Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Apr;39(2):243-252. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.243.
Diagnostic Value of Plain Abdominal Radiography in Stroke Patients With Bowel Dysfunction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Institute of Wonkwang Medical Science, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. mcjoo68@wku.ac.kr
- KMID: 2273046
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.243
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the diagnostic value of plain abdominal radiography in stroke patients with bowel dysfunction.
METHODS
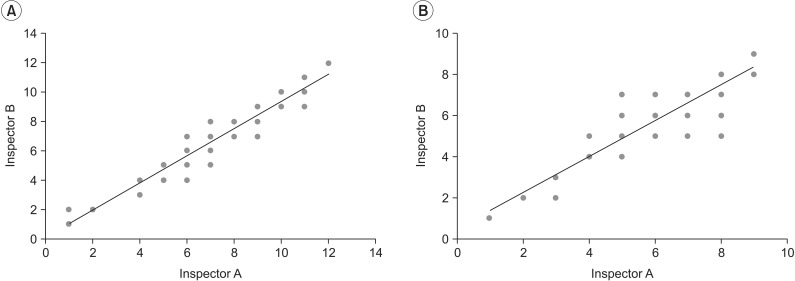
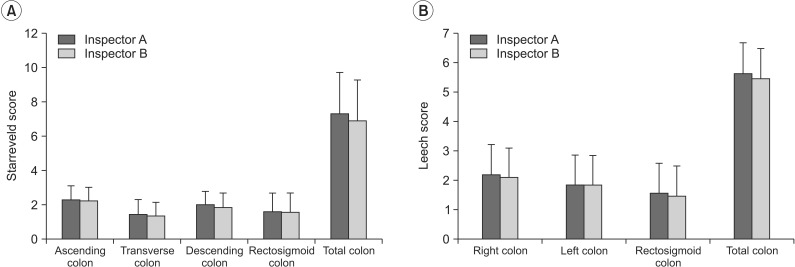
A total of 59 stroke patients were recruited and assigned into constipation or non-constipation group. Patients were interviewed to obtain clinical information, constipation score, and Bristol stool form scale. The total and segmental colon transit time (CTT) was measured using radio-opaque markers (Kolomark). The degree of stool retention was evaluated by plain abdominal radiography and scored by two different methods (Starreveld score and Leech score). The relationship between the clinical aspects, CTT, and stool retention score using plain abdominal radiography was determined.
RESULTS
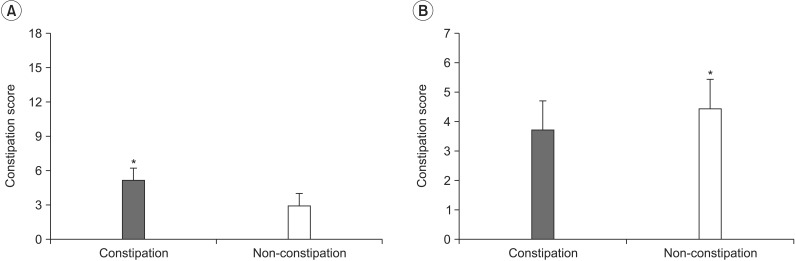
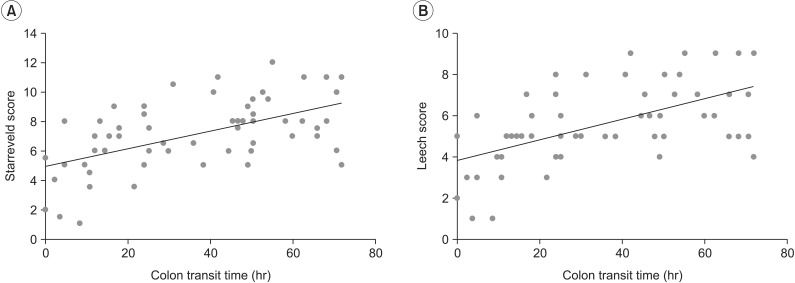
Average constipation score was 4.59+/-2.16. Average Bristol stool form scale was 3.86+/-1.13. The total and segmental CTTs showed significant differences between the constipation and non-constipation groups. There was statistically significant (p<0.05) correlation between the total CTT and constipation score or between Starreveld score and Leech score. Each segmental CTT showed significant correlation (p<0.05) between segmental stool retention scores.
CONCLUSION
The stool retention score showed significant correlation with constipation score as well as total and segmental CTT. Thus, plain abdominal radiography is a simple and convenient method for the evaluation of bowel dysfunction in stroke patients.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Scivoletto G, Fuoco U, Badiali D, Braccl F, Lucente LD, Patrelli A, et al. Gastrointestinal dysfunction following stroke. J Neurol Sci. 1997; 150:S151.2. Robain G, Chennevelle JM, Petit F, Piera JB. Incidence of constipation after recent vascular hemiplegia: a prospective cohort of 152 patients. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2002; 158(5 Pt 1):589–592. PMID: 12072827.3. Harari D, Norton C, Lockwood L, Swift C. Treatment of constipation and fecal incontinence in stroke patients: randomized controlled trial. Stroke. 2004; 35:2549–2555. PMID: 15486330.4. Ashraf W, Park F, Lof J, Quigley EM. An examination of the reliability of reported stool frequency in the diagnosis of idiopathic constipation. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:26–32. PMID: 8561138.5. Yi JH, Chun MH, Kim BR, Han EY, Park JY. Bowel function in acute stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:337–343. PMID: 22506142.
Article6. Lim YH, Kim DH, Lee MY, Joo MC. Bowel dysfunction and colon transit time in brain-injured patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012; 36:371–378. PMID: 22837973.
Article7. Leech SC, McHugh K, Sullivan PB. Evaluation of a method of assessing faecal loading on plain abdominal radiographs in children. Pediatr Radiol. 1999; 29:255–258. PMID: 10199902.
Article8. Starreveld JS, Pols MA, Van Wijk HJ, Bogaard JW, Poen H, Smout AJ. The plain abdominal radiograph in the assessment of constipation. Z Gastroenterol. 1990; 28:335–338. PMID: 2238762.9. Thompson WG, Longstreth GF, Drossman DA, Heaton KW, Irvine EJ, Muller-Lissner SA. Functional bowel disorders and functional abdominal pain. Gut. 1999; 45(Suppl 2):II43–II47. PMID: 10457044.
Article10. Cheon JH, Yoon IJ, Myung SJ, Byeon JS, Ko JE, Jung KW, et al. Use of constipation remedies not prescribed by physician: a study of patients at a constipation clinic. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2007; 13:45–52.11. O'Donnell LJ, Virjee J, Heaton KW. Detection of pseudodiarrhoea by simple clinical assessment of intestinal transit rate. BMJ. 1990; 300:439–440. PMID: 2107897.12. Arhan P, Devroede G, Jehannin B, Lanza M, Faverdin C, Dornic C, et al. Segmental colonic transit time. Dis Colon Rectum. 1981; 24:625–629. PMID: 7318630.
Article13. Suh SW, Park HJ, Jung HY, Rhee JC, Rhee PL, Kim JJ, et al. Comparison of 4- day 7-day methods in the evaluation of colon transit time. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2001; 38:241–246.14. Roth EJ. Medical complications encountered in stroke rehabilitation. Phys Med Rehabil Clin North Am. 1991; 2:563–577.
Article16. Seo JH, Song KS, Ko MH, Park SH. the change of neurogenic bowel dysfunction in spinal cord injury patients during admission. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2009; 33:441–447.17. Keighley MR, Henry MM, Bartolo DC, Mortensen NJ. Anorectal physiology measurement: report of a working party. Br J Surg. 1989; 76:356–357. PMID: 2720345.
Article18. Reuchlin-Vroklage LM, Bierma-Zeinstra S, Benninga MA, Berger MY. Diagnostic value of abdominal radiography in constipated children: a systematic review. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2005; 159:671–678. PMID: 15997002.19. Pensabene L, Buonomo C, Fishman L, Chitkara D, Nurko S. Lack of utility of abdominal x-rays in the evaluation of children with constipation: comparison of different scoring methods. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010; 51:155–159. PMID: 20453675.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Plain Abdominal Radiography in Infants and Children
- Plain Abdominal Radiograph as an Evaluation Method of Bowel Dysfunction in Patients With Spinal Cord Injury
- The Usefulness of the Dynamic Image of the Pharynx with Digital Radiography in Dysphagia Following Stroke
- Intussusception in Childhood: The Role of Plain Abdominal Radiographs
- A study on reliability of the abdominal plain film diagnosis in pediatric patients with suspected intussusception