Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Jun;36(3):414-417. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.414.
Multivessel Thromboembolism Associated with Dysfunction of Protein S
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon 442-723, Korea. seonghoon@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon 442-723, Korea.
- KMID: 2266750
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.414
Abstract
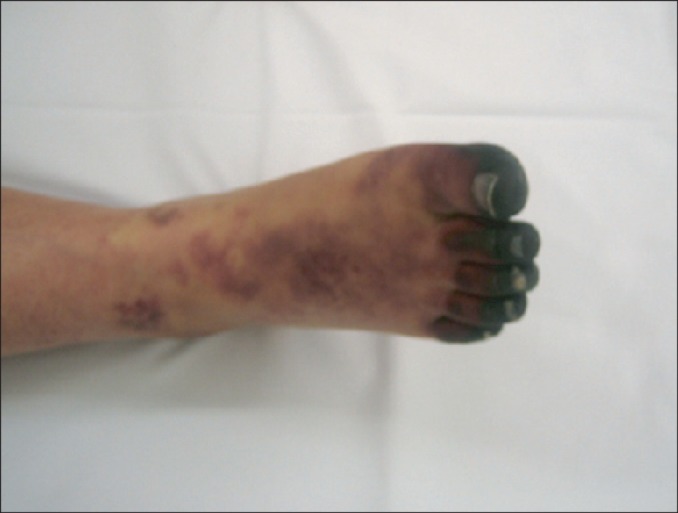
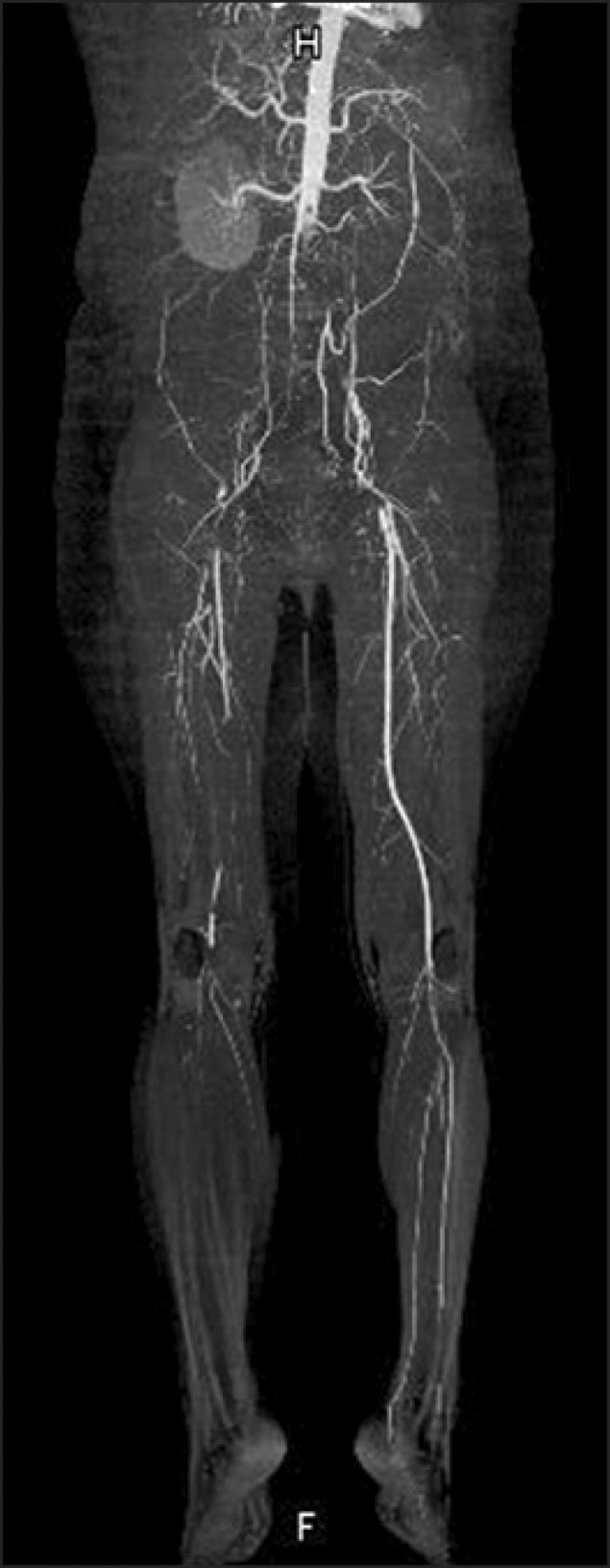
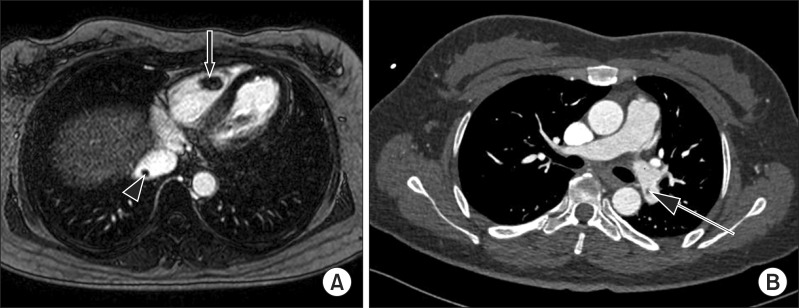
- Protein S is a vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor that acts as an anticoagulant. Deficiency of protein S increases the risk of thromboembolic events. We report a case of isolated protein S deficiency in a 39-year-old woman suffering arterial occlusion in both lower legs. She underwent a surgical procedure using thrombectomy and balloon angioplasty of her left lower extremity. Later, she had right trans-tibial amputation because of the reperfusion injury. Throughout the evaluation of thromboembolic events, we diagnosed a large thrombus in the right atrium and an asymptomatic pulmonary thromboembolism. The patient was successfully treated with right atrial thrombectomy and systemic anticoagulation. Careful evaluation for protein S levels may be necessary in patients with arterial thromboembolic events, especially young adults.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nizzi FA Jr, Kaplan HS. Protein C and S deficiency. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1999; 25:265–272. PMID: 10443958.
Article2. Gladson CL, Scharrer I, Hach V, Beck KH, Griffin JH. The frequency of type I heterozygous protein S and protein C deficiency in 141 unrelated young patients with venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1988; 59:18–22. PMID: 2966450.
Article3. Kim TW, Kang GW, Hong HL, Mun SH, Lee IH, Ahn KS. A case of acute bilateral renal infarction associated with protein S deficiency. Korean J Nephrol. 2010; 29:617–622.4. Aoyagi S, Nishimi M, Hiratsuka R, Takaseya T, Teshima H. Right atrial thrombus associated with combined valvular disease: case report. J Heart Valve Dis. 2001; 10:542–544. PMID: 11499604.5. Kronick G. European Working Group on Echocardiography. The European Cooperative Study on the clinical significance of right heart thrombi. Eur Heart J. 1989; 10:1046–1105. PMID: 2606115.6. Dykes AC, Walker ID, McMahon AD, Islam SI, Tait RC. A study of Protein S antigen levels in 3788 healthy volunteers: influence of age, sex and hormone use, and estimate for prevalence of deficiency state. Br J Haematol. 2001; 113:636–641. PMID: 11380449.7. Cumming AM, Shiach CR. The investigation and management of inherited thrombophilia. Clin Lab Haematol. 1999; 21:77–92. PMID: 10342066.
Article8. Broekmans AW, Conrad J. Hereditary protein C deficiency. Contemp Issues Haemost Thromb. 1988; 3:160–181.
Article9. Coller BS, Owen J, Jesty J, Horowitz D, Reitman MJ, Spear J, Yeh T, Comp PC. Deficiency of plasma protein S, protein C, or antithrombin III and arterial thrombosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1987; 7:456–462. PMID: 2960305.
Article10. Van Cott EM, Laposata M. Laboratory evaluation of hypercoaguable states. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988; 12:1141–1166. PMID: 9922930.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Behcet's Disease Associated with Protein S Deficiency
- Activated Protein C Anticoagulant System Dysfunction and Thrombophilia in Asia
- Unusual Complication of Crohn's Disease: Portal Hypertension Related with Rapid Progression of Portal Vein and Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis
- A Case of Central Retinal Vein Occlusion by Protein C Deficiency
- A Case of Pulmonary Thromboem-bolism associated with Protein C Deficiency