Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Dec;37(6):796-803. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.796.
Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Drooling in Tetraplegic Patients With Brain Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. yi0314@gmail.com
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2266558
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.796
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the effect of botulinum toxin type A (BTA) injection into the salivary gland and to evaluate the changes of drooling in varied postures in tetraplegic patients with brain injury.
METHODS
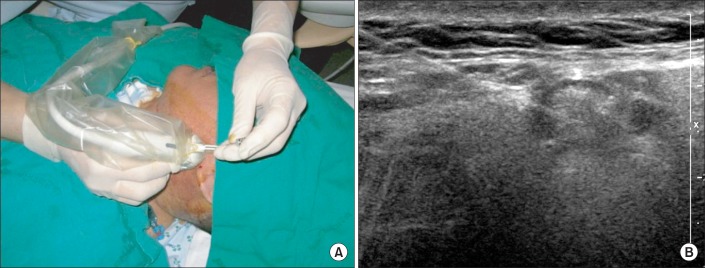
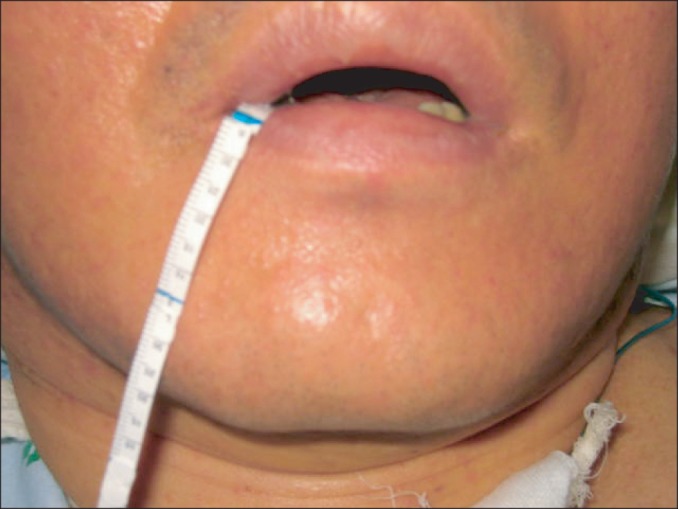
Eight tetraplegic patients with brain injury were enrolled. BTA was injected into each parotid and submandibular gland of both sides under ultrasonographic guidance. Drooling was measured by a questionnaire-based scoring system for drooling severity and frequency, and the sialorrhea was measured by a modified Schirmer test for the patients before the injection, 3 weeks and 3 months after the injection. Drooling was evaluated in each posture, such as supine, sitting, and tilt table standing, and during involuntary mastication, before and after the injection.
RESULTS
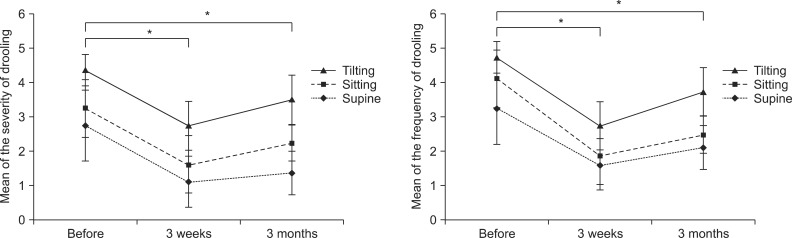
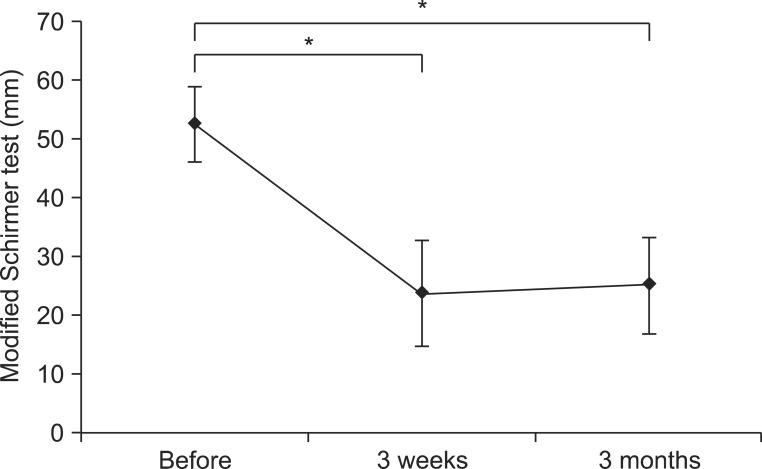
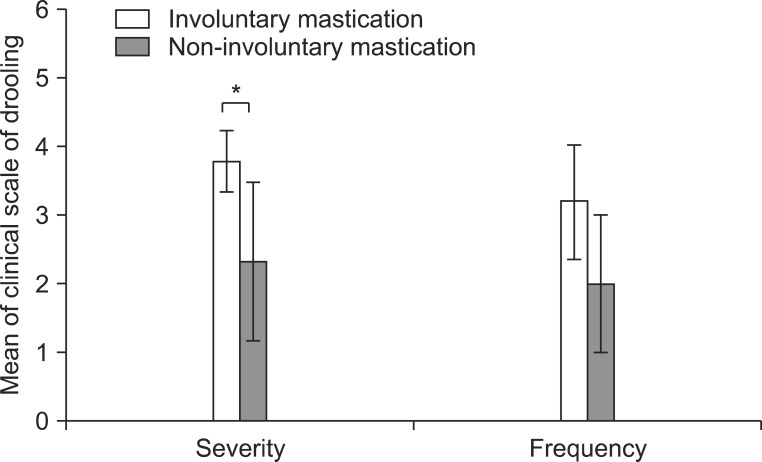
The severity and frequency of drooling and the modified Schirmer test improved significantly at 3 weeks and 3 months after the injection (p<0.05). Drooling was more severe and frequent in tilt table standing than in the sitting position and in sitting versus supine position (p<0.05). The severity of drooling was significantly increased in the patients with involuntary mastication (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Salivary gland injection of BTA in patients with tetraplegia resulting from brain injury who had drooling and sialorrhea could improve the symptoms for 3 months without complications. The severity and frequency of drooling were dependent on posture and involuntary mastication. Proper posture and involuntary mastication of the patients should be taken into account in planning drooling treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lim M, Mace A, Nouraei SA, Sandhu G. Botulinum toxin in the management of sialorrhoea: a systematic review. Clin Otolaryngol. 2006; 31:267–272. PMID: 16911641.
Article2. Bhatia KP, Munchau A, Brown P. Botulinum toxin is a useful treatment in excessive drooling in saliva. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999; 67:697. PMID: 10577041.3. Thomas-Stonell N, Greenberg J. Three treatment approaches and clinical factors in the reduction of drooling. Dysphagia. 1988; 3:73–78. PMID: 3271655.
Article4. van der Burg JJ, Jongerius PH, van Limbeek J, van Hulst K, Rotteveel JJ. Social interaction and self-esteem of children with cerebral palsy after treatment for severe drooling. Eur J Pediatr. 2006; 165:37–41. PMID: 16172877.
Article5. Suskind DL, Tilton A. Clinical study of botulinum-A toxin in the treatment of sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy. Laryngoscope. 2002; 112:73–81. PMID: 11802042.
Article6. Raval TH, Elliott CA. Botulinum toxin injection to the salivary glands for the treatment of sialorrhea with chronic aspiration. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2008; 117:118–122. PMID: 18357835.
Article7. Nunn JH. Drooling: review of the literature and proposals for management. J Oral Rehabil. 2000; 27:735–743. PMID: 11012847.
Article8. Cho P, Yap M. Schirmer test. I. A review. Optom Vis Sci. 1993; 70:152–156. PMID: 8446379.
Article9. Hussein I, Kershaw AE, Tahmassebi JF, Fayle SA. The management of drooling in children and patients with mental and physical disabilities: a literature review. Int J Paediatr Dent. 1998; 8:3–11. PMID: 9558540.
Article10. Stuchell RN, Mandel ID. Salivary gland dysfunction and swallowing disorders. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1988; 21:649–661. PMID: 3054718.
Article11. Hockstein NG, Samadi DS, Gendron K, Handler SD. Sialorrhea: a management challenge. Am Fam Physician. 2004; 69:2628–2634. PMID: 15202698.12. Garrett JR. The proper role of nerves in salivary secretion: a review. J Dent Res. 1987; 66:387–397. PMID: 3305622.
Article13. Jongerius PH, Rotteveel JJ, van den Hoogen F, Joosten F, van Hulst K, Gabreels FJ. Botulinum toxin A: a new option for treatment of drooling in children with cerebral palsy: presentation of a case series. Eur J Pediatr. 2001; 160:509–512. PMID: 11548191.
Article14. Klem C, Mair EA. Four-duct ligation: a simple and effective treatment for chronic aspiration from sialorrhea. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999; 125:796–800. PMID: 10406320.15. Meningaud JP, Pitak-Arnnop P, Chikhani L, Bertrand JC. Drooling of saliva: a review of the etiology and management options. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 101:48–57. PMID: 16360607.
Article16. Borg M, Hirst F. The role of radiation therapy in the management of sialorrhea. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998; 41:1113–1119. PMID: 9719122.
Article17. Stern Y, Feinmesser R, Collins M, Shott SR, Cotton RT. Bilateral submandibular gland excision with parotid duct ligation for treatment of sialorrhea in children: long-term results. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002; 128:801–803. PMID: 12117339.19. Kopera D. Botulinum toxin historical aspects: from food poisoning to pharmaceutical. Int J Dermatol. 2011; 50:976–980. PMID: 21781071.
Article20. Jost WH. Treatment of drooling in Parkinson's disease with botulinum toxin. Mov Disord. 1999; 14:1057. PMID: 10584695.
Article21. Bushara KO. Sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a hypothesis of a new treatment: botulinum toxin A injections of the parotid glands. Med Hypotheses. 1997; 48:337–339. PMID: 9160288.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Botulinum Toxin A Injection into Salivary Glands of Patients with Brain Lesion Suffering from Posterior Drooling
- Pharmacologic and Interventional Approach for Drooling
- Parotid and Submandibular Botulinum Toxin A Injection for Excessive Drooling Children
- Comparing the Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type B Injection at Different Dosages for Patient with Drooling due to Brain Lesion
- Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Morphology of Salivary Glands in Patients with Cerebral Palsy