Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Jun;36(3):340-346. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.340.
Effect of Botulinum Toxin A Injection into the Salivary Glands for Sialorrhea in Children with Neurologic Disorders
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu 700-712, Korea. sylee@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu 700-712, Korea.
- 3Department of Otolaryngology, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu 700-712, Korea.
- KMID: 2266739
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.340
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
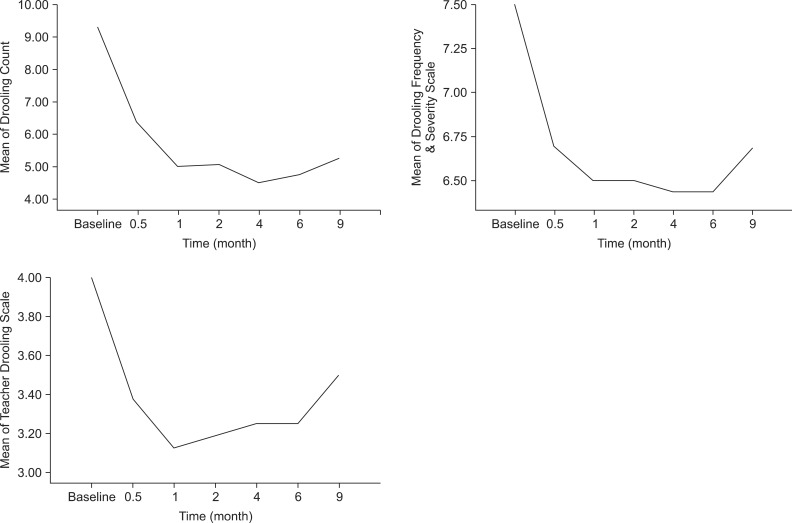
To determine the 9 month period effect of botulinum toxin A (BoNT-A) injection into the salivary gland in children with neurologic disorders and sialorrhea by qualified parent/caregiver-administered questionnaires. METHOD: A total of 17 patients (age 7.6+/-4.24 years) were enrolled in this study. The degree of sialorrhea was assessed at the baseline, 2 weeks, 1, 2, 4, 6 and 9 months after injection. The Drooling Count (DC) was assessed as an objective measurement. The Drooling Frequency and Severity Scale (DFS) and the Teacher Drooling Scale (TDS) were evaluated as a subjective measurement. BoNT-A (0.5 unit/kg) was injected into each submandibular and parotid gland under ultrasonography-guidance.
RESULTS
DC, DFS and TDS showed significant improvement at 2 weeks, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 9 months follow-up (p<0.05). Twelve of 17 cases (70.5%) showed more than 50% reduction in DC from the baseline value.
CONCLUSION
Ultrasonography-guided BoNT-A injection into the submandibular and parotid gland was a safe and effective method to treat sialorrhea in children with neurologic disorders.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Banerjee KJ, Glasson C, O'Flaherty SJ. Parotid and submandibular botulinum toxin A injections for sialorrhoea in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2006; 48:883–887. PMID: 17044954.
Article2. Fairhurst CB, Cockerill H. Management of drooling in children. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2011; 96:25–30. PMID: 20675519.3. Ellies M, Laskawi R, Götz W, Arglebe C, Tormählen G. Immunohistochemical and morphometric investigations of the influence of botulinum toxin on the submandibular gland of the rat. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1999; 256:148–152. PMID: 10234485.
Article4. Jongerius PH, Rotteveel JJ, van den Hoogen F, Joosten F, van Hulst K, Gabreels FJ. Botulinum toxin A: a new option for treatment of drooling in children with cerebral palsy. Presentation of a case series. Eur J Pediatr. 2001; 160:509–551. PMID: 11548191.
Article5. Bothwell JE, Clarke K, Dooley JM, Gordon KE, Anderson R, Wood EP, Camfield CS, Camfield PR. Botulinum toxin A as a treatment for excessive drooling in children. Pediatr Neurol. 2002; 27:18–22. PMID: 12160968.
Article6. Jongerius PH, van den Hoogen FJ, van Limbeek J, Gabreels FJ, van Hulst K, Rotteveel JJ. Effect of botulinum toxin in the treatment of drooling: a controlled clinical trial. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:620–627. PMID: 15342830.
Article7. Camp-Bruno JA, Winsberg BG, Green-Parsons AR, Abrams JP. Efficacy of benztropine therapy for drooling. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1989; 31:309–319. PMID: 2666205.
Article8. Bushara KO. Sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a hypothesis of a new treatment--botulinum toxin A injections of the parotid glands. Med Hypotheses. 1997; 48:337–339. PMID: 9160288.9. Simpson DM. Clinical trials of botulinum toxin in the treatment of spasticity. Muscle Nerve Suppl. 1997; 6:S169–S175. PMID: 9826988.
Article10. Fuster Torres MA, Berini Aytes L, Gay Escoda C. Salivary gland application of botulinum toxin for the treatment of sialorrhea. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007; 12:E511–E517. PMID: 17978775.11. Glickman S, Deaney CN. Treatment of relative sialorrhoea with botulinum toxin type A: description and rationale for an injection procedure with case report. Eur J Neurol. 2001; 8:567–571. PMID: 11784340.
Article12. Reid SM, Johnstone BR, Westbury C, Rawicki B, Reddihough DS. Randomized trial of botulinum toxin injections into the salivary glands to reduce drooling in children with neurological disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008; 50:123–128. PMID: 18201301.
Article13. Jongerius PH, Rotteveel JJ, van Limbeek J, Gabreels FJ, van Hulst K, van den Hoogen FJ. Botulinum toxin effect on salivary flow rate in children with cerebral palsy. Neurology. 2004; 63:1371–1375. PMID: 15505151.
Article14. Bhatia KP, Munchau A, Brown P. Botulinum toxin is a useful treatment in excessive drooling in saliva. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999; 67:697. PMID: 10577041.15. Tan EK, Lo YL, Seah A, Auchus AP. Recurrent jaw dislocation after botulinum toxin treatment for sialorrhoea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2001; 190:95–97. PMID: 11574113.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Morphology of Salivary Glands in Patients with Cerebral Palsy
- Effects of Botulinum Toxin A Injection into Salivary Glands of Patients with Brain Lesion Suffering from Posterior Drooling
- Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Sialorrhea
- A Case of Drooling during Sleep Treated with Wharton's Duct Relocation
- Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided and Non-ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Toxin Injection Into Cadaver Salivary Glands