Infect Chemother.
2013 Jun;45(2):225-229. 10.3947/ic.2013.45.2.225.
A Case of Acute Cerebral Aspergillosis Complicating Influenza A/H1N1pdm 2009
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hswon1@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2285004
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2013.45.2.225
Abstract
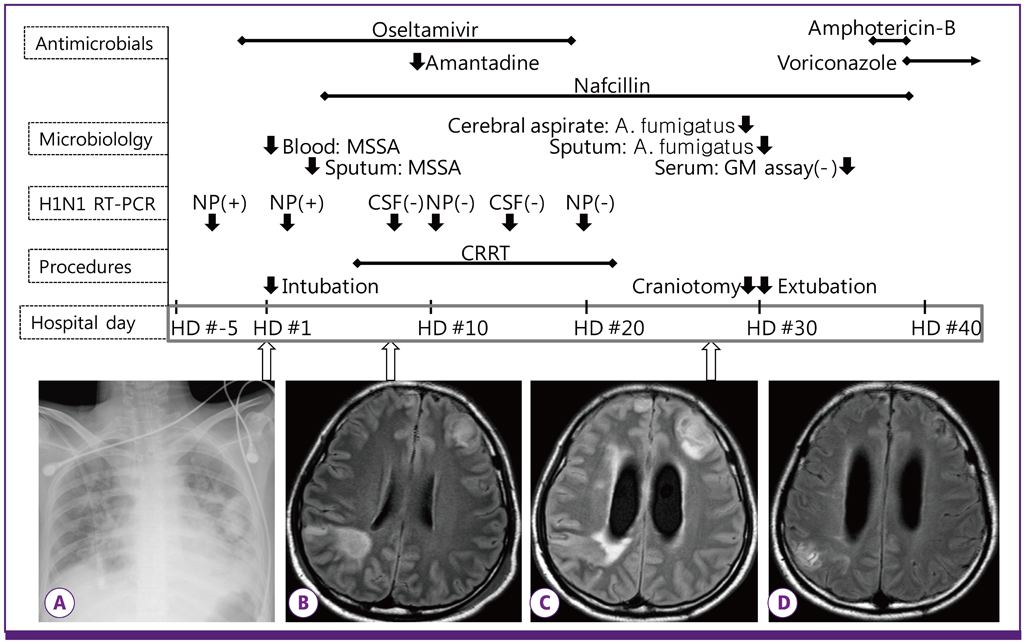
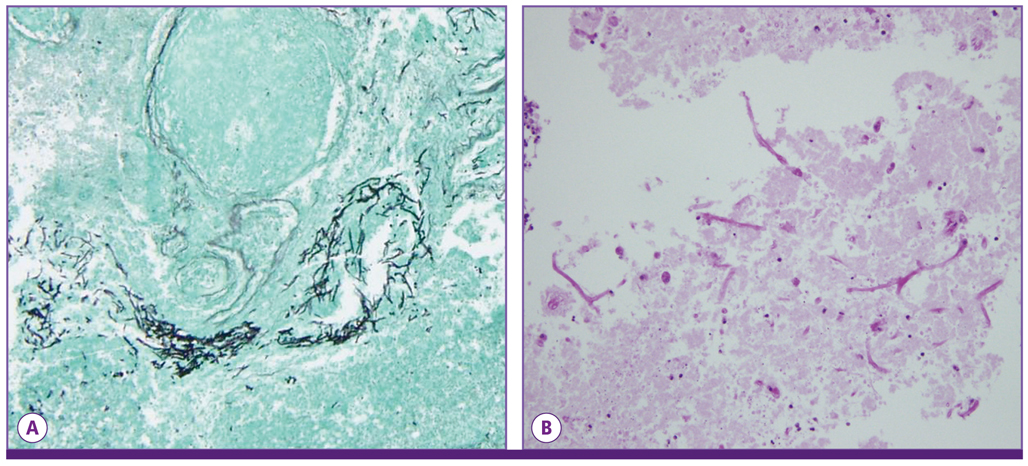
- Invasive aspergillosis is a rare complication in patients with influenza infection. Several cases of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis accompanying influenza infections were reported during the influenza A/H1N1pdm 2009. We encountered a case of acute cerebral aspergillosis in a patient with influenza A/H1N1pdm 2009 infection. A 24-year-old man with uncontrolled diabetes was diagnosed with influenza A/H1N1pdm 2009 infection. Initial evaluation indicated methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia and diabetic ketoacidosis along with influenza. During his hospital course, multiple new rim-enhancing mass lesions not evident in the initial evaluation developed in the fronto-parietal cortical and subcortical white matter and right cerebellum. Pathology and culture results confirmed the presence of Aspergillus fumigatus. Surgical drainage combined with a total of 18 weeks of antifungal therapy resulted in complete resolution of the infection. This case demonstrates that cerebral aspergillosis can present alongside influenza in patients with diabetes or those under intensive care. Clinical suspicion of invasive aspergillosis is required for a definite diagnosis and better prognosis in such cases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Passouant O, Mateu P, Commandini M, Brenkle K, Just B. Pulmonary aspergillosis in non-immunocompromised patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome during A (H1N1) infection. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2011. 30:e75–e76.
Article2. Stevens DA, Melikian GL. Aspergillosis in the 'nonimmunocompromised' host. Immunol Invest. 2011. 40:751–766.
Article3. Garcia-Vidal C, Barba P, Arnan M, Moreno A, Ruiz-Camps I, Gudiol C, Ayats J, Ortí G, Carratalà J. Invasive aspergillosis complicating pandemic influenza A (H1N1) infection in severely immunocompromised patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2011. 53:e16–e19.
Article4. Carfagna P, Brandimarte F, Caccese R, Campagna D, Brandimarte C, Venditti M. Occurrence of influenza A(H1N1)v infection and concomitant invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Mycoses. 2011. 54:549–551.
Article5. Kousha M, Tadi R, Soubani AO. Pulmonary aspergillosis: a clinical review. Eur Respir Rev. 2011. 20:156–174.
Article6. Dutkiewicz R, Hage CA. Aspergillus infections in the critically ill. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010. 7:204–209.7. Garnacho-Montero J, Amaya-Villar R, Ortiz-Leyba C, León C, Alvarez-Lerma F, Nolla-Salas J, Iruretagoyena JR, Barcenilla F. Isolation of Aspergillus spp. from the respiratory tract in critically ill patients: risk factors, clinical presentation and outcome. Crit Care. 2005. 9:R191–R199.8. Meersseman W, Vandecasteele SJ, Wilmer A, Verbeken E, Peetermans WE, Van Wijngaerden E. Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients without malignancy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004. 170:621–625.
Article9. Kwoun MO, Ling PR, Lydon E, Imrich A, Qu Z, Palombo J, Bistrian BR. Immunologic effects of acute hyperglycemia in nondiabetic rats. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1997. 21:91–95.
Article10. Janes SM, Barker KF, Mak V, Bell D. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in an insulin-dependent diabetic. Respir Med. 1998. 92:972–975.
Article11. Grizzanti JN, Knapp A. Diabetic ketoacidosis and invasive aspergillosis. Lung. 1981. 159:43–49.
Article12. Lederer JA, Rodrick ML, Mannick JA. The effects of injury on the adaptive immune response. Shock. 1999. 11:153–159.
Article13. Guarner J, Falcón-Escobedo R. Comparison of the pathology caused by H1N1, H5N1, and H3N2 influenza viruses. Arch Med Res. 2009. 40:655–661.
Article14. Lewis DE, Gilbert BE, Knight V. Influenza virus infection induces functional alterations in peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986. 137:3777–3781.15. Astry CL, Jakab GJ. Influenza virus-induced immune complexes suppress alveolar macrophage phagocytosis. J Virol. 1984. 50:287–292.
Article16. Lee FE, Daigle CC, Urban MA, Metlay LA, Treanor JJ, Trawick DR. Fever and progressive respiratory failure in three elderly family members. Chest. 2005. 128:1863–1864. 1865–1867.
Article17. Adalja AA, Sappington PL, Harris SP, Rimmele T, Kreit JW, Kellum JA, Boujoukos AJ. Isolation of Aspergillus in three 2009 H1N1 influenza patients. Influenza Other Respi Viruses. 2011. 5:225–229.18. Lat A, Bhadelia N, Miko B, Furuya EY, Thompson GR 3rd. Invasive aspergillosis after pandemic (H1N1) 2009. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010. 16:971–973.
Article19. Kim SH, Kim MN, Lee SO, Choi SH, Kim YS, Woo JH, Lim CM, Koh Y, Hong SB. Fatal pandemic influenza A/H1N1 infection complicated by probable invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses. 2012. 55:189–192.
Article20. Patterson TF, Kirkpatrick WR, White M, Hiemenz JW, Wingard JR, Dupont B, Rinaldi MG, Stevens DA, Graybill JR. I3 Aspergillus Study Group. Invasive aspergillosis. Disease spectrum, treatment practices, and outcomes. Medicine (Baltimore). 2000. 79:250–260.
Article21. Britt RH, Enzmann DR. Clinical stages of human brain abscesses on serial CT scans after contrast infusion. Computerized tomographic, neuropathological, and clinical correlations. J Neurosurg. 1983. 59:972–989.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Interstitial Pneumonia with Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
- A Case of chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis with pulmonary artery aneurysm
- Two Cases of Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum Complicating Viral Pneumonia Caused by Influenza A Virus, (H1N1 Subtype): A Case Report
- Numerous Cerebral Hemorrhages in a Patient with Influenza-Associated Encephalitis: A Case Report
- Invasive Aspergillosis Complicated by Occlusion of Internal Carotid Artery and Cerebral Infarction