Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2015 Jul;19(4):299-307. 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.4.299.
Effects of Local Pancreatic Renin-Angiotensin System on the Microcirculation of Rat with Severe Acute Pancreatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology Surgery, The Central Hospital of Wuhan, Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science & Technology, Wuhan 430014, Hubei, China. panzhijian1969@sina.com
- 2Department of gynecology and obstetrics, Fifth Hospital of Wuhan, Wuhan 430050, Hubei, China.
- 3Department of General Surgery, Fifth Hospital of Wuhan, Wuhan 430050, Hubei, China.
- KMID: 2285572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.4.299
Abstract
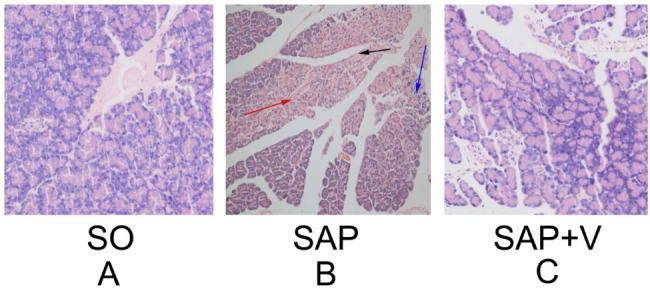
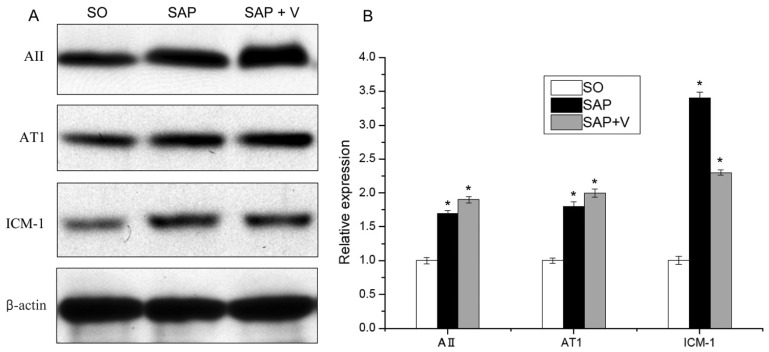
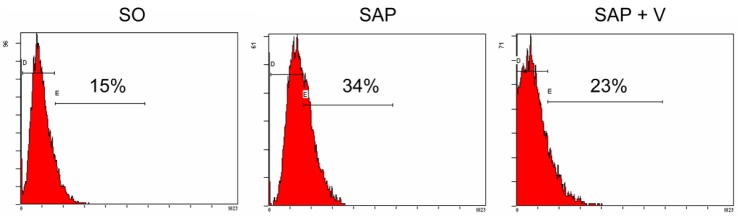
- Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) is normally related to multiorgan dysfunction and local complications. Studies have found that local pancreatic renin-angiotensin system (RAS) was significantly upregulated in drug-induced SAP. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of angiotensin II receptors inhibitor valsartan on dual role of RAS in SAP in a rat model and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms. 3.8% sodium taurocholate (1 ml/kg) was injected to the pancreatic capsule in order for pancreatitis induction. Rats in the sham group were injected with normal saline in identical locations. We also investigated the regulation of experimentally induced SAP on local RAS expression in the pancreas through determination of the activities of serum amylase, lipase and myeloperoxidase, histological and biochemical analysis, radioimmunoassay, fluorescence quantitative PCR and Western blot analysis. The results indicated that valsartan could effectively suppress the local RAS to protect against experimental acute pancreatitis through inhibition of microcirculation disturbances and inflammation. The results suggest that pancreatic RAS plays a critical role in the regulation of pancreatic functions and demonstrates application potential as AT1 receptor antagonists. Moreover, other RAS inhibitors could be a new therapeutic target in acute pancreatitis.
MeSH Terms
-
Amylases
Animals
Blotting, Western
Fluorescence
Inflammation
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
Lipase
Microcirculation*
Models, Animal
P-Selectin
Pancreas
Pancreatitis*
Peroxidase
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Radioimmunoassay
Rats*
Receptors, Angiotensin
Renin-Angiotensin System*
Taurocholic Acid
Valsartan
Amylases
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
Lipase
P-Selectin
Peroxidase
Receptors, Angiotensin
Taurocholic Acid
Figure
Reference
-
1. Akay C, Yaman H, Oztosun M, Cakir E, Yildirim AO, Eyi YE, Agilli M, Akgul EO, Aydin I, Kaldirim U, Tuncer SK, Eken A, Oztas E, Poyrazoglu Y, Yasar M, Ozkan Y. The protective effects of taurine on experimental acute pancreatitis in a rat model. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013; 32:522–529. PMID: 23536517.
Article2. Galuppo M, Nocentini G, Mazzon E, Ronchetti S, Esposito E, Riccardi L, Sportoletti P, Di Paola R, Bruscoli S, Riccardi C, Cuzzocrea S. The glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor family-related protein (GITR) is critical to the development of acute pancreatitis in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 2011; 162:1186–1201. PMID: 21091650.
Article3. Hartman H, Abdulla A, Awla D, Lindkvist B, Jeppsson B, Thorlacius H, Regnér S. P-selectin mediates neutrophil rolling and recruitment in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 2012; 99:246–255. PMID: 22109627.
Article4. Liu M, Shi L, Chen M, Chen S, Zou X. Effects of c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway on severe acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Pancreas. 2012; 41:358–366. PMID: 22015972.
Article5. Yubero S, Manso MA, Ramudo L, Vicente S, De Dios I. Dexamethasone down-regulates the inflammatory mediators but fails to reduce the tissue injury in the lung of acute pancreatitis rat models. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 25:319–324. PMID: 22691809.
Article6. Yang B, Bai B, Liu CX, Wang SQ, Jiang X, Zhu CL, Zhao QC. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on treatment of severe acute pancreatitis in rats. Cytotherapy. 2013; 15:154–162. PMID: 23321327.
Article7. Chan YC, Leung PS. The Renin-angiotensin system and reactive oxygen species: implications in pancreatitis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011; 15:2743–2755. PMID: 21644836.
Article9. Pickartz T, Mayerle J, Lerch MM. Autoimmune pancreatitis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 4:314–323. PMID: 17541445.
Article10. Hoque R, Malik AF, Gorelick F, Mehal WZ. Sterile inflammatory response in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2012; 41:353–357. PMID: 22415665.
Article11. Leung PS, Chan WP, Nobiling R. Regulated expression of pancreatic renin-angiotensin system in experimental pancreatitis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000; 166:121–128. PMID: 10996430.
Article12. Leung PS, Carlsson PO. Tissue renin-angiotensin system: its expression, localization, regulation and potential role in the pancreas. J Mol Endocrinol. 2001; 26:155–164. PMID: 11432370.
Article13. Oruc N, Ozutemiz O, Nart D, Yuce G, Celik HA, Ilter T. Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system in experimental acute pancreatitis in rats: a new therapeutic target? Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2010; 62:353–360. PMID: 19525099.
Article14. Skipworth JR, Szabadkai G, Olde Damink SW, Leung PS, Humphries SE, Montgomery HE. Review article: pancreatic renin-angiotensin systems in health and disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 34:840–852. PMID: 21851372.
Article15. Tsang SW, Cheng CH, Leung PS. The role of the pancreatic renin-angiotensin system in acinar digestive enzyme secretion and in acute pancreatitis. Regul Pept. 2004; 119:213–219. PMID: 15120483.
Article16. Tsang SW, Ip SP, Leung PS. Prophylactic and therapeutic treatments with AT 1 and AT 2 receptor antagonists and their effects on changes in the severity of pancreatitis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004; 36:330–339. PMID: 14643897.17. Leung PS. Current research of the RAS in pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010; 690:179–199. PMID: 20700843.
Article18. Tahmasebi M, Puddefoot JR, Inwang ER, Vinson GP. The tissue renin-angiotensin system in human pancreas. J Endocrinol. 1999; 161:317–322. PMID: 10320830.
Article19. de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger T. International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2000; 52:415–472. PMID: 10977869.20. Suzuki Y, Ruiz-Ortega M, Lorenzo O, Ruperez M, Esteban V, Egido J. Inflammation and angiotensin II. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003; 35:881–900. PMID: 12676174.
Article21. Zhou ZG, Chen YD, Sun W, Chen Z. Pancreatic microcirculatory impairment in experimental acute pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2002; 8:933–936. PMID: 12378645.
Article22. Skipworth JR, Nijmeijer RM, van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, Schulz HU, Kivimaki M, Kumari M, Cooper JA, Acharya J, Shankar A, Malago M, Humphries SE, Olde Damink SW, Montgomery HE. The effect of Renin Angiotensin system genetic variants in acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 2015; 261:180–188. PMID: 24743610.
Article23. Tsang SW, Cheng CH, Leung PS. The role of the pancreatic renin-angiotensin system in acinar digestive enzyme secretion and in acute pancreatitis. Regul Pept. 2004; 119:213–219. PMID: 15120483.
Article24. Ip SP, Tsang SW, Wong TP, Che CT, Leung PS. Saralasin, a nonspecific angiotensin II receptor antagonist, attenuates oxidative stress and tissue injury in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2003; 26:224–229. PMID: 12657946.
Article25. Tamizhselvi R, Koh YH, Sun J, Zhang H, Bhatia M. Hydrogen sulfide induces ICAM-1 expression and neutrophil adhesion to caerulein-treated pancreatic acinar cells through NF-kappaB and Src-family kinases pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2010; 316:1625–1636. PMID: 20211170.26. Subeq YM, Ke CY, Lin NT, Lee CJ, Chiu YH, Hsu BG. Valsartan decreases TGF-β1 production and protects against chlorhexidine digluconate-induced liver peritoneal fibrosis in rats. Cytokine. 2011; 53:223–230. PMID: 21129996.
Article27. Cole BK, Keller SR, Wu R, Carter JD, Nadler JL, Nunemaker CS. Valsartan protects pancreatic islets and adipose tissue from the inflammatory and metabolic consequences of a high-fat diet in mice. Hypertension. 2010; 55:715–721. PMID: 20100990.
Article28. Wu B, Lin R, Dai R, Chen C, Wu H, Hong M. Valsartan attenuates oxidative stress and NF-κB activation and reduces myocardial apoptosis after ischemia and reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013; 705:140–147. PMID: 23499691.
Article29. Lee BJ, Kim CD, Jung SW, Kwon YD, Kim YS, Yim HJ, Jeen YT, Lee HS, Kim JS, Chun HJ, Um SH, Lee SW, Choi JH, Ryu HS. Analysis of the factors that affect the mortality rate in severe acute pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 51:25–33. PMID: 18349559.30. Schmidt J, Rattner DW, Lewandrowski K, Compton CC, Mandavilli U, Knoefel WT, Warshaw AL. A better model of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy. Ann Surg. 1992; 215:44–56. PMID: 1731649.
Article31. Jaiswal N, Tallant EA, Jaiswal RK, Diz DI, Ferrario CM. Differential regulation of prostaglandin synthesis by angiotensin peptides in porcine aortic smooth muscle cells: subtypes of angiotensin receptors involved. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993; 265:664–673. PMID: 8496814.32. Greenstein RJ, Krakoff LR, Felton K. Activation of the renin system in acute pancreatitis. Am J Med. 1987; 82:401–404. PMID: 3548344.
Article33. Pupilli C, Lasagni L, Romagnani P, Bellini F, Mannelli M, Misciglia N, Mavilia C, Vellei U, Villari D, Serio M. Angiotensin II stimulates the synthesis and secretion of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor in human mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10:245–255. PMID: 10215323.
Article34. Schieffer B, Luchtefeld M, Braun S, Hilfiker A, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Drexler H. Role of NAD (P)H oxidase in angiotensin IIinduced JAK/STAT signaling and cytokine induction. Circ Res. 2000; 87:1195–1201. PMID: 11110778.35. Tsang SW, Ip SP, Wong TP, Che CT, Leung PS. Differential effects of saralasin and ramiprilat, the inhibitors of reninangiotensin system, on cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Regul Pept. 2003; 111:47–53. PMID: 12609748.
Article36. Chan YC, Leung PS. Involvement of redox-sensitive extracellular-regulated kinases in angiotensin II-induced interleukin-6 expression in pancreatic acinar cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009; 329:450–458. PMID: 19211919.
Article37. Yu JH, Lim JW, Kim H. Altered gene expression in ceruleinstimulated pancreatic acinar cells: pathologic mechanism of acute pancreatitis. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009; 13:409–416. PMID: 20054485.
Article38. Folch E, Salas A, Panés J, Gelpí E, Roselló-Catafau J, Anderson DC, Navarro S, Piqué JM, Fernández-Cruz L, Closa D. Role of P-selectin and ICAM-1 in pancreatitis-induced lung inflammation in rats: significance of oxidative stress. Ann Surg. 1999; 230:792–798. PMID: 10615934.39. Telek G, Ducroc R, Scoazec JY, Pasquier C, Feldmann G, Rozé C. Differential upregulation of cellular adhesion molecules at the sites of oxidative stress in experimental acute pancreatitis. J Surg Res. 2001; 96:56–67. PMID: 11180997.
Article40. Kvietys PR, Granger DN. Role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in the vascular responses to inflammation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012; 52:556–592. PMID: 22154653.
Article41. Park MY, Jeong YJ, Kang GC, Kim MH, Kim SH, Chung HJ, Jung JY, Kim WJ. Nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of human dental pulp cells is mediated by the mitochondria-dependent pathway. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014; 18:25–32. PMID: 24634593.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Renin Angiotensin System in Rabbit Corpus Cavernosum: Functional Characterization of Angiotensin II Receptors
- Renal Interstitial Fibrosis and Renin Angiotensin System Inhibition
- Colocalization of ANG II and mRNA for the Renin-Angiotensin System Components in Cultured Rat Glomerular Epithelial and Mesangial Cells
- Effect of Pinealectomy on the Renin-Angiotensin System in Sprague-Dawley Rats
- Role of Renin Angiotensin System in Clitoral avernosum Smooth Muscle