Ann Dermatol.
2013 Nov;25(4):493-495. 10.5021/ad.2013.25.4.493.
A Granulomatous Drug Eruption Induced by Entecavir
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea. cykim@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2265068
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2013.25.4.493
Abstract
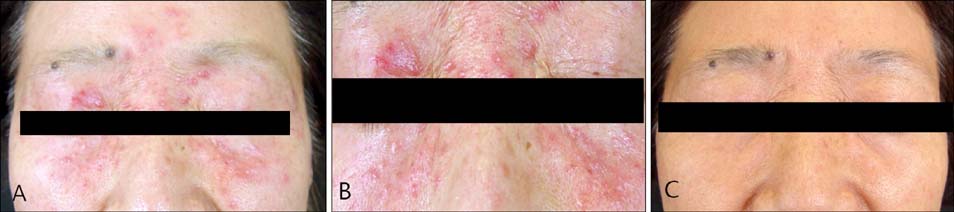
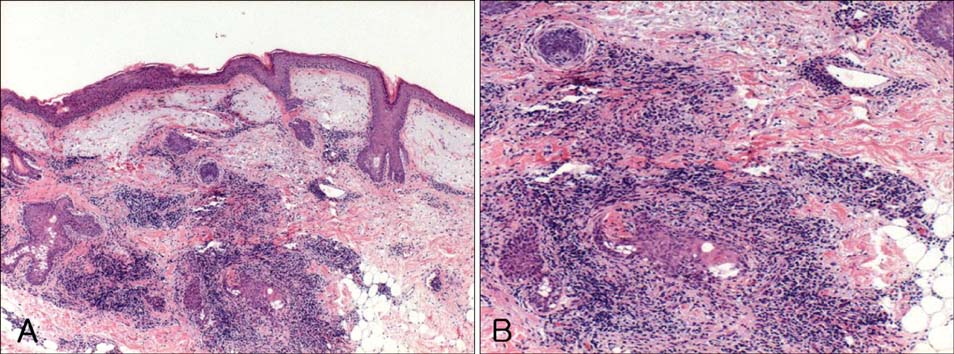
- Entecavir (Baraclude(R), Bristol-Myers Squibb) is a potent and selective antiviral agent that has demonstrated efficacy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. The most frequent adverse events attributed to entecavir include increased alanine aminotransferase, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, abdominal pain, cough, pyrexia, fatigue, and diarrhea. Although quite a few randomized double-blind studies including ones investigating adverse events along with these general symptoms have been reported, few cases of cutaneous adverse events have been described in detail. We demonstrate a case of granulomatous drug eruption as a cutaneous adverse event induced by entecavir.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chang TT, Gish RG, Hadziyannis SJ, Cianciara J, Rizzetto M, Schiff ER, et al. BEHoLD Study Group. A dose-ranging study of the efficacy and tolerability of entecavir in Lamivudine-refractory chronic hepatitis B patients. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129:1198–1209.
Article2. Ono SK, Kato N, Shiratori Y, Kato J, Goto T, Schinazi RF, et al. The polymerase L528M mutation cooperates with nucleotide binding-site mutations, increasing hepatitis B virus replication and drug resistance. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107:449–455.
Article3. Kobashi H, Takaguchi K, Ikeda H, Yokosuka O, Moriyama M, Imazeki F, et al. Efficacy and safety of entecavir in nucleoside-naive, chronic hepatitis B patients: phase II clinical study in Japan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:255–261.
Article4. Chang TT, Gish RG, de Man R, Gadano A, Sollano J, Chao YC, et al. BEHoLD AI463022 Study Group. A comparison of entecavir and lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:1001–1010.
Article5. de Man RA, Wolters LM, Nevens F, Chua D, Sherman M, Lai CL, et al. Safety and efficacy of oral entecavir given for 28 days in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2001; 34:578–582.
Article6. Lai CL, Rosmawati M, Lao J, Van Vlierberghe H, Anderson FH, Thomas N, et al. Entecavir is superior to lamivudine in reducing hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Gastroenterology. 2002; 123:1831–1838.
Article7. Sugiura K, Sugiura M, Takashi T, Naoki H, Itoh A. Immediate allergy, drug-induced eruption, by entecavir. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009; 23:487–489.
Article8. Horn TD, Burke PJ, Karp JE, Hood AF. Intravenous administration of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor causes a cutaneous eruption. Arch Dermatol. 1991; 127:49–52.
Article9. Lee MW, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Moon KC, Koh JK. Interstitial and granulomatous drug reaction presenting as erythema nodosum-like lesions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002; 82:473–474.
Article10. Magro CM, Crowson AN, Schapiro BL. The interstitial granulomatous drug reaction: a distinctive clinical and pathological entity. J Cutan Pathol. 1998; 25:72–78.
Article11. Fujita Y, Shimizu T, Shimizu H. A case of interstitial granulomatous drug reaction due to sennoside. Br J Dermatol. 2004; 150:1035–1037.
Article