J Breast Cancer.
2016 Jun;19(2):214-217. 10.4048/jbc.2016.19.2.214.
Eribulin Mesylate Combined with Local Treatment for Brain Metastasis from Breast Cancer: Two Case Reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Breast Center, Department of Surgery, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea. kitah@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Surgery, Gangnam Medical Research Center, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2308975
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2016.19.2.214
Abstract
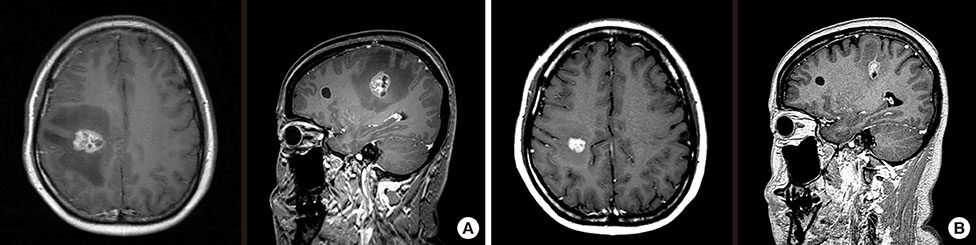
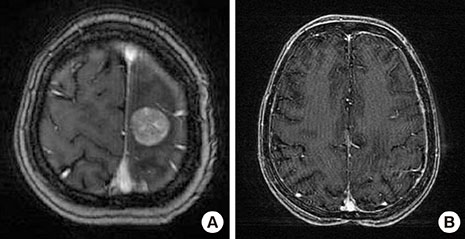
- The prognosis associated with brain metastasis arising from breast cancer is very poor. Eribulin is a microtubule dynamic inhibitor synthesized from halichondrin B, a natural marine product. In a phase III study (EMBRACE), eribulin improved overall survival in patients with heavily pretreated metastatic breast cancers. However, these studies included few patients with brain metastases. Metastatic brain tumors (MBT) were detected during first-line palliative chemotherapy in a 43-year-old woman with breast cancer metastasis to the lung and mediastinal nodes; the genetic subtype was luminal B-like human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative. Whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) followed by eribulin treatment continuously decreased the size, and induced regression, of the MBT with systemic disease stability for 12 months. Another 48-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer (HER2+ subtype) presented with MBT. Following surgical resection of the tumor, eribulin with concurrent WBRT showed regression of the MBT without systemic progression for 18 months.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lin NU, Bellon JR, Winer EP. CNS metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:3608–3617.
Article2. Arslan C, Dizdar O, Altundag K. Chemotherapy and biological treatment options in breast cancer patients with brain metastasis: an update. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014; 15:1643–1658.
Article3. Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW, Lane WW. Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma: autopsy study. Cancer. 1983; 52:2349–2354.
Article4. Shablak A. Eribulin for advanced breast cancer: a drug evaluation. J Breast Cancer. 2013; 16:12–15.
Article5. Bai RL, Paull KD, Herald CL, Malspeis L, Pettit GR, Hamel E. Halichondrin B and homohalichondrin B, marine natural products binding in the vinca domain of tubulin: discovery of tubulin-based mechanism of action by analysis of differential cytotoxicity data. J Biol Chem. 1991; 266:15882–15889.
Article6. Jordan MA, Kamath K, Manna T, Okouneva T, Miller HP, Davis C, et al. The primary antimitotic mechanism of action of the synthetic halichondrin E7389 is suppression of microtubule growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005; 4:1086–1095.
Article7. Cortes J, Vahdat L, Blum JL, Twelves C, Campone M, Roché H, et al. Phase II study of the halichondrin B analog eribulin mesylate in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer previously treated with an anthracycline, a taxane, and capecitabine. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:3922–3928.
Article8. Cortes J, O'Shaughnessy J, Loesch D, Blum JL, Vahdat LT, Petrakova K, et al. Eribulin monotherapy versus treatment of physician's choice in patients with metastatic breast cancer (EMBRACE): a phase 3 open-label randomised study. Lancet. 2011; 377:914–923.
Article9. Zhang RD, Price JE, Fujimaki T, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ. Differential permeability of the blood-brain barrier in experimental brain metastases produced by human neoplasms implanted into nude mice. Am J Pathol. 1992; 141:1115–1124.10. Tóth K, Vaughan MM, Peress NS, Slocum HK, Rustum YM. MDR1 P-glycoprotein is expressed by endothelial cells of newly formed capillaries in human gliomas but is not expressed in the neovasculature of other primary tumors. Am J Pathol. 1996; 149:853–858.11. Bart J, Nagengast WB, Coppes RP, Wegman TD, van der Graaf WT, Groen HJ, et al. Irradiation of rat brain reduces P-glycoprotein expression and function. Br J Cancer. 2007; 97:322–326.
Article12. Mima T, Toyonaga S, Mori K, Taniguchi T, Ogawa Y. Early decrease of P-glycoprotein in the endothelium of the rat brain capillaries after moderate dose of irradiation. Neurol Res. 1999; 21:209–215.
Article13. Matsuoka H, Tsurutani J, Tanizaki J, Iwasa T, Komoike Y, Koyama A, et al. Regression of brain metastases from breast cancer with eribulin: a case report. BMC Res Notes. 2013; 6:541.
Article14. Funahashi Y, Okamoto K, Adachi Y, Semba T, Uesugi M, Ozawa Y, et al. Eribulin mesylate reduces tumor microenvironment abnormality by vascular remodeling in preclinical human breast cancer models. Cancer Sci. 2014; 105:1334–1342.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Eribulin for Advanced Breast Cancer: A Drug Evaluation
- Patient Management with Eribulin in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Clinical Practice Guide
- Malignant Adenomyoepithelioma of the Breast and Responsiveness to Eribulin
- Rectal metastasis arising from breast cancer: a case report
- A Case of Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis with a 16-Year Time Interval without Evidence of Cancer Recurrence