Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2014 Jul;6(4):325-332. 10.4168/aair.2014.6.4.325.
Specific B-cell Epitope of Per a 1: A Major Allergen of American Cockroach (Periplaneta americana) and Anatomical Localization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Office for Research and Development, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand.
- 2Graduate Program in Microbiology, Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand.
- 3Department of Tropical Pathology, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailandand.
- 4Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailandand.
- 5Department of Molecular Tropical Medicine and Genetics, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailandand.
- 6Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand. anchalee.tun@mahidol.ac.th
- KMID: 2260213
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.4.325
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Cockroach (CR) is a common source of indoor allergens, and Per a 1 is a major American CR (Periplaneta americana) allergen; however, several attributes of this protein remain unknown. This study identifies a novel specific B cell epitope and anatomical locations of Per a 1.0105.
METHODS
Recombinant Per a 1.0105 (rPer a 1.0105) was used as BALB/c mouse immunogen for the production of monoclonal antibodies (MAb). The MAb specific B cell epitope was identified by determining phage mimotopic peptides and pair-wise alignment of the peptides with the rPer a 1.0105 amino acid sequence. Locations of the Per a 1.0105 in P. americana were investigated by immunohistochemical staining.
RESULTS
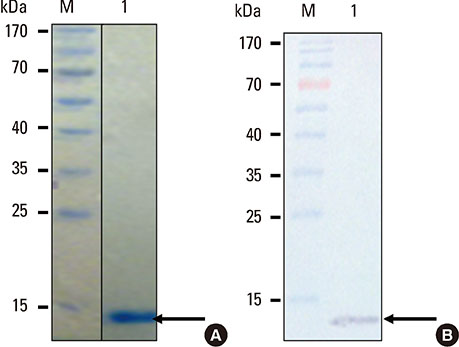
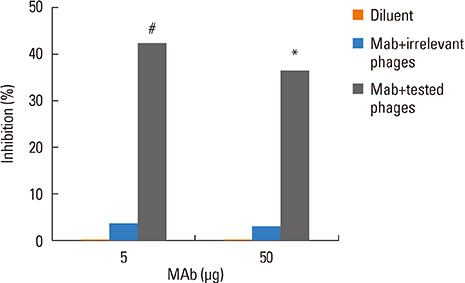
The rPer a 1.0105 (~13 kDa) had 100%, 98% and > or =90% identity to Per a 1.0105, Per a 1.0101, and Cr-PII, respectively. The B-cell epitope of the Per a 1.0105 specific-MAb was located at residues99 QDLLLQLRDKGV110 contained in all 5 Per a 1.01 isoforms and Per a 1.02. The epitope was analogous to the Bla g 1.02 epitope; however, this B-cell epitope was not an IgE inducer. Per a 1.0105 was found in the midgut and intestinal content of American CR but not in the other organs. The amount of the Per a 1 was ~544 degrees Cg per gram of feces.
CONCLUSIONS
The novel Per a 1 B-cell epitope described in this study is a useful target for allergen quantification in samples; however, the specific MAb can be used as an allergen detection reagent. The MAb based-affinity resin can be made for allergen purification, and the so-purified protein can serve as a standard and diagnostic allergen as well as a therapeutic vaccine component. The finding that the Per a 1 is contained in the midgut and feces is useful to increase yield and purity when preparing this allergen.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gore JC, Schal C. Cockroach allergen biology and mitigation in the indoor environment. Annu Rev Entomol. 2007; 52:439–463.2. Ahluwalia SK, Matsui EC. The indoor environment and its effects on childhood asthma. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 11:137–143.3. Cohn RD, Arbes SJ Jr, Jaramillo R, Reid LH, Zeldin DC. National prevalence and exposure risk for cockroach allergen in U.S. households. Environ Health Perspect. 2006; 114:522–526.4. Huss K, Adkinson NF Jr, Eggleston PA, Dawson C, Van Natta ML, Hamilton RG. House dust mite and cockroach exposure are strong risk factors for positive allergy skin test responses in the Childhood Asthma Management Program. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:48–54.5. Matsui EC, Wood RA, Rand C, Kanchanaraksa S, Swartz L, Curtin-Brosnan J, Eggleston PA. Cockroach allergen exposure and sensitization in suburban middle-class children with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:87–92.6. Chew GL, Perzanowski MS, Canfield SM, Goldstein IF, Mellins RB, Hoepner LA, Ashby-Thompson M, Jacobson JS. Cockroach allergen levels and associations with cockroach-specific IgE. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:240–245.7. Rosenstreich DL, Eggleston P, Kattan M, Baker D, Slavin RG, Gergen P, Mitchell H, McNiff-Mortimer K, Lynn H, Ownby D, Malveaux F. The role of cockroach allergy and exposure to cockroach allergen in causing morbidity among inner-city children with asthma. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:1356–1363.8. Chapman MD, Vailes LD, Hayden ML, Platts-Mills TA, Arruda LK. Cockroach allergens and their role in asthma. In : Kay AB, editor. Allergy and allergic diseases. Oxford: Blackwell Science;1997. p. 942–951.9. Schou C, Lind P, Fernandez-Caldas E, Lockey RF, Løwenstein H. Identification and purification of an important cross-reactive allergen from American (Periplaneta americana) and German (Blattella germanica) cockroach. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990; 86:935–946.10. Diraphat P, Sookrung N, Chaicumpa W, Pumhirun P, Vichyanond P, Tapchaisri P, Kalambaheti T, Mahakunkijchareon Y, Sakolvaree Y, Bunnag C. Recombinant American cockroach component, Per a 1, reactive to IgE of allergic Thai patients. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2003; 21:11–20.11. Sookrung N, Chaicumpa W. A revisit to cockroach allergens. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2010; 28:95–106.12. Wu CH, Luo SF, Wong DW. Analysis of cross-reactive allergens from American and German cockroaches by human IgE. Allergy. 1997; 52:411–416.13. Pomés A, Wünschmann S, Hindley J, Vailes LD, Chapman MD. Cockroach allergens: function, structure and allergenicity. Protein Pept Lett. 2007; 14:960–969.14. Gore JC, Schal C. Gene expression and tissue distribution of the major human allergen Bla g 1 in the German cockroach, Blattella germanica L. (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae). J Med Entomol. 2004; 41:953–960.15. Sookrung N, Diraphat P, Chaicumpa W, Tongtawe P, Sakolvaree Y, Tapchaisri P, Mahakittikun V, Tungtrongchitr A, Vichyanond P, Bunnag C. Cockroach allergen detection and cockroach allergens of allergic Thai patients. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2003; 21:1–9.16. Kulkeaw K, Sakolvaree Y, Srimanote P, Tongtawe P, Maneewatch S, Sookrung N, Tungtrongchitr A, Tapchaisri P, Kurazono H, Chaicumpa W. Human monoclonal ScFv neutralize lethal Thai cobra, Naja kaouthia, neurotoxin. J Proteomics. 2009; 72:270–282.17. Thueng-in K, Thanongsaksrikul J, Srimanote P, Bangphoomi K, Poungpair O, Maneewatch S, Choowongkomon K, Chaicumpa W. Cell penetrable humanized-VH/V(H)H that inhibit RNA dependent RNA polymerase (NS5B) of HCV. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e49254.18. Tungtrongchitr A, Sookrung N, Chaicumpa W, Indrawattana N, Meechan T, Thavara U, Visitsunthorn N, Bunnag C. Comparison of allergenic components and biopotency in whole body extracts of wild and laboratory reared American cockroaches, Periplaneta americana. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2012; 30:231–238.19. Tawatsin A, Thavara U, Chompoosri J, Kong-ngamsuk W, Chansang C, Paosriwong S. Cockroach surveys in 14 provinces of Thailand. J Vector Ecol. 2001; 26:232–238.20. Tungtrongchitr A, Sookrung N, Munkong N, Mahakittikun V, Chinabut P, Chaicumpa W, Bunnag C, Vichyanond P. The levels of cockroach allergen in relation to cockroach species and allergic diseases in Thai patients. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2004; 22:115–121.21. Wu CH, Lee MF, Yang JS, Tseng CY. IgE-binding epitopes of the American cockroach Per a 1 allergen. Mol Immunol. 2002; 39:459–464.22. Sanderson SD, Cheruku SR, Padmanilayam MP, Vennerstrom JL, Thiele GM, Palmatier MI, Bevins RA. Immunization to nicotine with a peptide-based vaccine composed of a conformationally biased agonist of C5a as a molecular adjuvant. Int Immunopharmacol. 2003; 3:137–146.23. Sookrung N, Chaicumpa W, Tungtrongchitr A, Vichyanond P, Bunnag C, Ramasoota P, Tongtawe P, Sakolvaree Y, Tapchaisri P. Periplaneta americana arginine kinase as a major cockroach allergen among Thai patients with major cockroach allergies. Environ Health Perspect. 2006; 114:875–880.24. Thanongsaksrikul J, Srimanote P, Maneewatch S, Choowongkomon K, Tapchaisri P, Makino S, Kurazono H, Chaicumpa W. A V H H that neutralizes the zinc metalloproteinase activity of botulinum neurotoxin type A. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:9657–9666.25. Chavanayarn C, Thanongsaksrikul J, Thueng-In K, Bangphoomi K, Sookrung N, Chaicumpa W. Humanized-single domain antibodies (VH/VHH) that bound specifically to Naja kaouthia phospholipase A2 and neutralized the enzymatic activity. Toxins (Basel). 2012; 4:554–567.26. Yi MH, Jeong KY, Kim CR, Yong TS. IgE-binding reactivity of peptide fragments of Bla g 1.02, a major German cockroach allergen. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2009; 27:121–129.27. Meechan P, Tungtrongchitr A, Chaisri U, Maklon K, Indrawattana N, Chaicumpa W, Sookrung N. Intranasal, liposome-adjuvanted cockroach allergy vaccines made of refined major allergen and whole-body extract of Periplaneta americana. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013; 161:351–362.28. Lehane MJ. Peritrophic matrix structure and function. Annu Rev Entomol. 1997; 42:525–550.29. Kato N, Dasgupta R, Smartt CT, Christensen BM. Glucosamine: fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase: gene characterization, chitin biosynthesis and peritrophic matrix formation in Aedes aegypti. Insect Mol Biol. 2002; 11:207–216.30. Pascoa V, Oliveira PL, Dansa-Petretski M, Silva JR, Alvarenga PH, Jacobs-Lorena M, Lemos FJ. Aedes aegypti peritrophic matrix and its interaction with heme during blood digestion. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2002; 32:517–523.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- IgE-Binding Epitope Mapping and Tissue Localization of the Major American Cockroach Allergen Per a 2
- Enzymatic Activities of Allergen Extracts from Three Species of Dust Mites and Cockroaches Commonly Found in Korean Home
- Comparative Microbiome Analysis of Three Species of Laboratory-Reared Periplaneta Cockroaches
- IgE Binding Reactivity of Peptide Fragments of Bla g 4, a Major German Cockroach Allergen
- Reactivity of German Cockroach Allergen, Bla g 2, Peptide Fragments to IgE Antibodies in Patients' Sera