Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Dec;36(6):841-848.
Comparing the Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type B Injection at Different Dosages for Patient with Drooling due to Brain Lesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul 131-130, Korea. amaranth@hanmail.net
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
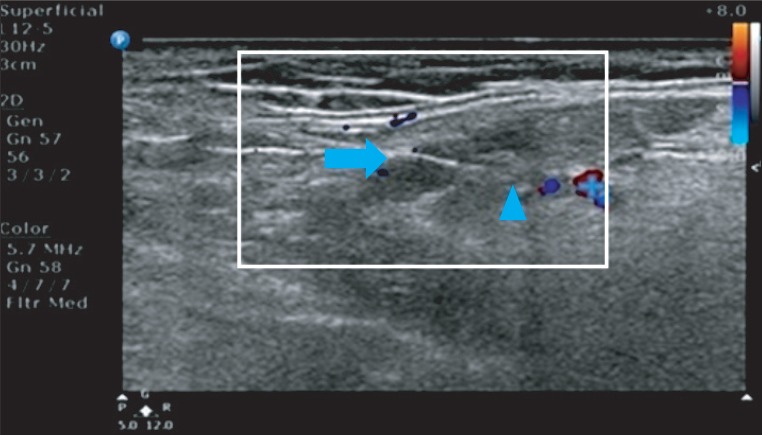
To investigate Botulinum toxin type B (BNT-B) injection's effect and duration depending on dose for patients with brain lesion. METHOD: Twenty one patients with brain lesion and severe drooling were included and divided into three groups. All patients received conventional dysphagia therapy. Group A patients (n=7) received an injection of 1,500 units and group B patients (n=7) received an injection of 2,500 units of BNT-B in submandibular gland under ultrasound guidance. Group C patients (n=7) received conventional dysphagia therapy. Saliva secretion was assessed quantitatively at baseline and at weeks 1, 2, 4, 8, and 12. The severity and frequency of drooling was assessed using the Drooling Quotient (DQ) by patients and/or caregivers.
RESULTS
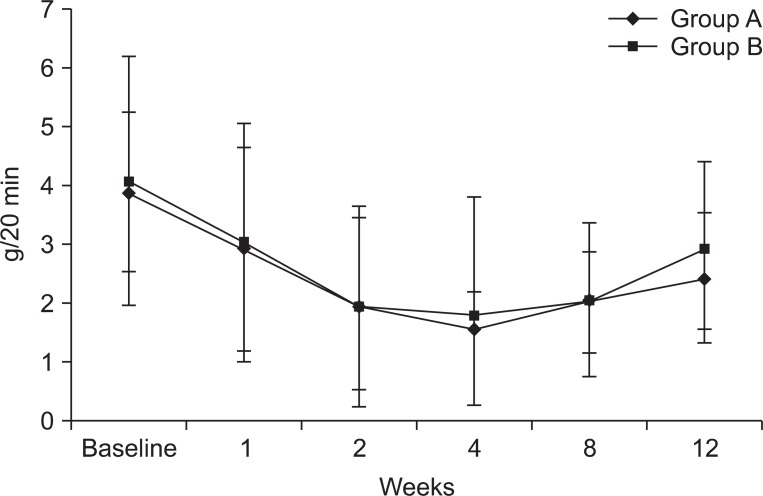
Group A and B reported a distinct improvement of the symptoms within 2 weeks after BNT-B injection. Compared to the baseline, the mean amount of saliva decreased significantly throughout the study. However, there was no meaningful difference between the two groups. The greatest reductions were achieved at 2 weeks and lasted up to 8 weeks after BNT-B injection. Group C did not show any differences.
CONCLUSION
Local injection of 1,500 units of BNT-B into salivary glands under ultrasonic guidance proved to be a safe and effective dose for drooling in patient with brain lesion, as did 2,500 units.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hockstein NG, Samadi DS, Gendron K, Handler SD. Sialorrhea: a management challenge. Am Fam Physician. 2004; 69:2628–2634. PMID: 15202698.2. Hussein I, Kershaw AE, Tahmassebi JF, Fayle SA. The management of drooling in children and patient with mental and physical disablities: a literature review. Int J Paediatr Dent. 1998; 8:3–11. PMID: 9558540.3. Proulx M, de Courval FP, Wiseman MA, Panisset M. Salivary production in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2005; 20:204–207. PMID: 15389996.
Article4. Giess R, Naumann M, Werner E, Riemann R, Beck M, Puls I, Reiners C, Toyka KV. Injections of botulinum toxin A into the salivary glands improve sialorrhoea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000; 69:121–123. PMID: 10864618.
Article5. Suskind DL, Tilton A. Clinical study of botulinum-A toxin in the treatment of sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy. Laryngoscope. 2002; 112:73–81. PMID: 11802042.
Article6. Banerjee KJ, Glasson C, O'Flaherty SJ. Parotid and submandibular botulinum toxin A injections for sialorrhoea in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2006; 48:883–887. PMID: 17044954.
Article7. Mankarious LA, Bottrill ID, Huchzermyer PM, Bailey CM. Long-term follow-up of submandibular duct rerouting for the treatment of sialorrhea in the pediatric population. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999; 120:303–307. PMID: 10064629.
Article8. Brin MF, Lew MF, Adler CH, Comella CL, Factor SA, Jankovic J, O'Brien C, Murray JJ, Wallace JD, Willmer-Hulme A, et al. Safery and efficacy of NeuroBlock (botulinum toxin type B) in type A-resistant cervical dystonia. Neurology. 1999; 53:1431–1438. PMID: 10534247.9. Bushara KO. Sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a hypothesis of a new treatment - botulinum toxin A injections of the parotid glands. Med Hypotheses. 1997; 48:337–339. PMID: 9160288.
Article10. Lagalla G, Millevolte M, Capecci M, Provinciali L, Ceravolo MG. Long-lasting benefits of botulinum toxin type B in Parkinson's disease-related drooling. J Neurol. 2009; 256:563–567. PMID: 19401804.
Article11. Ondo WG, Hunder C, Moore W. A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of botulium toxin B for sialorrhea in Parkinson's diease. Neurology. 2004; 62:37–40. PMID: 14718694.12. Enfors BO. The parotid and submandibular secretion in man. Quantitative recordings of the normal and pathological activity. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1962; 172:1–67. PMID: 13890202.13. Jongerius PH, van Hulst K, vanden Hoogen FJ, Rotteveel JJ. The treatment of posterior drooling by botulinum toxin in a child with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005; 41:351–353. PMID: 16131993.
Article14. Banerjee KJ, Glasson C, O'Flaherty SJ. Parotid and submandibular botulinum toxin A injections for sialorrhoea in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2006; 48:883–887. PMID: 17044954.
Article15. Freed ML, Freed L, Chatburn RL, Christian M. Electrical stimulation for swallowing disorders caused by stroke. Respir Care. 2001; 46:466–474. PMID: 11309186.16. Kim H, Lee Y, Weiner D, Kaye R, Cahill AM, Yudkoff M. Botulinum toxin type A injection to salivary glands: combination with single event multilevel chemoineirolysis in 2 children with severe spastic qudriplegic cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006; 87:141–144. PMID: 16401453.17. Blasco PA, Allaire JH. Drooling in the developmentally disabled: management practices and recommendations. Consortium on drooling. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1992; 34:849–862. PMID: 1397726.18. Bae H, Park CI, Rha DW, Nam HS, Vaq SG, Min KH, Park JB. Factors affecting drooling in adult patients with traumatic brain injury. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2006; 30:424–429.19. Jongerius PH, Joosten F, Hoogen FJ, Gabreels FJ, Rotteveel JJ. The treatment of drooling by ultrasound-quided intraglandular injections of botulinum toxin type A into the salivary glands. Laryngoscope. 2003; 113:107–111. PMID: 12514392.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Botulinum Toxin A Injection into Salivary Glands of Patients with Brain Lesion Suffering from Posterior Drooling
- Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Morphology of Salivary Glands in Patients with Cerebral Palsy
- Pharmacologic and Interventional Approach for Drooling
- Parotid and Submandibular Botulinum Toxin A Injection for Excessive Drooling Children
- Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Drooling in Tetraplegic Patients With Brain Injury