Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2013 Dec;6(4):259-262.
Epileptic Nystagmus and Vertigo Associated with Bilateral Temporal and Frontal Lobe Epilepsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. ysped@inha.ac.kr
Abstract
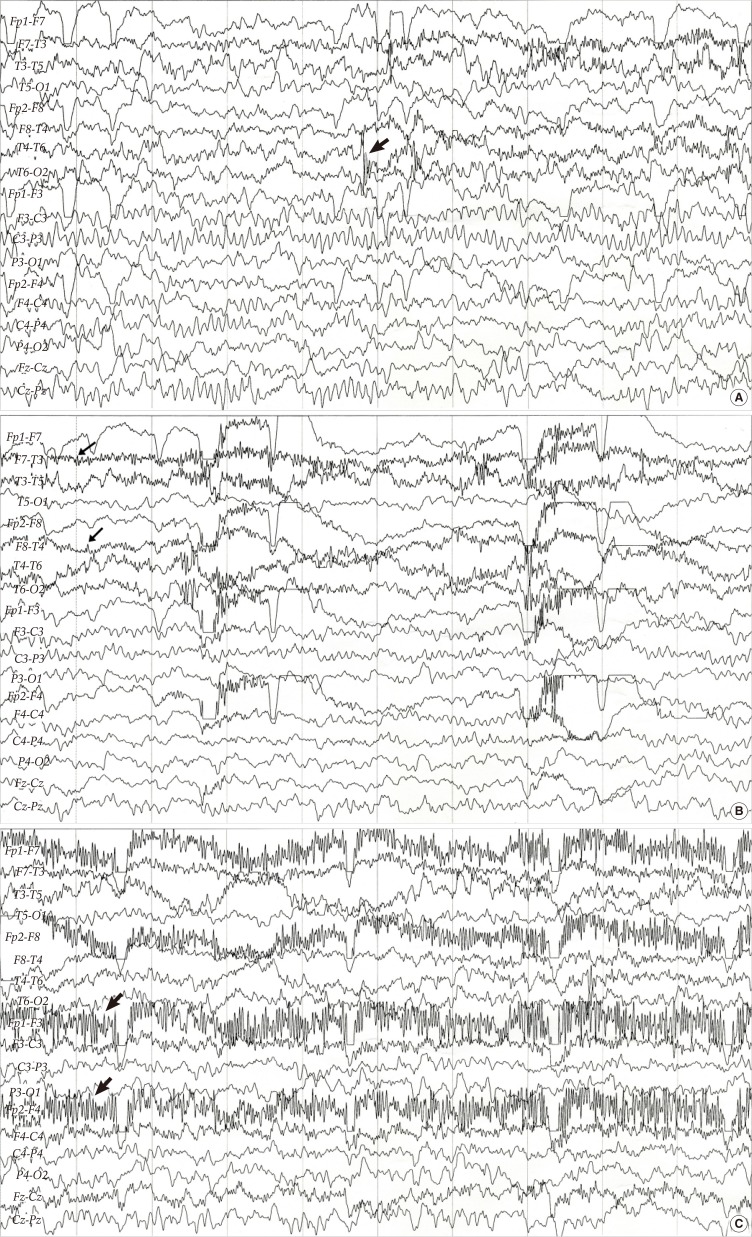
- Epileptic nystagmus is defined as a quick, repetitive jerky movement of the eyeball associated with seizure activity. In cases of epileptic nystagmus associated with ictal discharge from multiple brain areas, localization of the exact epileptogenic zone could be extremely difficult. In a nine-year-old patient with epileptic nystagmus and vertigo associated with bilateral temporal and frontal lobe epilepsy, we could infer the epileptic focus by interpreting the patient's clinical picture, characteristics of nystagmus, and findings of electroencephalography.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bajwa R, Jay WM, Asconape J. Neuro-ophthalmologic manifestations of epilepsy. Semin Ophthalmol. 2006; Oct-Dec. 21(4):255–261. PMID: 17182413.
Article2. Nicita F, Papetti L, Spalice A, Ursitti F, Massa R, Properzi E, et al. Epileptic nystagmus: description of a pediatric case with EEG correlation and SPECT findings. J Neurol Sci. 2010; 11. 298(1-2):127–131. PMID: 20832824.
Article3. Kellinghaus C, Skidmore C, Loddenkemper T. Lateralizing value of epileptic nystagmus. Epilepsy Behav. 2008; 11. 13(4):700–702. PMID: 18707021.
Article4. Bower CM, Cotton RT. The spectrum of vertigo in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995; 8. 121(8):911–915. PMID: 7619420.
Article5. Weber YG, Roesche J, Lerche H. Epileptic nystagmus: two case reports, clinical and pathophysiological review of the literature. J Neurol. 2006; 6. 253(6):767–771. PMID: 16511649.6. Kogeorgos J, Scott DF, Swash M. Epileptic dizziness. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1981; 2. 282(6265):687–689.
Article7. Bense S, Stephan T, Yousry TA, Brandt T, Dieterich M. Multisensory cortical signal increases and decreases during vestibular galvanic stimulation (fMRI). J Neurophysiol. 2001; 2. 85(2):886–899. PMID: 11160520.
Article8. Kaplan PW, Tusa RJ. Neurophysiologic and clinical correlations of epileptic nystagmus. Neurology. 1993; 12. 43(12):2508–2514. PMID: 8255448.
Article9. Stolz SE, Chatrian GE, Spence AM. Epileptic nystagmus. Epilepsia. 1991; 12. 32(6):910–918. PMID: 1743165.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Non-epileptic paroxysmal events during sleep: Differentiation from epileptic seizures
- Evaluation of Memory Impairment in Patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Using the Wechsler Memory Scale
- Epileptic Nystagmus Associated with Occipital Lobe Epilepsy
- Clinical Characteristics of Complex Partial Seizures: a Temporal versus a Frontal Lobe Onset
- A Case of Gelastic Epilepsy, probable Orbito-frontal Origin