Korean Circ J.
2012 Jan;42(1):54-57. 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.1.54.
A Case of Late Stent Thrombosis Following Platelet Transfusion in a Patient With Aplastic Anemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. neosoo70@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 2297909
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2012.42.1.54
Abstract
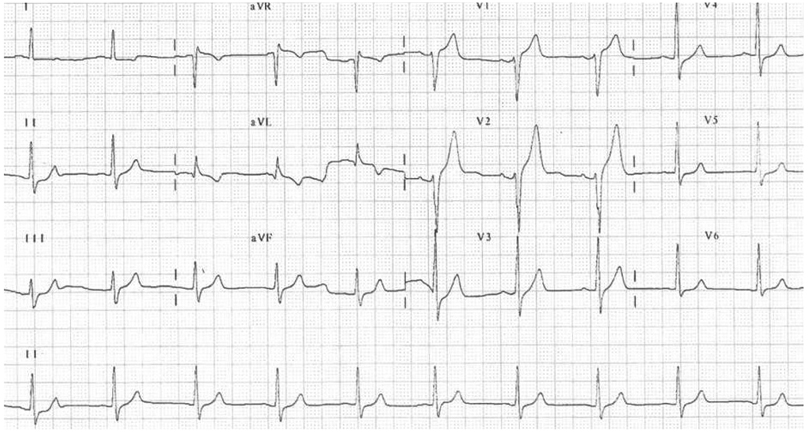
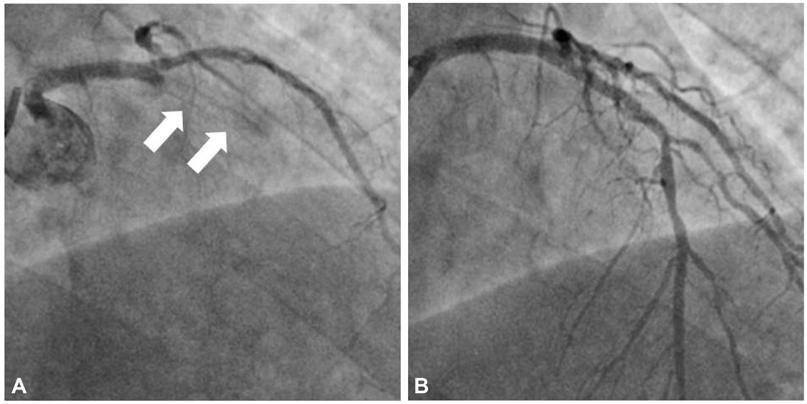
- Aplastic anemia is a condition in which the bone marrow fails to produce adequate numbers of peripheral blood elements. The incidences of atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction in patients with congenital coagulation disorders and chronic thrombocytopenia are very low. In this paper, a case of late stent thrombosis within a drug-eluting stent occurring after platelet transfusion in a patient with aplastic anemia is presented. The authors' observations emphasize the risks of platelet transfusion and the authors' support withholding such a treatment unless vitally indicated, in patients with coronary artery stent implantation and even in those on dual antiplatelet therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Toyama M, Watanabe S, Kobayashi T, et al. Two cases of acute myocardial infarction associated with aplastic anemia during treatment with anabolic steroids. Jpn Heart J. 1994. 35:369–373.2. Fisher M, Appleby M, Rittoo D, Cotter L. Myocardial infarction with extensive intracoronary thrombus induced by anabolic steroids. Br J Clin Pract. 1996. 50:222–223.3. Andrade J, Al Ali A, Saw J, Wong GC. Acute stent thrombosis in a patient with giant cell arteritis. Can J Cardiol. 2008. 24:e25–e26.4. Sabovic M, Zorman SK. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, which is released from blood product transfusions, might be associated with (sub)acute thrombosis after coronary dilatation and stenting: a case report. Heart Vessels. 2003. 18:47–49.5. Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and atherothrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1993. 70:138–143.6. Urano T, Sakakibara K, Rydzewski A, Urano S, Takada Y, Takada A. Relationship between euglobulin clot lysis time and the plasma levels of tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Thromb Haemost. 1990. 63:82–86.7. Cornet AD, Klein LJ, Groeneveld AB. Coronary stent occlusion after platelet transfusion: a case series. J Invasive Cardiol. 2007. 19:E297–E299.8. Méndez TC, Díaz O, Enríquez L, Baz JA, Fernández F, Goicolea J. Severe thrombocytopenia refractory to platelet transfusions, secondary to abciximab readministration, in a patient previously diagnosed with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a possible etiopathogenic link. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2004. 57:789–791.9. Emerson GG, Herndon CN, Sreih AG. Thrombotic complications after intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in two patients. Pharmacotherapy. 2002. 22:1638–1641.10. Paolini R, Fabris F, Cella G. Acute myocardial infarction during treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Am J Hematol. 2000. 65:177–178.11. Anderson D, Ali K, Blanchette V, et al. Guidelines on the use of intravenous immune globulin for hematologic conditions. Transfus Med Rev. 2007. 21:2 Suppl 1. S9–S56.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Aplastic Anemia in Pregnancy Refractory to Platelet Transfusion
- General Anesthesia for Cesarean Section of a Parturient with Aplastic Anemia Refractory to Platelet Transfusion
- Late Stent Thrombosis Associated with Late Stent Malapposition after Drug-Eluting Stenting: A Case Report
- Intraoperative Coagulation Management by TEG in a Patient with Aplastic Anemia: A case report
- Periodontal treatment of a patient with aplastic anemia