Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2008 Dec;1(4):189-195.
Toll-like Receptors 2 and 4 and Their Mutations in Patients with Otitis Media and Middle Ear Effusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. yeo2park@yahoo.co.kr
- 2East-West Medical Research Institute, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
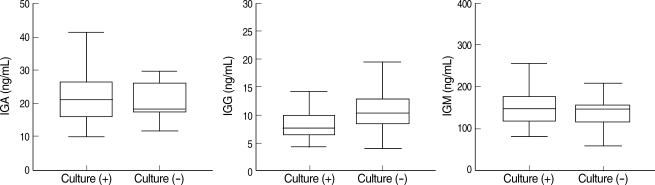
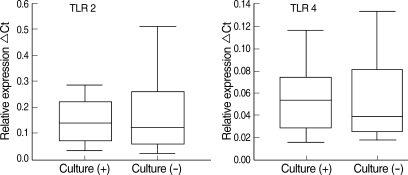
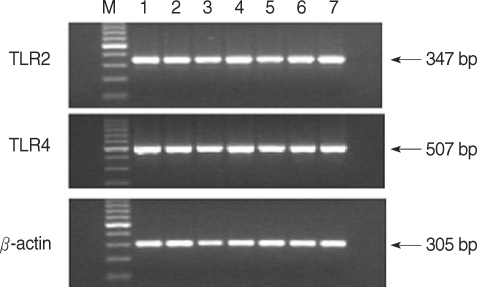
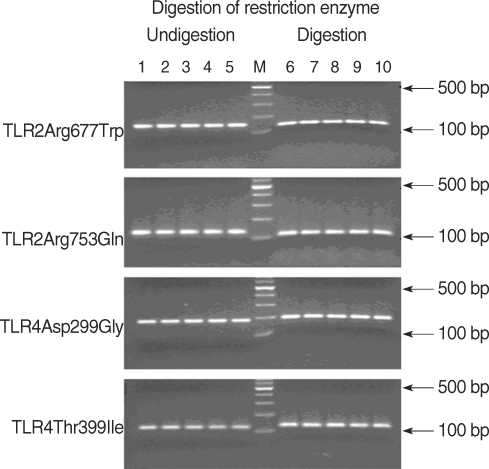
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) detect microbial infections and they can directly induce innate host defense responses. TLR 2 has been shown to be primarily involved in the recognition of peptidoglycans and lipoteichoic acid of gram positive bacteria. TLR 4 recognizes lipopolysaccharides and lipoteichoic acids from both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Both mutations lead a reduced capacity to elicit inflammation and they increase the risk for gram-positive and negative infections. This study was performed to investigate the expressions of TLR 2 and 4 and their mutations in patients suffering with otitis media and middle ear effusion. METHODS: Middle ear fluid samples were collected from 40 otitis media effusion (OME) patients who had ventilating tubesinserted. Bacteria in the effusion fluid were detected by standard bacterial culture. The secreted IgG, IgA and IgM were measured by Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. TLR 2 and 4 were assessed by performing RT-PCR. The genomic DNA from each patient was isolated from the middle ear fluid samples that were collected from 60 OME patients, and the presence of mutations was determined by performing restriction digestion and DNA sequencing analysis. RESULTS: Among the 40 middle ear fluid samples, bacteria were detected in 13 middle ear fluid samples. The amounts of IgM, IgA, and IgG were 151.20+/-60.94 ng/mL, 21.59+/-7.96 ng/mL and 11.55+/-16.98 ng/mL, respectively. TLR 2 and 4 were expressed in the middle ear fluid and the expression of TLR 2 was higher than that of TLR 4. However, there was no correlation between the expressions of TLR 2 and 4, and the concentration of immunoglobulin or the presence of bacteria (P>0.05). There ware no mutations of TLR 2 (Arg753Gln, Arg677Trp) and TLR 4 (Asp299Gly, Thr399Ile). CONCLUSION: TLR 2 and 4 were expressed in all the middle ear fluid samples of OME, but the mutations of TLR 2 and 4 were not detected. TLR 2 and 4 may play a vital role in the immunological responses of patients with OME.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Bacteria
Digestion
DNA
Ear, Middle
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Humans
Immunoglobulin A
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin M
Immunoglobulins
Inflammation
Lipopolysaccharides
Otitis
Otitis Media
Otitis Media with Effusion
Peptidoglycan
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Stress, Psychological
Teichoic Acids
Toll-Like Receptors
DNA
Immunoglobulin A
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin M
Immunoglobulins
Lipopolysaccharides
Peptidoglycan
Teichoic Acids
Toll-Like Receptors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Klein JO, Tos M, Hussl B, Naunton RF, Ohyhyama M, Van Cauwenberge PB. Recent advances in otitis media: definition and classification. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1989; 4. 139:10. PMID: 2494923.2. Kitajiri M, Sando I, Takahara T. Postnatal development of the eustachian tube and its surrounding structures: preliminary study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1987; Mar–Apr. 96(2 Pt 1):191–198. PMID: 3566059.
Article3. Tos M, Bak-Pedersen K. New aspects in the pathogenesis of chronic secretory otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol. 1973; 4. 75(4):269–270. PMID: 4702613.
Article4. Senturia BH, Gessert CF, Carr CD, Baumann ES. Studies concerned with tubotympanitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1958; 6. 67(2):440–467. PMID: 13571868.5. Rovers MM, Schilder AG, Zielhuis GA, Rosenfeld RM. Otitis media. Lancet. 2004; 2. 07. 363(9407):465–473. PMID: 14962529.
Article6. Medzhitov R, Janeway CA Jr. Innate immunity: the virtues of a nonclonal system of recognition. Cell. 1997; 10. 31. 91(3):295–298. PMID: 9363937.
Article7. Yang RB, Mark MR, Gurney AL, Godowski PJ. Signaling events induced by lipopolysaccharide-activated toll-like receptor 2. J Immunol. 1999; 7. 15. 163(2):639–643. PMID: 10395652.8. Horng T, Barton GM, Medzhitov R. TIRAP: an adapter molecule in the Toll signaling pathway. Nat Immunol. 2001; 9. 2(9):835–841. PMID: 11526399.
Article9. Fitzgerald KA, Palsson-McDermott EM, Bowie AG, Jefferies CA, Mansell AS, Brady G, et al. Mal (MyD88-adapter-like) is required for Toll-like receptor-4 signal transduction. Nature. 2001; 9. 413(6851):78–83. PMID: 11544529.
Article10. Aliprantis AO, Yang RB, Mark MR, Suggett S, Devaux B, Radolf JD, et al. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor-2. Science. 1999; 7. 30. 285(5428):736–739. PMID: 10426996.
Article11. Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Takada H, Ogawa T, et al. Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity. 1999; 10. 11(4):443–451. PMID: 10549626.12. Malley R, Henneke P, Morse SC, Cieslewicz MJ, Lipsitch M, Thompson CM, et al. Recognition of pneumolysin by Toll-like receptor 4 confers resistance to pneumococcal infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003; 2. 18. 100(4):1966–1971. PMID: 12569171.
Article13. Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol. 2001; 8. 2(8):675–680. PMID: 11477402.
Article14. Hirschfeld M, Weis JJ, Toshchakov V, Salkowski CA, Cody MJ, Ward DC, et al. Signaling by toll-like receptor 2 and 4 agonists results in differential gene expression in murine macrophages. Infect Immun. 2001; 3. 69(3):1477–1482. PMID: 11179315.
Article15. Hornung V, Rothenfusser S, Britsch S, Krug A, Jahrsdörfer B, Giese T, et al. Quantitative expression of toll-like receptor 1-10 mRNA in cellular subsets of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and sensitivity to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. J Immunol. 2002; 5. 01. 168(9):4531–4537. PMID: 11970999.
Article16. Chaudhary PM, Ferguson C, Nguyen V, Nguyen O, Massa HF, Eby M, et al. Cloning and characterization of two Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor-like genes TIL3 and TIL4: evidence for a multi-gene receptor family in humans. Blood. 1998; 6. 01. 91(11):4020–4027. PMID: 9596645.
Article17. Diamond G, Legarda D, Ryan LK. The innate immune response of the respiratory epithelium. Immunol Rev. 2000; 2. 173:27–38. PMID: 10719665.
Article18. Vandermeer J, Sha Q, Lane AP, Schleimer RP. Innate immunity of the sinonasal cavity: expression of messenger RNA for complement cascade components and toll-like receptors. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004; 12. 130(12):1374–1380. PMID: 15611395.19. Claeys S, de Belder T, Holtappels G, Gevaert P, Verhasselt B, van Cauwenberge P, et al. Human beta-defensins and toll-like receptors in the upper airway. Allergy. 2003; 8. 58(8):748–753. PMID: 12859553.
Article20. Shuto T, Imasato A, Jono H, Sakai A, Xu H, Watanabe T, et al. Glucocorticoids synergistically enhance nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced Toll-like receptor 2 expression via a negative cross-talk with p38 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem. 2002; 5. 10. 277(19):17263–17270. PMID: 11867630.21. Toubi E, Shoenfeld Y. Toll-like receptors and their role in the development of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity. 2004; 5. 37(3):183–188. PMID: 15497450.
Article22. Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, Sanjo H, et al. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature. 2000; 12. 07. 408(6813):740–745. PMID: 11130078.
Article23. Pasare C, Medzhitov R. Control of B-cell responses by Toll-like receptors. Nature. 2005; 11. 17. 438(7066):364–368. PMID: 16292312.
Article24. Arbour NC, Lorenz E, Schutte BC, Zabner J, Kline JN, Jones M, et al. TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat Genet. 2000; 6. 25(2):187–191. PMID: 10835634.
Article25. Agnese DM, Calvano JE, Hahm SJ, Coyle SM, Corbett SA, Calvano SE, et al. Human toll-like receptor 4 mutations but not CD14 polymorphisms are associated with an increased risk of gram-negative infections. J Infect Dis. 2002; 11. 15. 186(10):1522–1525. PMID: 12404174.
Article26. Montes AH, Asensi V, Alvarez V, Valle E, Ocaña MG, Meana A, et al. The Toll-like receptor 4 (Asp299Gly) polymorphism is a risk factor for Gram-negative and haematogenous osteomyelitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006; 3. 143(3):404–413. PMID: 16487238.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Middle ear histopathology in children with otitis media with effusion
- Clinical Approaches for Understanding the Expression Levels of Pattern Recognition Receptors in Otitis Media with Effusion
- Development of Animal Models of Otitis Media
- Expression of Toll-like Receptors 2 and 4 and Immunoglobulins in Children wih Recurrent Otitis Media with Effusion
- Expression of Mast Cell Tryptase in the Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion