects of Time and Temperature Variables on PT and aPTT Test of Stored Plasma and Whole Blood. J Clin Pathol Exam Sci. 2000. 32:40–47.19. Oh SH, Do SG. Reference Values of Body Weight, Blood Pressure, Hematology and Serum Biochemistry in the Sprague-Dawley (SD) Rats from 24 to 30 Months. Lab Anim Res. 2001. 17:275–282.20. Emori T, Takahashi M, Nagase S. Comparative studies on lactate dehydrogenase in serum and plasma of rats. Jikken Dobutsu. 1978. 27(2):167–175.21. Mariko H, Mamoru N, Masayuki Y. Clinical Chemistry of the Animal. Influence Factors to Be Considered on Establishment of the Reference Data of ALT, AST and ALP in Rats. Japanese Journal of Clinical Chemistry. 2001. 30:142–152.22. Fox JG, Anderson LC, Loew FM, Quimby FW. Laboratory Animal Medicine. 2002. 2nd ed. Academic Press;95–104.23. Okamura T, Suzuki S, Ogawa T, Kobayashi J, Kusuoka O, Hatayama K, Mochizuki M, Hoshiya T, Okazaki S, Tamura K. Background Data for General Toxicology Parameters in RccHan:WIST Rats at 8, 10, 19 and 32 Weeks of Age. J Toxicol Pathol. 2011. 24(4):195–205.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Age-dependent change trends of clinicopathological parameters in F344 rats
- Reference Data of the Main Physiological Parameters in Control Sprague-Dawley Rats from Pre-clinical Toxicity Studies
- 13-week subchronic toxicity study of a novel ginsenoside composition from ginseng leaves in rats
- Acute Oral or Dermal and Repeated Dose 90-Day Oral Toxicity of Tetrasodium Pyrophosphate in Spraque Dawley (SD) Rats
- Effect of Chlorella intake on Cadmium metabolism in rats