Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2009 Sep;2(3):131-135.
IgA and Differentiation-associated Transcription Factors in Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yeo2park@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4East-West Medical Research Institute, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
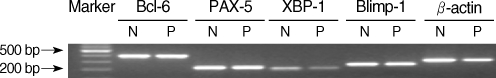
Inadequate antibody responses to pathogens may lead to the recurrence of otitis media with effusion (OME). Although B-cell production by antibodies is controlled by transcription factors, the status of these factors has not been assessed in patients with OME. METHODS: Expression of immunoglobulin was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Expression of transcription factors Bcl-6, Blimp-1, Pax-5, and XBP-1 was assessed by RT-PCR in the middle-ear fluid of 29 children with >4 OME episodes in 12 months or >3 episodes in 6 months (the OME-prone group) and in 32 children with <3 OME episodes in 12 months (OME group). The relationship between recurrence of OME and expression levels of immunoglobulins and transcription factors in middle-ear fluid was determined. RESULTS: The concentration of IgA in middle-ear fluid was significantly lower in the OME-prone than in the OME group, as was the expression of mRNA encoding the transcription factors Blimp-1 and XBP-1 (P<0.05 each). Expression of mRNA encoding the transcription factors Bcl-6 and Pax-5 was more intense in the OME-prone than in the OME group, but these differences were not significant (P>0.05). CONCLUSION: Lower concentrations of IgA, Blimp-1 and XBP-1 in middle ear fluid of patients with OME may be related to OME recurrence and chronicity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cummings CW, Flint PW, Harker LA, Haughey BH, Richardson MA, Robbins KT, et al. . Cummings otolaryngology: head and neck surgery. 2005. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby Co.2. Bluestone CD, Klein JO. Clinical practice guideline on otitis media with effusion in young children: strengths and weaknesses. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995; 4. 112(4):507–511. PMID: 7700654.
Article3. Howie VM, Ploussard JH, Sloyer JL, Johnston RB Jr. Immunoglobulins of the middle ear fluid in acute otitis media: relationship to serum immunoglobulin concentrations and bacterial cultures. Infect Immun. 1973; 4. 7(4):589–593. PMID: 4148623.
Article4. Tumang JR, Frances R, Yeo SG, Rothstein TL. Spontaneously Ig-secreting B-1 cells violate the accepted paradigm for expression of differentiation-associated transcription factors. J Immunol. 2005; 3. 174(6):3173–3177. PMID: 15749846.5. Howie VM, Ploussard JH, Sloyer J. The otitis-prone condition. Am J Dis Child. 1975; 6. 129(6):676–678. PMID: 239591.
Article6. Skotnicka B, Hassmann E. Cytokines in children with otitis media with effusion. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2000; 257(6):323–326. PMID: 10993552.
Article7. Juhn SK, Sipilä P, Jung TT, Edlin J. Biochemical pathology of otitis media with effusion. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1984; 414:45–51. PMID: 6598270.
Article8. Yamanaka N, Somekawa Y, Suzuki T, Kataura A. Immunologic and cytologic studies in otitis media with effusion. Acta Otolaryngol. 1987; Nov–Dec. 104(5-6):481–486. PMID: 3434270.
Article9. Liu YS, Lang R, Lim DJ, Birck HG. Microorganism in chronic otitis media with effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976; 85(2):Suppl 25. 245–249. PMID: 5041.10. Sloyer JL Jr, Howie VM, Ploussard JH, Schiffman G, Johnston RB Jr. Immune response to acute otitis media: association between middle ear fluid antibody and the clearing of clinical infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1976; 9. 4(3):306–308. PMID: 9424.
Article11. Ruohola A, Meurman O, Nikkari S, Skottman T, Salmi A, Waris M, et al. Microbiology of acute otitis media in children with tympanostomy tubes: prevalences of bacteria and viruses. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 12. 43(11):1417–1422. PMID: 17083014.
Article12. Freijd A, Hammarström L, Persson MA, Smith CI. Plasma anti-pneumococcal antibody activity of the IgG class and subclasses in otitis prone children. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984; 5. 56(2):233–238. PMID: 6733969.13. Takada R, Harabuchi Y, Himi T, Kataura A. Antibodies specific to outer membrane antigens of Moraxella catarrhalis in sera and middle ear effusions from children with otitis media with effusion. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1998; 12. 46(3):185–195. PMID: 10190589.
Article14. Ichimiya I, Kawauchi H, Mogi G. Analysis of immunocompetent cells in the middle ear mucosa. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990; 3. 116(3):324–330. PMID: 2407271.
Article15. Kusam S, Dent A. Common mechanisms for the regulation of B cell differentiation and transformation by the transcriptional repressor protein BCL-6. Immunol Res. 2007; 37(3):177–186. PMID: 17873402.
Article16. Angelin-Duclos C, Cattoretti G, Lin KI, Calame K. Commitment of B lymphocytes to a plasma cell fate is associated with Blimp-1 expression in vivo. J Immunol. 2000; 11. 165(10):5462–5471. PMID: 11067898.
Article17. Lin KI, Angelin-Duclos C, Kuo TC, Calame K. Blimp-1-dependent repression of Pax-5 is required for differentiation of B cells to immunoglobulin M-secreting plasma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2002; 7. 22(13):4771–4780. PMID: 12052884.18. Shaffer AL, Yu X, He Y, Boldrick J, Chan EP, Staudt LM. BCL-6 represses genes that function in lymphocyte differentiation, inflammation, and cell cycle control. Immunity. 2000; 8. 13(2):199–212. PMID: 10981963.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Decreased Serum Immunoglobulin in Recurrent Otitis Media with Effusion
- Development of Animal Models of Otitis Media
- Middle ear histopathology in children with otitis media with effusion
- Experimental otitis media with effusion induced by lipopolysaccharides from E. coli: the effects of endotoxin to the chronically of OME
- Prognostic significance of mastoid pneumatization in childhood otitis media with effusion: temporal bone CT evaluation