A Nationwide Survey of Inhalant Allergens Sensitization and Levels of Indoor Major Allergens in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- 2Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2260684
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.3.222
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The higher prevalence of respiratory allergic disease may be due to increased exposure to inhalation allergens. We conducted a survey of allergic diseases in autumn and winter with detection of major indoor allergens in major cities in Korea.
METHODS
We enrolled 110 subjects from the fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey with stratified, cluster, and systematic sampling procedures. All participants answered a health questionnaire as well as underwent a skin prick test (SPT) and ImmunoCAP for 11 indoor major allergens. We also measured the levels of 5 major allergens (Der f 1, Der p 1, Can f 1, Bla g 1, and Asp f 1) in fine indoor dust from the houses of 60 subjects with a 2-site ELISA.
RESULTS
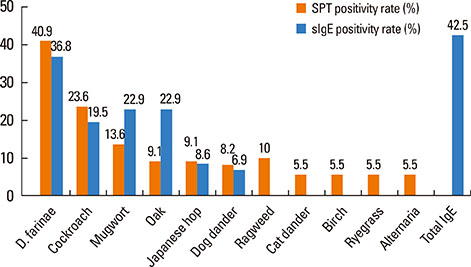
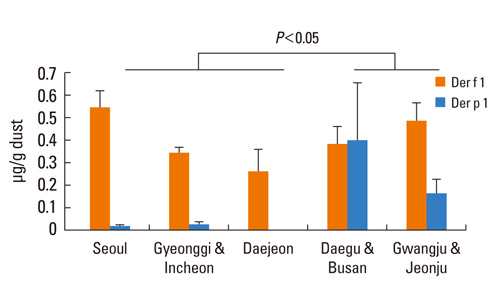
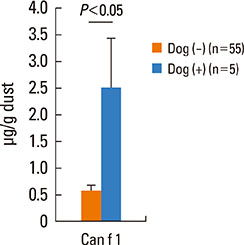
The prevalence of allergic rhinitis and asthma were 25.5% and 7.3%, respectively. The most common sensitized allergens identified by SPT and ImmunoCAP were Dermatophagoides farinae (40.9%, 36.8%), followed by cockroach (23.6%, 19.5%), mugwort (13.6%, 22.9%), oak (9.1%, 22.9%), Japanese hop (9.1%, 8.6%), and dog dander (8.2%, 6.9%). There was a modest discrepancy between SPT and ImmunoCAP. Der f 1 and Der p 1 were detected in 91.7% and 45.0% of the enrolled houses, respectively. Der f 1 indicated high concentrations in all specific provinces in Korea; however, Der p 1 measured high only in the south. Dog dander allergens were present in 71.7% of houses; however, Bla g 1 was present in only 11.7% of houses and Asp f 1 was not detected in any houses.
CONCLUSIONS
The most important inhalant allergens in Korea are house dust mites followed by cockroach, mugwort, oak, Japanese hop, and dog dander in indoor environment, in which The dominant species of house dust mites were different according to region.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 11 articles
-
Comparison between Newly Developed and Commercial Inhalant Skin Prick Test Reagents Using In Vivo and In Vitro Methods
Sang Chul Lee, Da Woon Sim, Jongsun Lee, Kyoung Yong Jeong, Kyung Hee Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Jung Dong Kim, Jung-Won Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(13):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e101.Different Responses in Induction of Allergen Specific Immunoglobulin G4 and IgE-Blocking Factors for Three Mite Subcutaneous Immunotherapy Products
Kyung Hee Park, Sang Chul Lee, Young Woong Son, Kyoung Yong Jeong, Yoo Seob Shin, Jung U Shin, Da Woon Sim, Hye Jung Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Kwang Hoon Lee, Jung-Won Park
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(6):1427-1434. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1427.Standardization of Weed Pollen Extracts, Japanese Hop and Mugwort, in Korea
Kyoung Yong Jeong, Mina Son, Soo-Young Choi, Kyung Hee Park, Hye Jung Park, Chein-Soo Hong, Jae-Hyun Lee, Jung-Won Park
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(2):399-406. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.399.Clinical diagnostic guidelines for allergic rhinitis: diagnosis
Young Hyo Kim, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Jeong-Hee Choi, Dong-Kyu Kim, Young Yoo, Bora Lee, Mi-Ae Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Won-Young Kim, Jeong Hee Kim, Yang Park, So Yeon Park, Woo Yong Bae, Keejae Song, Min-Suk Yang, Sang Min Lee, Young-Mok Lee, Hyun Jong Lee, Jae-Hong Cho, Hye Mi Jee, Young-Il Koh,
J Korean Med Assoc. 2017;60(1):81-88. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2017.60.1.81.Effects of Vacuuming Mattresses on Allergic Rhinitis Symptoms in Children
You Hoon Jeon, Yong Ju Lee, Myung Hyun Sohn, Hae Ran Lee
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(5):655-663. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.5.655.Comparison of skin prick test and serum specific IgE measured by ImmunoCAP system for various inhalant allergens
Young-Hee Nam, Dong-Sub Jeon, Soo-Keol Lee
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(1):47-53. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.1.47.Neutrophil oxidative burst as a diagnostic indicator of IgG-mediated anaphylaxis
Dong Il Won, Sujeong Kim, Eun Hee Lee
Blood Res. 2018;53(4):299-306. doi: 10.5045/br.2018.53.4.299.Patterns of Inhalant Allergen Sensitization and Geographical Variation in Korean Adults: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Min-Gyu Kang, Mi-Yeong Kim, Woo-Jung Song, Sujeong Kim, Eun-Jung Jo, Seung-Eun Lee, Jae-Woo Kwon, Sang-Min Lee, Chan-Sun Park, Hye-Kyung Park, Heung-Woo Park, Yoon-Seok Chang, Jaechun Lee, Young-Min Lee, Young-Koo Jee, Jong-Myung Lee, Inseon S. Choi, Sang-Heon Cho
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(6):499-508. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.6.499.Evaluation of the allergenic relationship between
Humulus japonicus andHumulus lupulus pollen allergens
Chang-Gyu Jung, Eun-Mi Yang, Ji-Ho Lee, Hyun Mi Kim, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(4):217-222. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.4.217.The Relationship between the Causative Allergens of Allergic Diseases and Environments in Korea Over a 8-Year-Period: Based on Skin Prick Test from 2006 to 2015
Chan-Soon Park, Boo-Young Kim, Soo Whan Kim, Joo Hyung Lee, Soo Kweon Koo, Kyung-Su Kim, Seon Tae Kim, Yong-Dae Kim, Jeong Hong Kim, Jin Kook Kim, Chang Hoon Kim, Hyun Jun Kim, Hyo Yeol Kim, Ki-Sang Rha, Hwan-Jung Roh, Dong-Joon Park, Seung-Heon Shin, Sang-Chul Lim, Jae-Hoon Lee, Heung Man Lee, Heung Gu Lee, Young Ha Kim, Jin Hee Cho
J Rhinol. 2018;25(2):91-98. doi: 10.18787/jr.2018.25.2.91.Optimization of Allergen Panels for Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis
Jieun Lee, Jin Kook Kim, Kyung Soo Kim, Chae-Seo Rhee
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2019;62(11):609-616. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2019.00451.
Reference
-
1. Suh M, Kim HH, Sohn MH, Kim KE, Kim C, Shin DC. Prevalence of allergic diseases among Korean school-age children: a nationwide cross-sectional questionnaire study. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:332–338.2. Lee SI, Shin MH, Lee HB, Lee JS, Son BK, Koh YY, Kim KE, Ahn YO. Prevalences of symptoms of asthma and other allergic diseases in korean children: a nationwide questionnaire survey. J Korean Med Sci. 2001; 16:155–164.3. Beasley R, Ellwood P, Asher I. International patterns of the prevalence of pediatric asthma the ISAAC program. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2003; 50:539–553.4. Bateman ED, Hurd SS, Barnes PJ, Bousquet J, Drazen JM, FitzGerald M, Gibson P, Ohta K, O'Byrne P, Pedersen SE, Pizzichini E, Sullivan SD, Wenzel SE, Zar HJ. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur Respir J. 2008; 31:143–178.5. Downs SH, Marks GB, Sporik R, Belosouva EG, Car NG, Peat JK. Continued increase in the prevalence of asthma and atopy. Arch Dis Child. 2001; 84:20–23.6. Park HS, Choi GS, Cho JS, Kim YY. Epidemiology and current status of allergic rhinitis, asthma, and associated allergic diseases in Korea: ARIA Asia-Pacific workshop report. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2009; 27:167–171.7. Strachan DP. The role of environmental factors in asthma. Br Med Bull. 2000; 56:865–882.8. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Steering Committee. Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and atopic eczema: ISAAC. Lancet. 1998; 351:1225–1232.9. Ellwood P, Asher MI, Beasley R, Clayton TO, Stewart AW. ISAAC Steering Committee. The international study of asthma and allergies in childhood (ISAAC): phase three rationale and methods. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2005; 9:10–16.10. Hong SJ, Lee MS, Sohn MH, Shim JY, Han YS, Park KS, Ahn YM, Son BK, Lee HB. Korean ISAAC Study Group. Self-reported prevalence and risk factors of asthma among Korean adolescents: 5-year follow-up study, 1995-2000. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:1556–1562.11. Jeong KY, Hong CS, Lee JS, Park JW. Optimization of allergen standardization. Yonsei Med J. 2011; 52:393–400.12. Voorhorst R, Spieksma FT, Varekamp H, Leupen MJ, Lyklema AW. The house-dust mite (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus) and the allergens it produces. Identity with the house-dust allergen. J Allergy. 1967; 39:325–339.13. Miyamoto T, Oshima S, Ishizaki T, Sato SH. Allergenic identity between the common floor mite (Dermatophagoides farinae Hughes, 1961) and house dust as a causative antigen in bronchial asthma. J Allergy. 1968; 42:14–28.14. Jeong KY, Park JW, Hong CS. House dust mite allergy in Korea: the most important inhalant allergen in current and future. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:313–325.15. Lee SY, Kwon JW, Seo JH, Song YH, Kim BJ, Yu J, Park KS, Kim H, Kim EJ, Lee JS, Hong SJ. Prevalence of atopy and allergic diseases in Korean children: associations with a farming environment and rural lifestyle. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012; 158:168–174.16. Morris DO. Human allergy to environmental pet danders: a public health perspective. Vet Dermatol. 2010; 21:441–449.17. Oh JW, Kang IJ, Kim SW, Kook MH, Kim BS, Cheong JT, Lee HB. The association between the concentration of pollen and outbreak of pollinosis in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009; 19:4–11.18. Oh JW, Lee HR, Kim JS, Lee KI, Kang YJ, Kim SW, Kook MH, Kang HY, Kim JS, Lee MH, Lee HB, Kim KE, Pyun BY, Lee SI, Han MJ. Aerobiological study of pollen and mold in the 10 states of Korea. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2000; 10:22–33.19. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–174.20. Lee YW, Sohn JH, Lee JH, Hong CS, Park JW. Allergen-specific IgE measurement with the IMMULITE 2000 system: intermethod comparison of detection performance for allergen-specific IgE antibodies from Korean allergic patients. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 401:25–32.21. Lee JH, Park KH, Kim HS, Kim KW, Sohn MH, Kim CH, Lee JS, Hong CS, Park JW. Specific IgE measurement using AdvanSure® system: Comparison of detection performance with ImmunoCAP® system in Korean allergy patients. Clin Chim Acta. 2012; 413:914–919.22. Park JW, Kim KS, Jin HS, Kim CW, Kang DB, Choi SY, Yong TS, Oh SH, Hong CS. Der p 2 isoallergens have different allergenicity, and quantification with 2-site ELISA using monoclonal antibodies is influenced by the isoallergens. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:1042–1047.23. van Ree R, Chapman MD, Ferreira F, Vieths S, Bryan D, Cromwell O, Villalba M, Durham SR, Becker WM, Aalbers M, André C, Barber D, Cistero Bahima A, Custovic A, Didierlaurent A, Dolman C, Dorpema JW, Di Felice G, Eberhardt F, Fernandez Caldas E, Fernandez Rivas M, Fiebig H, Focke M, Fötisch K, Gadermaier G, Das RG, Gonzalez Mancebo E, Himly M, Kinaciyan T, Knulst AC, Kroon AM, Lepp U, Marco FM, Mari A, Moingeon P, Monsalve R, Neubauer A, Notten S, Ooievaar-de Heer P, Pauli G, Pini C, Purohit A, Quiralte J, Rak S, Raulf-Heimsoth M, San Miguel Moncin MM, Simpson B, Tsay A, Vailes L, Wallner M, Weber B. The CREATE project: development of certified reference materials for allergenic products and validation of methods for their quantification. Allergy. 2008; 63:310–326.24. van Ree R. Indoor allergens: relevance of major allergen measurements and standardization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:270–277.25. Park JW, Kim HS, Byen JW, Koe SH, Hong YK, Kim CW, Choe K, Hong CS. The prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in asthmatics with positive skin reactivity to Aspergillus fumigatus antigens. Korean J Allergy. 1997; 17:510–521.26. Ree HI, Jeon SH, Lee IY, Hong CS, Lee DK. Fauna and geographical distribution of house dust mites in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1997; 35:9–17.27. Kosik-Bogacka DI, Kalisinska E, Henszel L, Kuzna-Grygiel W. Seasonal dynamics of house dust mites in dust samples collected from sleeping places in north-western Poland. Zoonoses Public Health. 2012; 59:8–15.28. Medjo B, Atanaskovic-Markovic M, Nikolic D, Spasojevic-Dimitrijeva B, Ivanovski P, Djukic S. Association between pet-keeping and asthma in school children. Pediatr Int. 2013; 55:133–137.29. Smallwood J, Ownby D. Exposure to dog allergens and subsequent allergic sensitization: an updated review. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012; 12:424–428.30. Ling M, Long AA. Pet dander and difficult-to-control asthma: therapeutic options. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2010; 31:385–391.31. Berge M, Munir AK, Dreborg S. Concentrations of cat (Fel d1), dog (Can f1) and mite (Der f1 and Der p1) allergens in the clothing and school environment of Swedish schoolchildren with and without pets at home. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1998; 9:25–30.32. Patchett K, Lewis S, Crane J, Fitzharris P. Cat allergen (Fel d 1) levels on school children's clothing and in primary school classrooms in Wellington, New Zealand. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 100:755–759.33. Park YB, Mo EK, Lee JY, Kim JH, Kim CH, Hyun IG, Choi JH. Association Between Pet Ownership and the Sensitization to Pet Allergens in Adults With Various Allergic Diseases. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:295–300.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A comparison of Sensitization to Major Indoor & Outdoor Inhalant Allergens in Children with Respiratory Allergic Diseases
- Change of Inhalant Allergen Sensitization in Children with Allergic Respiratory Diseases during Recent 10 Years
- Early Exposure to Inhalant Allergens and Sensitization
- Change of causative inhalant allergens in respiratory allergic patients in Chungbuk district
- Changing sensitization rate to common inhalant allergens in our environment