J Korean Bone Joint Tumor Soc.
2013 Dec;19(2):92-96. 10.5292/jkbjts.2013.19.2.92.
Heterotopic Ossification Mimics Neurogenic Tumor: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. osjymoon@naver.com
- KMID: 1961765
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5292/jkbjts.2013.19.2.92
Abstract
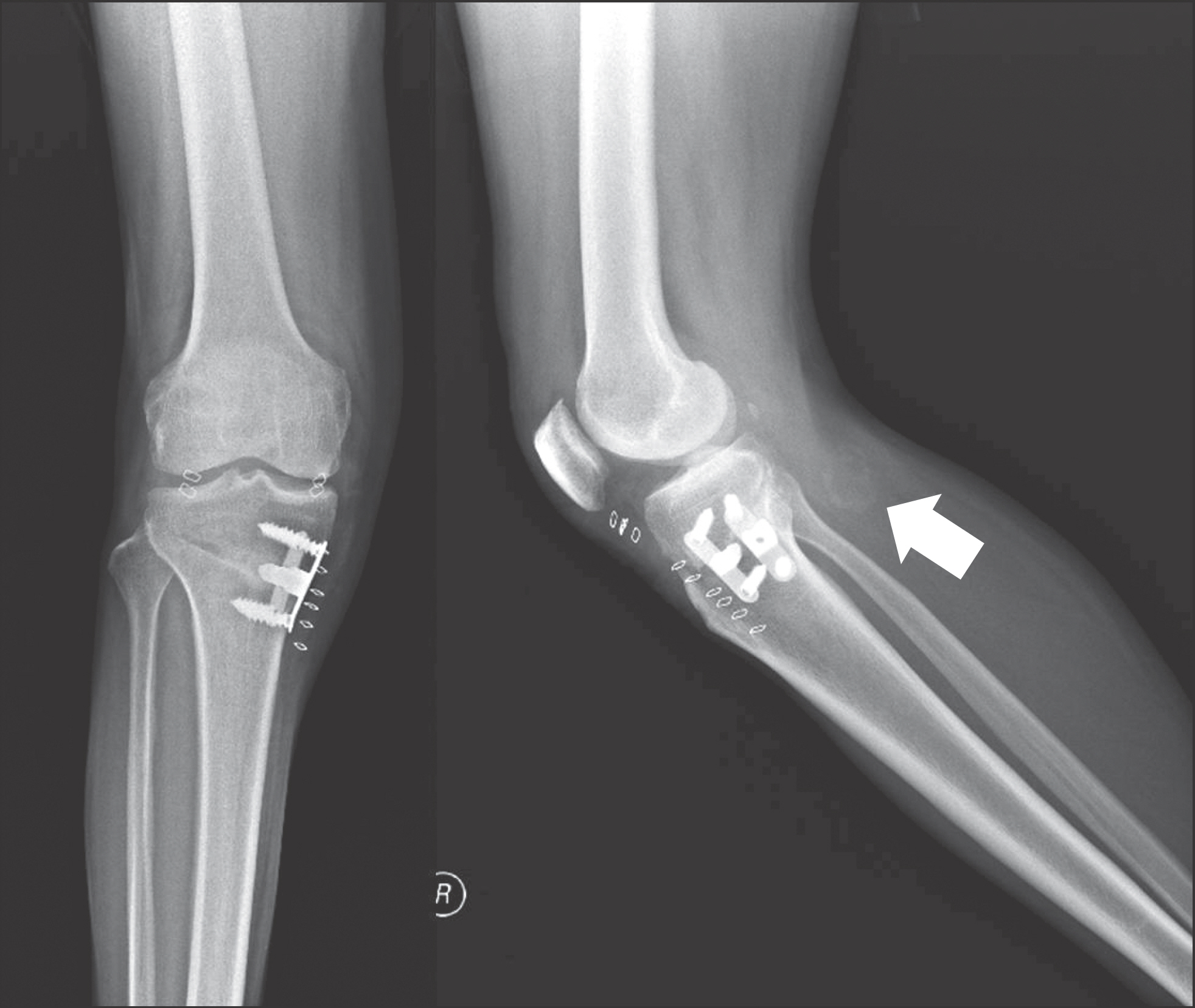
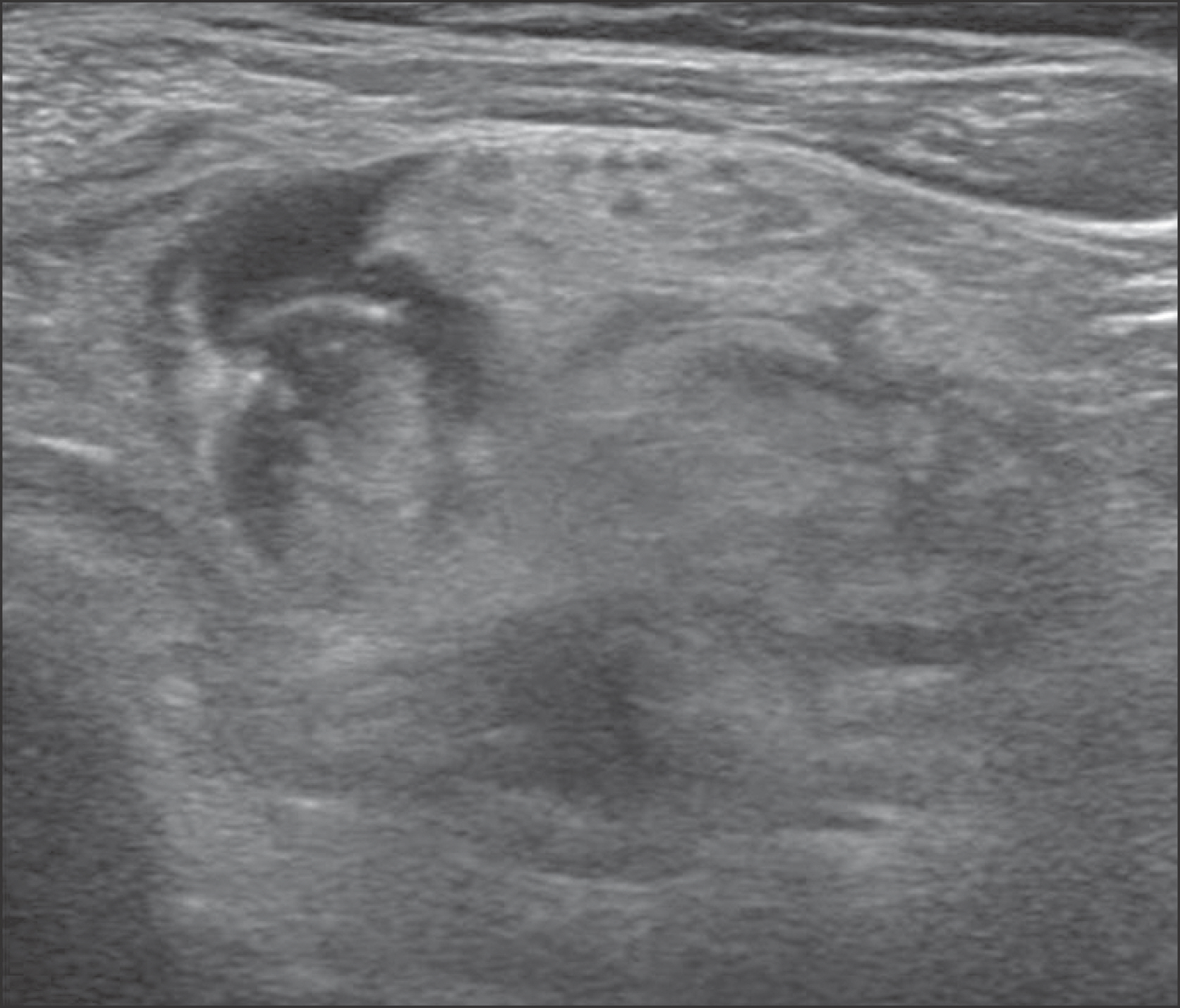
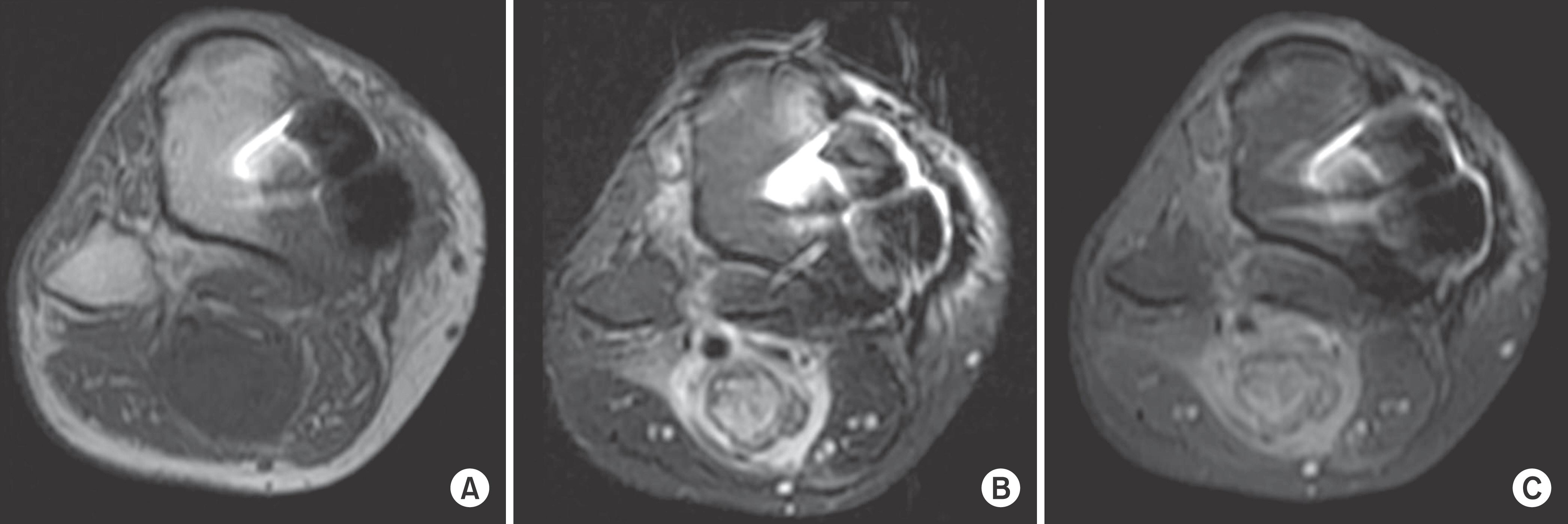
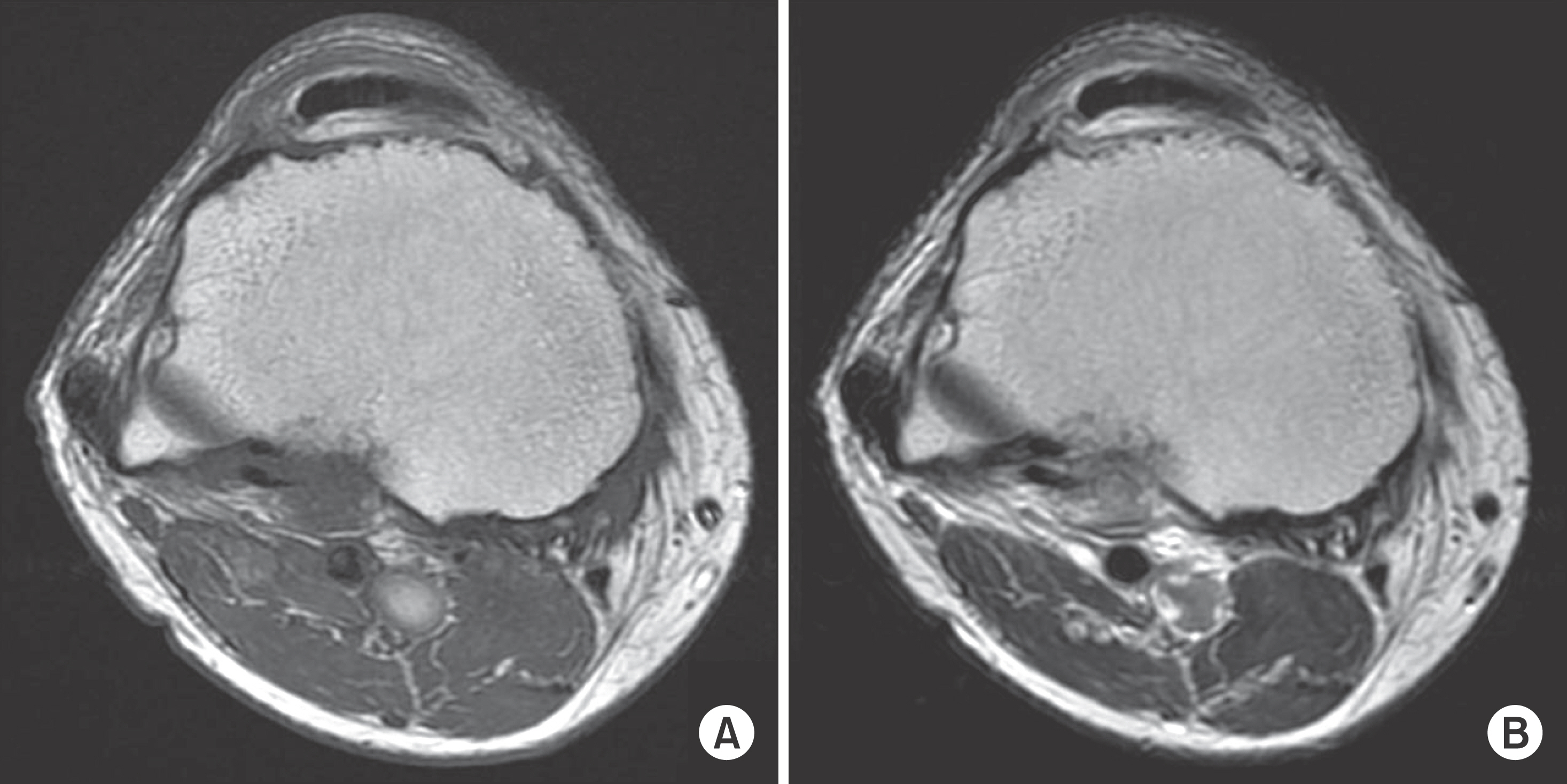
- Heterotopic ossification is an abnormal bone formation after surgery or without any reason. Large joint, such as hip and knee joint, is a known most common site. Operation itself and postoperative early range of motion exercise are risk factors. We present a case of heterotopic ossification mimics neurogenic tumor after high tibial osteotomy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
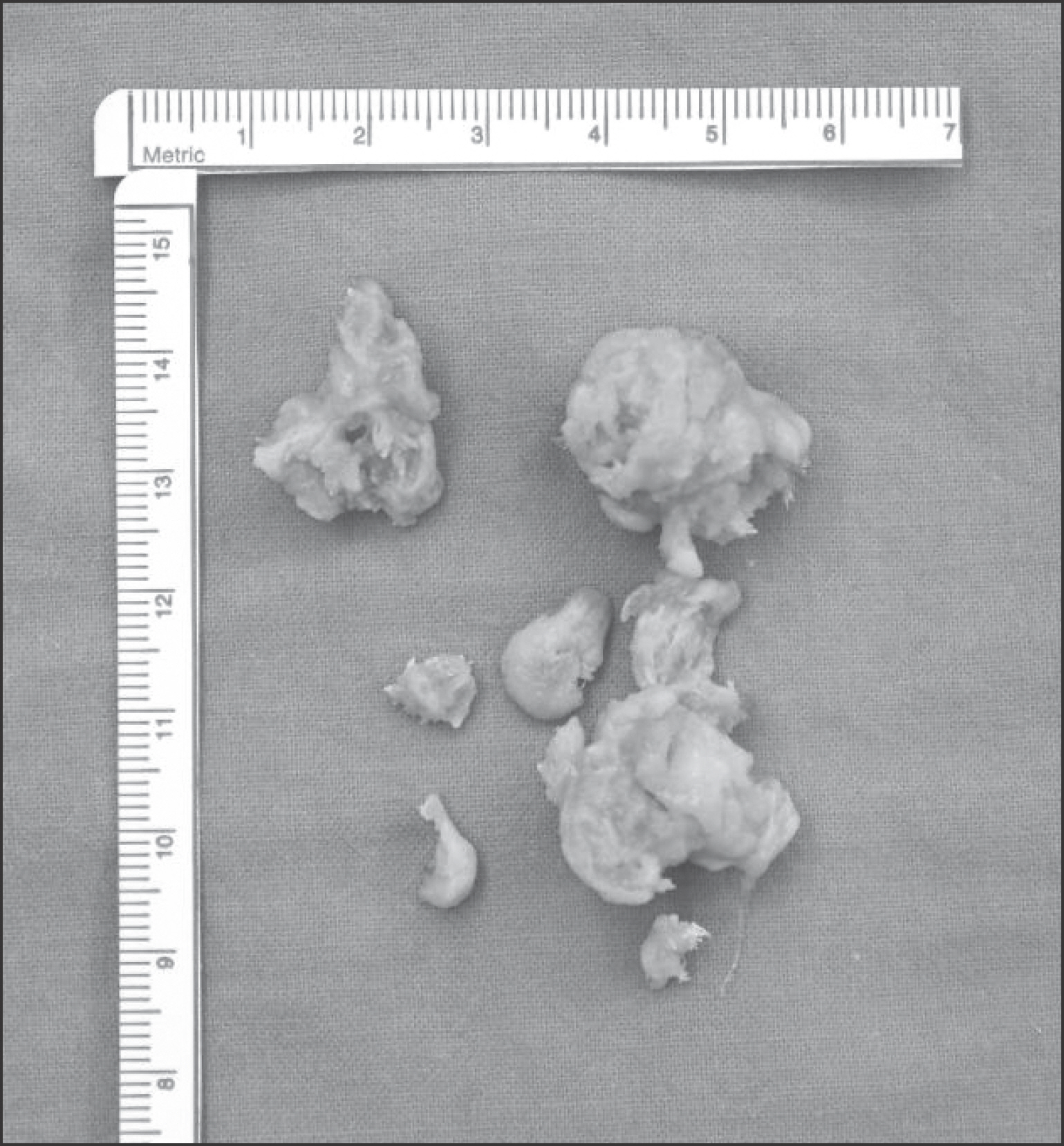
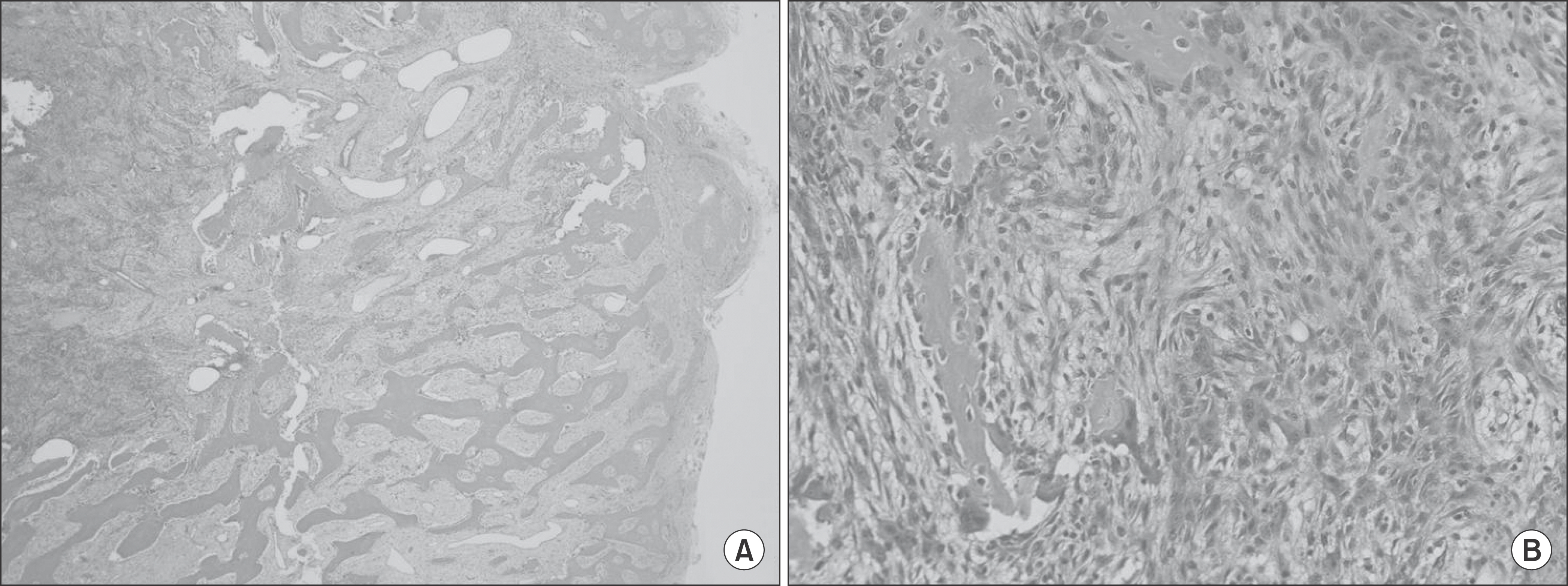
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Harwin SF, Stein AJ, Stern RE, Kulick RG. Heterotopic ossification following primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1993; 8:113–6.
Article2. Cook J, Scott RD. Bony ankylosis following total knee arthroplasty: a case report. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20:122–4.3. Furia JP, Pellegrini VD Jr. Heterotopic ossification following primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1995; 10:413–9.
Article4. Hasegawa M, Ohashi T, Uchida A. Heterotopic ossification around distal femur after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2002; 122:274–8.
Article5. Figgie HE 3rd, Goldberg VM, Heiple KG, Moller HS 3rd, Figgie MP. The incidence and significance of heterotopic ossification following total knee arthroplasty. Adv Orthop Surg. 1986; 10:12–7.6. Mollan RA. Serum alkaline phosphatase in heterotopic para-articular ossification after total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979; 61B:432–4.
Article7. Isobe K, Shimizu T, Akahane T, Kato H. Imaging of ancient schwannoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:331–6.
Article8. Pape HC, Marsh S, Morley JR, Krettek C, Giannoudis PV. Current concepts in the development of heterotopic ossification. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:783–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Osteomyelitis in Heterotopic Ossification after Trochanteric Pressure Sore Reconstruction: A Case Report
- Heterotopic Ossification of a Partially Ruptured Achilles Tendon (A Case Report)
- Heterotopic Enchondral Ossification in Metastatic Colonic Adenocarcinoma: A case report
- Heterotopic Ossification of the Elbow after Medial Epicondylectomy
- Heterotopic Ossification Combined with Infection in the Hand: A Case Report