J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2015 Dec;15(4):251-255.
An 18-year-old patient with Prader-Willi syndrome: a case report on dental management under sedation and general anesthesia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. stberryfield@gmail.com
Abstract
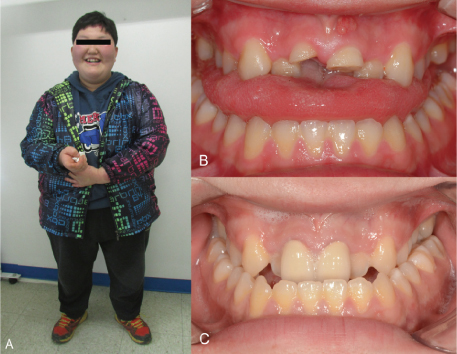
- Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is a rare genetic disorder reported rarely in dentistry. Dental practitioners should know the features of PWS because affected patients have a variety of dental symptoms. The current report describes a case of PWS. An 18-year-old male patient presented with traumatic injuries. Initial emergency treatments were performed under sedation, and further treatments were conducted under general anesthesia. After adequate healing, periodic follow-up and dietary management according to the patient's age and nutritional phase were recommended. Dental management of PWS patients consists of active preventive measures in addition to dietary consultation according to age and nutritional phase.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Prader A, Labhart A, Willi H. Ein syndrome von adipositas, kleinwuchs, kryptorchismus und oligophrenie nach myatonieartigem zustand im neugeborenenalter. Schweiz Med Wschr. 1956; 86:1260–1261.2. Cassidy SB, Schwartz S, Miller JL, Driscoll DJ. Prader-willi syndrome. Genet Med. 2012; 14:10–26.
Article3. Powis L, Oliver C. The prevalence of aggression in genetic syndromes: A review. Res Dev Disabil. 2014; 35:1051–1071.
Article4. Buiting K. Prader-willi syndrome and angelman syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2010; 154C:365–376.
Article5. McAllister CJ, Whittington JE, Holland AJ. Development of the eating behaviour in prader-willi syndrome: Advances in our understanding. Int J Obes (Lond). 2011; 35:188–197.
Article6. Miller JL, Lynn CH, Driscoll DC, Goldstone AP, Gold JA, Kimonis V, et al. Nutritional phases in prader-willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2011; 155A:1040–1049.
Article7. Whittington J, Holland A. Neurobehavioral phenotype in prader-willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2010; 154C:438–447.
Article8. Reus L, Zwarts M, van Vlimmeren LA, Willemsen MA, Otten BJ, Nijhuis-van der Sanden MW. Motor problems in prader-willi syndrome: A systematic review on body composition and neuromuscular functioning. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011; 35:956–969.
Article9. Bailleul-Forestier I, Verhaeghe V, Fryns JP, Vinckier F, Declerck D, Vogels A. The oro-dental phenotype in prader-willi syndrome: A survey of 15 patients. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2008; 18:40–47.
Article10. Greenwood RE, Small IC. Case report of the prader-willi syndrome. J Clin Periodontol. 1990; 17:61–63.
Article11. Salako NO, Ghafouri HM. Oral findings in a child with prader-labhart-willi syndrome. Quintessence Int. 1995; 26:339–341.12. Saeves R, Nordgarden H, Storhaug K, Sandvik L, Espelid I. Salivary flow rate and oral findings in prader-willi syndrome: A case-control study. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2012; 22:27–36.
Article13. Saeves R, Espelid I, Storhaug K, Sandvik L, Nordgarden H. Severe tooth wear in prader-willi syndrome. A case-control study. BMC Oral Health. 2012; 12:12.
Article14. Saeves R, Reseland JE, Kvam BM, Sandvik L, Nordgarden H. Saliva in prader-willi syndrome: Quantitative and qualitative characteristics. Arch Oral Biol. 2012; 57:1335–1341.
Article15. Kim MK, Lee WY, Kang JH, Kang JH, Kim BT, Kim SM, et al. 2014 clinical practice guidelines for overweight and obesity in korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2014; 29:405–409.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prader-Willi Syndrome: A case report
- A Case of Prader Willi syndrome
- Experience with reversal of a neuromuscular block with sugammadex in a child with Prader-Willi syndrome: A case report
- Anesthetic Management in Pediatric Patient with Prader-Willi Syndrome: A case report
- Anesthetic management in a pediatric patient with infantile phase Prader-Willi Syndrome: A case report