Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Apr;39(2):318-322. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.318.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Painful Chronic Neurogenic Heterotopic Ossification After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. sunnywind78@gmail.com
- KMID: 2273056
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.318
Abstract
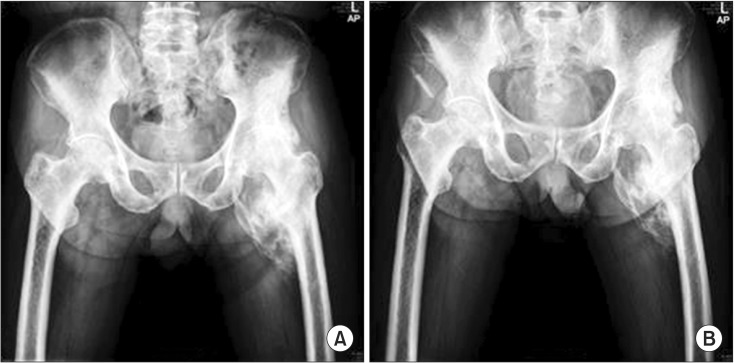
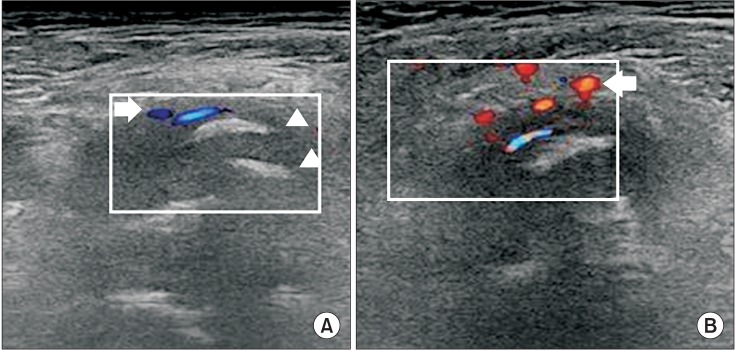
- Neurogenic heterotopic ossification (NHO) is a process of benign bone formation and growth in soft tissues surrounding major synovial joints and is associated with central nervous system (CNS) injuries. It is a common complication in major CNS injuries, such as traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, and stroke. Here, we report the case of a 72-year-old male, who experienced a traumatic brain injury and painful chronic NHO around the left hip joint. Three applications of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) were administered to the area of NHO, which resulted in pain relief and an improvement in the loss of motion in the left hip joint. Improvements were also noted in walking performance and activities of daily living, although the size of NHO remained unchanged. Therapeutic effects of ESWT lasted for 12 weeks.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Intramuscular Hematoma Following Radial Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Chronic Neurogenic Heterotopic Ossification: A Case Report
Howard Kim, Ji Hwan Cheon, Dong Youl Lee, Ji Hong Cheon, Youn Kyung Cho, Sung Hoon Lee, Eun Young Kang
Ann Rehabil Med. 2017;41(3):498-504. doi: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.3.498.
Reference
-
1. Sullivan MP, Torres SJ, Mehta S, Ahn J. Heterotopic ossification after central nervous system trauma: a current review. Bone Joint Res. 2013; 2:51–57. PMID: 23610702.2. Wang CJ. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; 7:11. PMID: 22433113.
Article3. Mariotto S, de Prati AC, Cavalieri E, Amelio E, Marlinghaus E, Suzuki H. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in inflammatory diseases: molecular mechanism that triggers anti-inflammatory action. Curr Med Chem. 2009; 16:2366–2372. PMID: 19601786.
Article4. Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, Weng LH, Hsu CC, Huang CS, et al. Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction: a study in rabbits. J Orthop Res. 2003; 21:984–989. PMID: 14554209.
Article5. Takahashi N, Wada Y, Ohtori S, Saisu T, Moriya H. Application of shock waves to rat skin decreases calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Auton Neurosci. 2003; 107:81–84. PMID: 12963418.
Article6. Varghese G, Williams K, Desmet A, Redford JB. Nonarticular complication of heterotopic ossification: a clinical review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1991; 72:1009–1013. PMID: 1953312.7. van Kuijk AA, Geurts AC, van Kuppevelt HJ. Neurogenic heterotopic ossification in spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2002; 40:313–326. PMID: 12080459.
Article8. Sarafis KA, Karatzas GD, Yotis CL. Ankylosed hips caused by heterotopic ossification after traumatic brain injury: a difficult problem. J Trauma. 1999; 46:104–109. PMID: 9932691.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Painful Heterotopic Ossification after Traumatic Transtibial Amputation
- Heterotopic Ossification Mimics Neurogenic Tumor: A Case Report
- Treatment of Nonunion of Tibia with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy: A Case Report
- Current Concepts in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
- Intramuscular Hematoma Following Radial Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Chronic Neurogenic Heterotopic Ossification: A Case Report