Korean J Nutr.
2011 Dec;44(6):465-473. 10.4163/kjn.2011.44.6.465.
Anti-atherosclerotic Effect of Green Tea in Poluynsaturated Fatty Acids-treated Apo E KO Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Food and Nutrition and Research Institute of Obesity Sciences, Sungshin Women's University, Seoul 136-742, Korea. mlee@sungshin.ac.kr
- KMID: 2268606
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/kjn.2011.44.6.465
Abstract
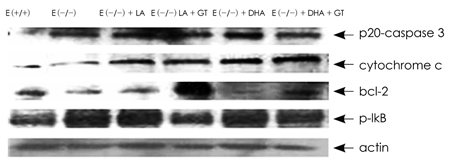
- Dietary fatty acids are under intense research to identify anti-atherogenic mechanisms, so we investigated green tea powder (GT) as a protector against atherogenesis originating from lipid peroxidation such as 4-hydroxynonemal (4-HNE) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in different dietary fatty acid-treated apo E KO mice. Growth rate and dietary efficiency were lower in apo E KO mice with or without LA compared to wild type. Plasma total cholesterol (TC) and triacylglycerol (TG) did not correspond to values in other tissues, but TG in heart tissue decreased significantly by GT after linoleic acid (LA) or docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) was administered. LA induced apoptosis as evidenced by changes in aorta morphology and immunohistochemistry. Lipid peroxides (LPO) was increased in apo E KO mice with or without LA corresponding to the accumulation of 4-HNE or MDA in the proximal aorta above the atria. GT consumption tended to reduce the primary causal mechanism of atherogenic phenomena such as oxidizability in both LA and DHA treated atherogenic mice. A high polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) diet involved the changes on stress-induced apoptotic signaling by increasing caspase 3, cytochrome c, and nuclear factor-kappaB in the heart tissue, but decreasing the bcl-2 protein. However, GT remarkably reduced the expression of apoptotic signaling, in contrast to the PUFA diet. Therefore, the potential of GT as an anti-atherosclerotic dietary antioxidant was tested in this study.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Aorta
Apolipoproteins E
Apoptosis
Atherosclerosis
Caspase 3
Cholesterol
Cytochromes c
Diet
Fatty Acids
Fatty Acids, Unsaturated
Heart
Immunohistochemistry
Linoleic Acid
Lipid Peroxidation
Lipid Peroxides
Malondialdehyde
Mice
Plasma
Tea
Triglycerides
Apolipoproteins E
Caspase 3
Cholesterol
Cytochromes c
Fatty Acids
Fatty Acids, Unsaturated
Linoleic Acid
Lipid Peroxides
Malondialdehyde
Tea
Triglycerides
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Statistics Office. 2008 Annual Report on the cause of Death Statistics. 2009. Republics of Korea:2. Romos KS, Melchert RB, Chacon E, Acosta D Jr. Toxic responses of the heart and vascular systems. Casarett & Doull's Toxicology. 2011. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;597–651.3. Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993. 362(6423):801–809.
Article4. Oh H, Mun H, Lee M. Effect of CLA (Conjugated Linoletic Acid) on the Anti-Atherosclerotic Factors in Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells. Korean J Nutr. 2004. 37(3):182–192.5. Natio HK. Atherogenesis Current topics on etiology and risk factors. Clin Chem. 1995. 41(1):132–113.6. Kim WS, Kim YS. Paraxonase Polymorphism as a new genetic marker of atherosclerosis. Korean J Lipidol. 1996. 6(2):81–86.7. Jang YS, Kim OY, Kwon SJ, Lee JH, Chung NS, Kwon SJ, Huh KB. Influence of alcohol consumption and smoking habits on cardiovascular risk factors and antioxidant status in healthy men. Korean J Med. 1999. 56(4):437–449.8. Witztum JL, Steinberg D. Role of oxidised low density lipoprotein in atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1991. 88(6):1785–1792.
Article9. Kris-Etherton PM, Krummel D, Russell ME, Dreon D, Mackey S, Borchers J, Wood PD. The effect of diet on plasma lipids, lipoproteins, and coronary heart disease. J Am Diet Assoc. 1988. 88(11):1373–1400.
Article10. Park BS, Response surface. n-6 and P/S ratio on reduction of plasma lipids in rats. J Korean Oil Chem Soc. 2004. 21(2):148–155.11. Levy RI. Choesterol, lipoproteins, apoproteins and hearts disease: present status and future prospects. Clin Chem. 1981. 27(5):653–662.
Article12. Dyerberg J, Bang HO, Stofferson E, Moncada S, Vane JR. Eicosapentaenoic acid and prevention of thrombosis and atherosclerosis? Lancet. 1978. 2(8081):117–119.
Article13. Hu ML, Frankel EN, Leibovitz BE, Tappel AL. Effect of dietary lipids and vitamin E on in vitro lipid eroxidation in rat liver and kidney homogenates. J Nutr. 1989. 119(11):1574–1582.
Article14. Buckingham KW. Effect of dietary polyunsaturated/saturated fatty acid ratio and dietary vitamin E on lipid peroxidation in the rat. J Nutr. 1985. 115(11):1425–1435.
Article15. Staprans I, Rapp JH, Pan XM, Feingold KR. The effect of oxidized lipids in the diet on serum lipoprotein peroxides in control and diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1993. 92(2):638–643.
Article16. Fujiki H. Two stages of cancer prevention with green tea. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1999. 125(11):589–597.
Article17. Arts IC, Hollman PC, Feskens EJ, Bueno de Mesquita HB, Kromhout D. Catechin intake might explain the inverse relation between tea consumption and ischemic heart disease: the Zutphen Elderly Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001. 74(2):227–232.
Article18. Yang TT, Koo MW. Inhibitory effect of Chinese green tea on endothelial cell-induced LDL oxidation. Atherosclerosis. 2000. 148(1):67–73.
Article19. Miura Y, Chiba T, Tomita I, Koizumi H, Miura S, Umegaki K, Hara Y, Ikeda M, Tomita T. Tea catechins prevent the development of atherosclerosis in apoprotein E-deficient mice. J Nutr. 2001. 131(1):27–32.
Article20. Yang CS, Wang ZY. Tea and cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994. 85(13):1038–1049.
Article21. Suganuma M, Okabe S, Sueoka N, Sueoka E, Matsuyama S, Imai K, Nakachi K, Fujiki H. Green tea and cancer chemoprevention. Mutat Res. 1999. 428(1-2):339–344.
Article22. Kim SO, Lee MY. Effects of Ethylacetate Fraction of Onion on Lipid Metabolism in High Cholesterol-Fed Rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2001. 30(4):673–678.23. Miyazaki , Miwa S, Kodama H, Yamada H, Nagata K, Toriumi W, Kitamura K, Kume E. Hepatic and intestinal changes in rats treated with T-0126, a microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (mtp) inhibitor. J Toxicol Sci. 2007. 32(2):161–177.
Article24. Chang CY, Chen YL, Yang SC, Huang GC, Tsi D, Huang CC, Chen JR, Li JS. Effect of schisandrin B and sesamin mixture on CCl(4)-induced hepatic oxidative stress in rats. Phytother Res. 2009. 23(2):251–256.
Article25. Kim JS, Kim SH, Han YN. Effects of Unsaturated Fatty Acid Diets and Feeding Periods on the Antithrombosis, the Hematological Changes in the Blood and Fatty Acid Compositions of Platelets in Rats. Korean J Nutr. 1992. 25(5):339–350.26. Bulliyya G, Reddy KK, Reddy GP, Reddy PC, Reddanna P, Kumari KS. Lipid profiles among fish-consuming coastal and non-fish-consuming inland populations. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1990. 44(6):481–485.27. Tonooka F, Matsumoto N, Ishigaki A, Hara Y. The effects of crude catechins of tea on the food in take and body fat in rat. Proceeding of International Symposium Tea Science. 1991. –336.28. Jin HH, Yang JL, Chung JH, Kim Y. Hypocholesterolemic effects of green tea in cholesterol-fed rats. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2004. 33(1):47–51.
Article29. Kim ES, Kim MK. Effect of dried leaf powders and ethanol extracts of persimmon, green tea and pine needle on lipid metabolism and antioxidative capacity in rats. Korean J Nutr. 1999. 32(4):337–352.30. Nestel PJ, Havenstein N, Whyte HM, Scott TJ, Cook LJ. Lowering of plasma cholesterol and enhanced sterol excretion with the consumption of polyunsaturated ruminant fats. N Engl J Med. 1973. 288(8):379–382.
Article31. Kwon MN, Yang JL, Chung JH, Kim YH. Effect of flavonoid (+)-catechin as stabilizer in rat fed fresh and peroxidized fish oil. J Korean Food Nutr. 1993. 22(4):381–391.32. Matsuda H, Chisaka T, Kubomura Y, Yamahara J, Sawada T, Fujimura H, Kimura H. Effects of crude drugs on experimental hypercholesterolemia. I. Tea and its active principles. J Ethnopharmacol. 1986. 17(3):213–224.
Article33. Vahouny GV, Khalafi R, Satchithanandam S, Watkins DW, Story JA, Cassidy MM, Kritchevsky D. Dietary fiber supplementation and fecal bile acids, neutral steroids and divalent cations in rats. J Nutr. 1987. 117(12):2009–2015.
Article34. Cho SH, Choi YS. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status is affected by different vitamin E levels when feeding fish oil. Lipids. 1994. 29(1):47–52.
Article35. Choi YS, Cho SH, Im JK. Lipid peroxidation and vitamins e and a levels in tissues of rats fed fish oil or soybean oil supplemented with vitamin E. Korean J Nutr. 1995. 28(10):967–975.36. Jorgensen KA, Dyerberg K. Draper HH, editor. Prostacyclin, thromboxane and atherosclerosis. Advances in Nutritional Research. 1983. 64–66.37. Tijburg LB, Wiseman SA, Meijer GW, Weststrate JA. Effects of green tea, black tea and dietary lipophilic antioxidants on LDL oxidizability and atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolaemic rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1997. 135(1):37–47.
Article38. Faraco PR, Ledgerwood EC, Vandenabeele P, Prins JB, Bradley JR. Tumor necrosis factor induces distinct patterns of caspase activation in WEHI-164 Cells associated with apoptosis or necrosis depending on cell cycle stage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. 261(2):385–392.
Article39. Chen ZY, Istfan NW. Docosahexaenoic acid is a potent inducer of apoptosis in HT-29 colon cancer cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2000. 63(5):301–308.
Article40. Diep QN, Intengan HD, Schiffrin EL. Endothelin-1 attenuates omega3 fatty acid -induced apoptosis by inhibition of caspase 3. Hypertension. 2000. 35(1 Pt 2):287–291.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Lifestyle Modification
- Dietary effect of green tea extract on hydration improvement and metabolism of free amino acid generation in epidermis of UV-irradiated hairless mice
- Evaluation of the Anti-inflammatory Effect of a Moisturizer Containing Green-Tea Extracts
- Association Between Green Tea Consumption and Lung Cancer Risk
- Transactivation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha by green tea extracts