Korean J Hematol.
2006 Mar;41(1):41-45. 10.5045/kjh.2006.41.1.41.
A Patient with IgA Monoclonal Gammopathy Presenting as Myelomatous Pleural Effusion with Axillary Node Involvement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Abbot Korea Limited, Seoul, Korea. kssong@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2252326
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2006.41.1.41
Abstract
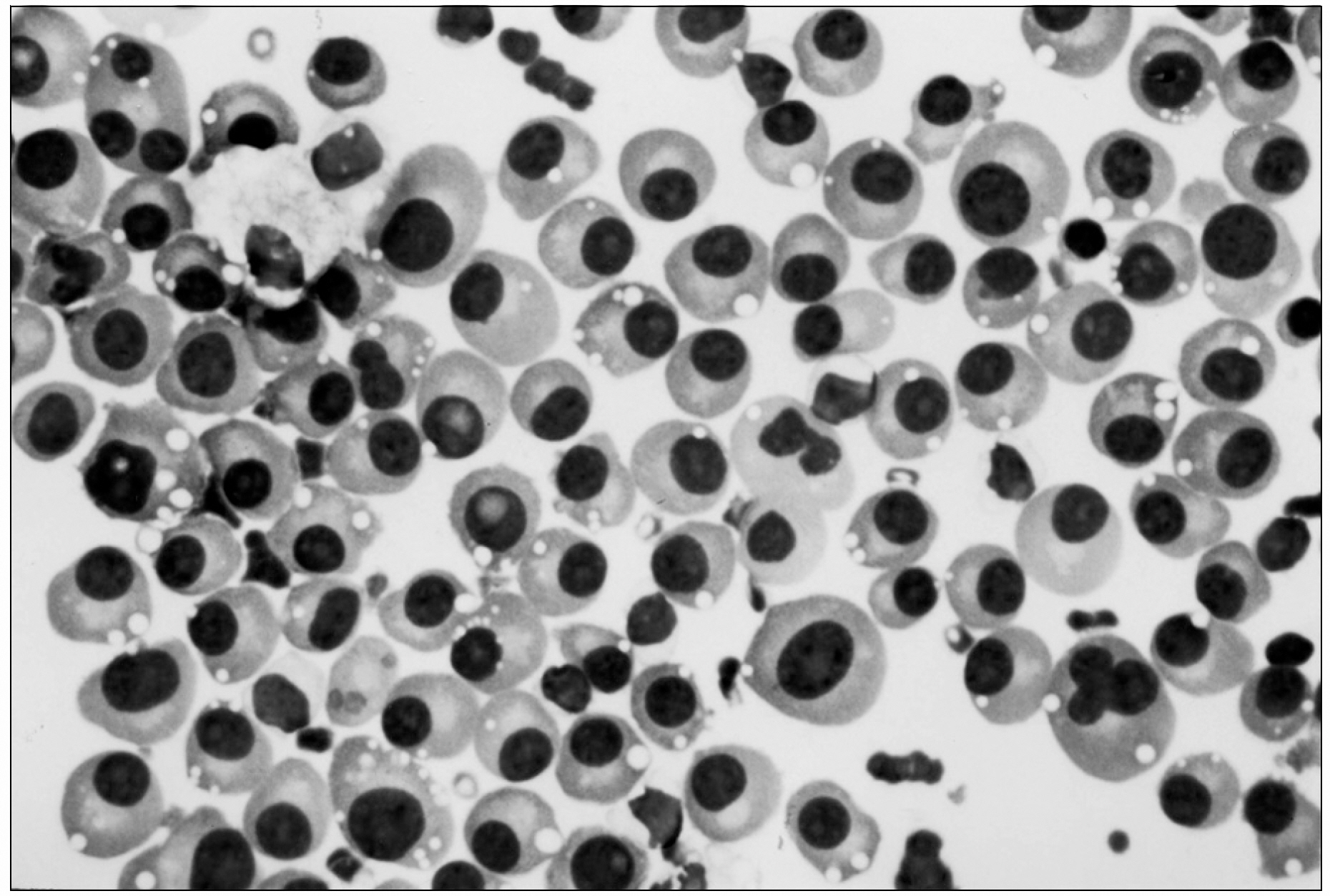
- Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells that produce monoclonal immunoglobulin, and the neoplastic plasma cells typically accumulate in the bone marrow with occasional involvement of other organs. Pleural effusion that is associated with multiple myeloma has been infrequently reported (<6%) and myelomatous pleural effusion is extremely rare (<1%). A 73-year-old woman was admitted to the department of dermatology for skin lesions on both arms and both ankles. A chest radiograph taken on admission showed a nodular lesion in the right upper lung and pleural effusion. Analysis of the pleural fluid revealed many atypical plasma cells, elevated levels of IgA (27.95g/L) and lambda light chain (9.16g/L), and monoclonal IgA-lambda paraprotein on immunofixation. The serum concentrations of IgA were elevated (33.08g/L) while the concentrations of IgG and IgM were decreased. Bone marrow aspirate smears contained increased levels of immature-appearing atypical plasma cells. This is only the third case of myelomatous pleural effusion that has been reported in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Bataille R., Harousseau J. Multiple myeloma. New Engl J Med. 1997. 336:1657–64.
Article2). Safa AM., Van Ordstrand HS. Pleural effusion due to multiple myeloma. Chest. 1973. 64:246–8.
Article3). Hwang HK., Lee CK., Lee KH., Hyun MS., Shim BS., Lee HW. A case of multiple myeloma with pleural effusion. Korean J Hematol. 1992. 27:161–5.4). Kintzer JS., Rosenow EC., Kyle RA. Thoracic and pulmonary abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Arch Intern Med. 1978. 138:727–30.
Article5). Hata H., Matsuzaki H., Tanaka K, et al. Ectopic production of salivary-type amylase by a IgA-lambda-type multiple myeloma. Cancer. 1988. 62:1511–5.6). Kwan WC., Lam SC., Klimo P. Kappa light-chain myeloma with pleural involvement. Chest. 1984. 86:494–6.
Article7). Kamal MK., Williams E., Poskitt TR. IgD myeloma with malignant pleural effusion. South Med J. 1987. 80:657–8.
Article8). Rodriguez JN., Pereira A., Martinez JC., Conde J., Pujol E. Pleural effusion in multiple myeloma. Chest. 1994. 105:622–4.
Article9). Kim YM., Lee KK., Oh HS, et al. Myelomatous effusion with poor response to chemotherapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2000. 15:243–6.
Article10). Hughes JC., Votaw ML. Pleural effusion in multiple myeloma. Cancer. 1979. 44:1150–4.
Article11). Sasser RL., Yam LT., Li CY. Myeloma with involvement of the serous cavities. Cytologic and immuno-chemical diagnosis and literature review. Acta Cytol. 1990. 34:479–85.12). Kamble R., Wilson CS., Fassas A, et al. Malignant pleural effusion of multiple myeloma: prognostic factors and outcome. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005. 46:1137–42.
Article13). McMillen JJ., Krueger SK., Dyer GA. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis in association with immunoglobulin A myeloma. Ann Intern Med. 1986. 105:709–10.
Article14). Bayer-Garner IB., Smoller BR. Leukocytoclastic (small vessel) vasculitis in multiple myeloma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003. 28:521–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Myelomatous effusion with poor response to chemotherapy
- Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Pericardium Accompanied by Monoclonal Gammopathy: A Case Report with CT and PET Imaging Findings
- Cytologic Diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Effusion in Multiple Myeloma: Two Case Reports
- Myelomatous Pleural Effusion with Elevated ADA Activity
- Diagnostic Value of Immunoglobulin in Malignant Pleural Effusions