Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Jan;7(1):60-68. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.1.60.
Cross-Reactivity Between the Soybean Protein P34 and Bovine Caseins
- Affiliations
-
- 1Centro de Investigacion y Desarrollo en Criotecnologia de Alimentos, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, UNLP - CONICET, La Plata, Argentina. silvana@biol.unlp.edu.ar guidoc@biol.unlp.edu.ar
- 2Instituto de Estudios Inmunologicos y Fisiopatologicos, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, UNLP - CONICET, La Plata, Argentina.
- 3Laboratorio de Nanomateriales. Centro de Investigacion y Desarrollo en Fermentaciones Industriales, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, UNLP - CONICET, La Plata, Argentina.
- KMID: 2260153
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.1.60
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Soy-based formulas are widely used as dairy substitutes to treat milk allergy patients. However, reactions to soy have been reported in a small proportion of patients with IgE-mediated milk allergies. The aim of this work was to explore whether P34, a mayor soybean allergen, is involved in this cross-reactivity.
METHODS
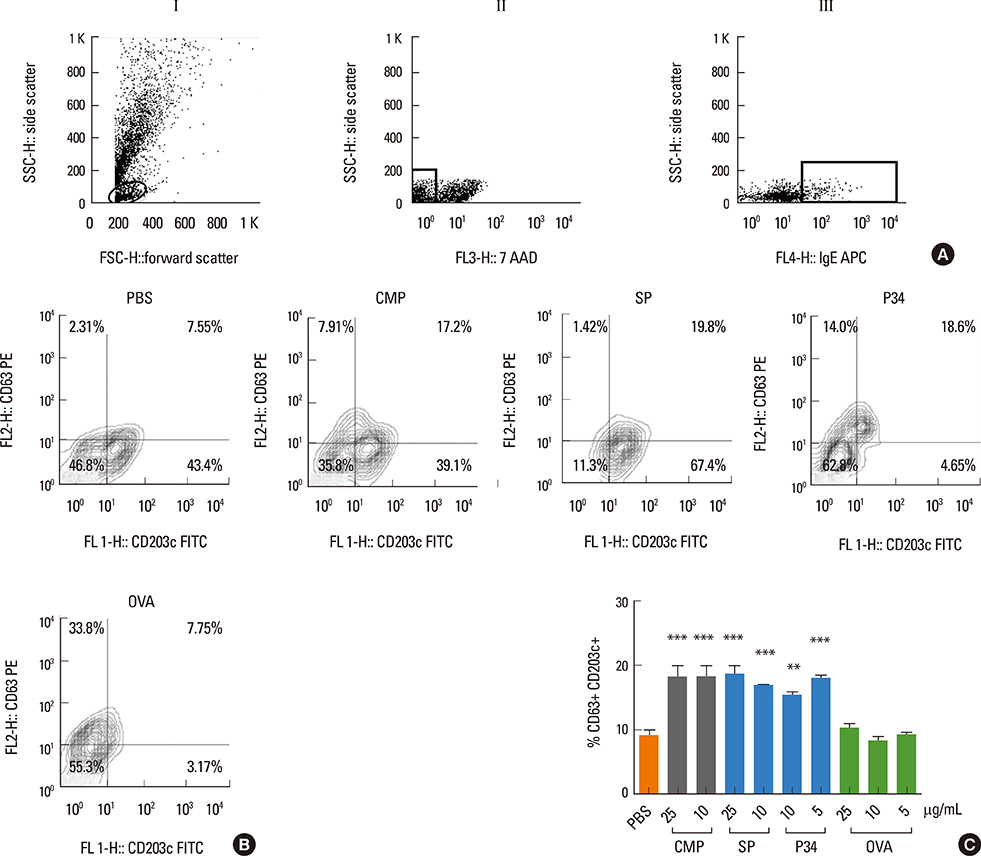
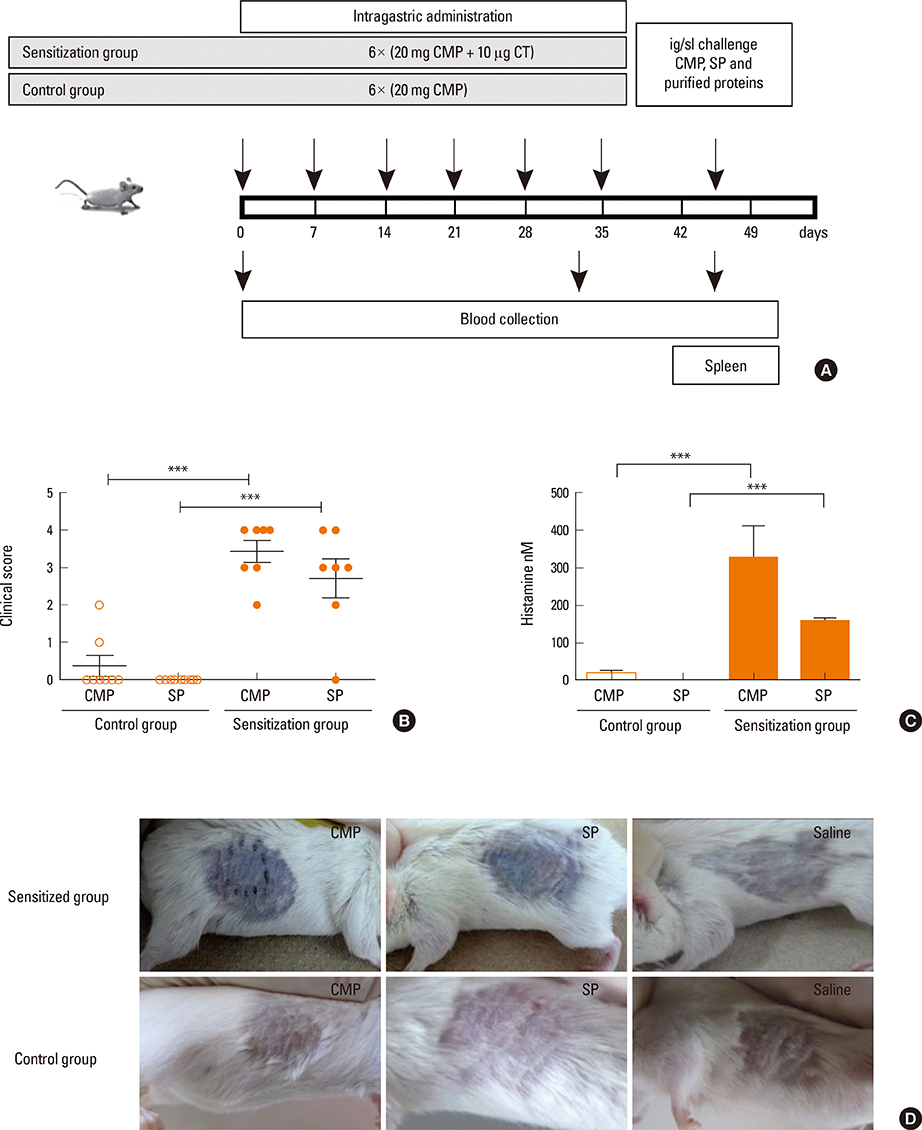
In vitro recognition of P34 was evaluated by immunoblotting, competitive ELISA and basophil activation tests (BAT) using sera from allergic patients. In vivo cross-reactivity was examined using an IgE-mediated milk allergy mouse model.
RESULTS
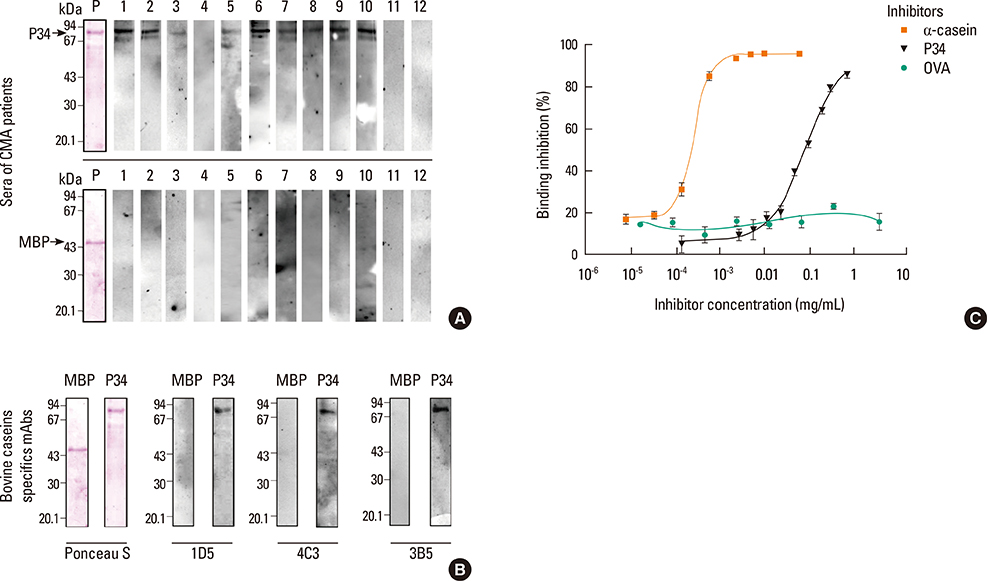
P34 was recognized by IgE antibodies from the sera of milk allergic patients, casein-specific monoclonal antibodies, and sera from milk-allergic mice. Spleen cells from sensitized mice incubated with milk, soy or P34 secreted IL-5 and IL-13, while IFN-gamma remained unchanged. In addition, the cutaneous test was positive with cow's milk proteins (CMP) and P34 in the milk allergy mouse model. Moreover, milk-sensitized mice developed immediate symptoms following sublingual exposure to P34.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results demonstrate that P34 shares epitopes with bovine casein, which is responsible for inducing hypersensitivity symptoms in milk allergic mice. This is the first report of the in vivo cross-allergenicity of P34.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antibodies
Antibodies, Monoclonal
Basophils
Caseins*
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Epitopes
Food Hypersensitivity
Humans
Hypersensitivity
Immunoblotting
Immunoglobulin E
Interleukin-13
Interleukin-5
Mice
Milk
Milk Hypersensitivity
Milk Proteins
Soy Milk
Soybeans*
Spleen
Antibodies
Antibodies, Monoclonal
Caseins
Epitopes
Immunoglobulin E
Interleukin-13
Interleukin-5
Milk Proteins
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Survey of IgE Reactivity to Nonbiting Midges in Korea and Identification of IgE-Binding Protein
Myung-hee Yi, Ju Yeong Kim, Kyoung Yong Jeong, Han-Il Ree, Tai-Soon Yong
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(5):644-654. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.5.644.
Reference
-
1. Wang J, Sampson HA. Food allergy: recent advances in pathophysiology and treatment. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2009; 1:19–29.2. Lehrer SB, Ayuso R, Reese G. Current understanding of food allergens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002; 964:69–85.3. Gu X, Beardslee T, Zeece M, Sarath G, Markwell J. Identification of IgE-binding proteins in soy lecithin. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001; 126:218–225.4. Gómez-Ollés S, Cruz MJ, Bogdanovic J, Wouters IM, Doekes G, Sander I, Morell F, Rodrigo MJ. Assessment of soy aeroallergen levels in different work environments. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37:1863–1872.5. Codina R, Ardusso L, Lockey RF, Crisci CD, Jaén C, Bertoya NH. Identification of the soybean hull allergens involved in sensitization to soybean dust in a rural population from Argentina and N-terminal sequence of a major 50 KD allergen. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:1059–1063.6. Baur X, Pau M, Czuppon A, Fruhmann G. Characterization of soybean allergens causing sensitization of occupationally exposed bakers. Allergy. 1996; 51:326–330.7. Ballmer-Weber BK, Holzhauser T, Scibilia J, Mittag D, Zisa G, Ortolani C, Oesterballe M, Poulsen LK, Vieths S, Bindslev-Jensen C. Clinical characteristics of soybean allergy in Europe: a double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:1489–1496.8. Giampietro PG, Ragno V, Daniele S, Cantani A, Ferrara M, Businco L. Soy hypersensitivity in children with food allergy. Ann Allergy. 1992; 69:143–146.9. Magnolfi CF, Zani G, Lacava L, Patria MF, Bardare M. Soy allergy in atopic children. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996; 77:197–201.10. Bruno G, Giampietro PG, Del Guercio MJ, Gallia P, Giovannini L, Lovati C, Paolucci P, Quaglio L, Zoratto E, Businco L. Soy allergy is not common in atopic children: a multicenter study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1997; 8:190–193.11. Ogawa T, Bando N, Tsuji H, Okajima H, Nishikawa K, Sasaoka K. Investigation of the IgE-binding proteins in soybeans by immunoblotting with the sera of the soybean-sensitive patients with atopic dermatitis. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 1991; 37:555–565.12. Ogawa T, Tsuji H, Bando N, Kitamura K, Zhu YL, Hirano H, Nishikawa K. Identification of the soybean allergenic protein, Gly m Bd 30K, with the soybean seed 34-kDa oil-body-associated protein. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1993; 57:1030–1033.13. Ogawa T, Bando N, Tsuji H, Nishikawa K, Kitamura K. Alpha-subunit of beta-conglycinin, an allergenic protein recognized by IgE antibodies of soybean-sensitive patients with atopic dermatitis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1995; 59:831–833.14. Hiemori M, Ito H, Kimoto M, Yamashita H, Nishizawa K, Maruyama N, Utsumi S, Tsuji H. Identification of the 23-kDa peptide derived from the precursor of Gly m Bd 28K, a major soybean allergen, as a new allergen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004; 1675:174–183.15. Krishnan HB, Kim WS, Jang S, Kerley MS. All three subunits of soybean beta-conglycinin are potential food allergens. J Agric Food Chem. 2009; 57:938–943.16. Kalinski A, Weisemann JM, Matthews BF, Herman EM. Molecular cloning of a protein associated with soybean seed oil bodies that is similar to thiol proteases of the papain family. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265:13843–13848.17. Ji C, Boyd C, Slaymaker D, Okinaka Y, Takeuchi Y, Midland SL, Sims JJ, Herman E, Keen N. Characterization of a 34-kDa soybean binding protein for the syringolide elicitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:3306–3311.18. Herman E. Soybean allergenicity and suppression of the immunodominant allergen. Crop Sci. 2005; 45:462–467.19. Helm R, Cockrell G, Herman E, Burks A, Sampson H, Bannon G. Cellular and molecular characterization of a major soybean allergen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1998; 117:29–37.20. Helm RM, Cockrell G, Connaughton C, West CM, Herman E, Sampson HA, Bannon GA, Burks AW. Mutational analysis of the IgE-binding epitopes of P34/Gly m Bd 30K. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 105:378–384.21. Mittag D, Vieths S, Vogel L, Becker WM, Rihs HP, Helbling A, Wüthrich B, Ballmer-Weber BK. Soybean allergy in patients allergic to birch pollen: clinical investigation and molecular characterization of allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:148–154.22. Kleine-Tebbe J, Vogel L, Crowell DN, Haustein UF, Vieths S. Severe oral allergy syndrome and anaphylactic reactions caused by a Bet v 1- related PR-10 protein in soybean, SAM22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002; 110:797–804.23. Rozenfeld P, Docena GH, Añón MC, Fossati CA. Detection and identification of a soy protein component that cross-reacts with caseins from cow's milk. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002; 130:49–58.24. Curciarello R, Lareu JF, Fossati CA, Docena GH, Petruccelli S. Immunochemical characterization of Glycine max L. Merr. var Raiden, as a possible hypoallergenic substitute for cow's milk-allergic patients. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:1559–1565.25. Curciarello R, Smaldini PL, Candreva AM, González V, Parisi G, Cauerhff A, Barrios I, Blanch LB, Fossati CA, Petruccelli S, Docena GH. Targeting a cross-reactive Gly m 5 soy peptide as responsible for hypersensitivity reactions in a milk allergy mouse model. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e82341.26. Smaldini P, Curciarello R, Candreva A, Rey MA, Fossati CA, Petruccelli S, Docena GH. In vivo evidence of cross-reactivity between cow's milk and soybean proteins in a mouse model of food allergy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012; 158:335–346.27. Docena GH, Fernandez R, Chirdo FG, Fossati CA. Identification of casein as the major allergenic and antigenic protein of cow's milk. Allergy. 1996; 51:412–416.28. Fiocchi A, Brozek J, Schünemann H, Bahna SL, von Berg A, Beyer K, Bozzola M, Bradsher J, Compalati E, Ebisawa M, Guzman MA, Li H, Heine RG, Keith P, Lack G, Landi M, Martelli A, Rancé F, Sampson H, Stein A, Terracciano L, Vieths S. World Allergy Organization (WAO) Diagnosis and Rationale for Action against Cow's Milk Allergy (DRACMA) guidelines. World Allergy Organ J. 2010; 3:57–161.29. Klemola T, Vanto T, Juntunen-Backman K, Kalimo K, Korpela R, Varjonen E. Allergy to soy formula and to extensively hydrolyzed whey formula in infants with cow's milk allergy: a prospective, randomized study with a follow-up to the age of 2 years. J Pediatr. 2002; 140:219–224.30. Docena G, Rozenfeld P, Fernández R, Fossati CA. Evaluation of the residual antigenicity and allergenicity of cow's milk substitutes by in vitro tests. Allergy. 2002; 57:83–91.31. Petruccelli S, Chirdo FG, Añón MC. Immunochemical reactivity of soybean β-conglycinin subunits. Food Agric Immunol. 2005; 16:17–28.32. Nallamsetty S, Austin BP, Penrose KJ, Waugh DS. Gateway vectors for the production of combinatorially-tagged His6-MBP fusion proteins in the cytoplasm and periplasm of Escherichia coli. Protein Sci. 2005; 14:2964–2971.33. Wallowitz ML, Chen RJ, Tzen JT, Teuber SS. Ses i 6, the sesame 11S globulin, can activate basophils and shows cross-reactivity with walnut in vitro. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37:929–938.34. Bhatia J, Greer F. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. Use of soy protein-based formulas in infant feeding. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:1062–1068.35. Halpern SR, Sellars WA, Johnson RB, Anderson DW, Saperstein S, Reisch JS. Development of childhood allergy in infants fed breast, soy, or cow milk. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973; 51:139–151.36. Zeiger RS, Sampson HA, Bock SA, Burks AW Jr, Harden K, Noone S, Martin D, Leung S, Wilson G. Soy allergy in infants and children with IgE-associated cow's milk allergy. J Pediatr. 1999; 134:614–622.37. Orsi M, Fernández A, Follett FR, Marchisone S, Saieg G, Busoni VB, Tabacco O, Toca C. Cow's milk protein allergy: proposed guidelines for the management of children with cow's milk protein allergy. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2009; 107:459–467.38. Morita H, Kaneko H, Ohnishi H, Kato Z, Kondo N. Antigen-specific immune response to endotoxin-free recombinant P34. Allergy. 2011; 66:985–986.39. Wills-Karp M, Nathan A, Page K, Karp CL. New insights into innate immune mechanisms underlying allergenicity. Mucosal Immunol. 2010; 3:104–110.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Soy Protein and Isoflavones on Bone Markers and Hormones in Growing Male Rats
- Effects of Soybean Protein on Bone Mineral Density and Bone Mineral Content in Ovariectomized Rats
- Effects of Soy Protein and Isoflavones on Bone Mineral Density in Crowing Female Rats
- Early recognized antigen (p34) of Toxoplasma gondii after peroral ingestion of tissue cyst forming strain (Me49 strain) in mice
- Effect of Soy Protein Hydrolyzate on Lipid Metabolism and Antioxidant Activity in the Rat