Korean Circ J.
2009 Dec;39(12):538-544. 10.4070/kcj.2009.39.12.538.
N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Overweight and Obese Patients With and Without Diabetes: An Analysis Based on Body Mass Index and Left Ventricular Geometry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Maryknoll Medical Center, Busan, Korea. kyoungim74@dreamwiz.com
- KMID: 2225642
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2009.39.12.538
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
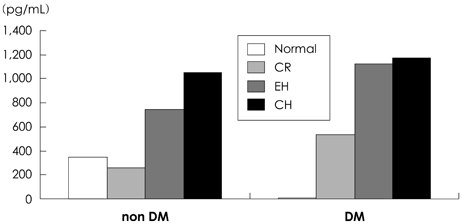
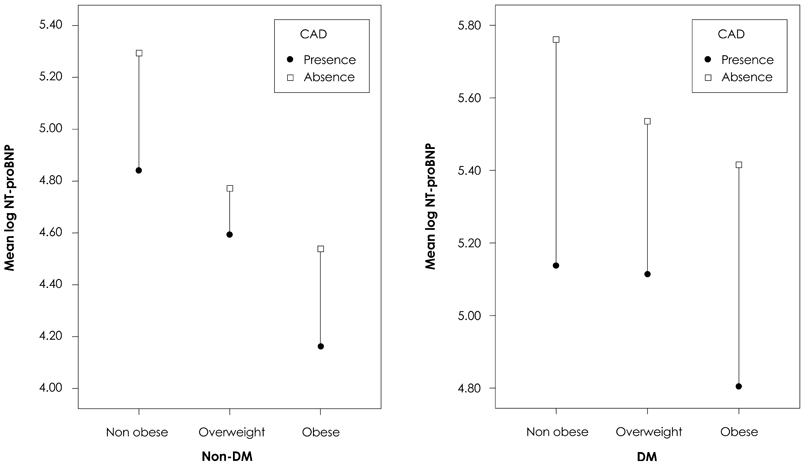
Several recent studies have shown that there is an inverse relationship between plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and body mass index (BMI) in subjects with and without heart failure. Obesity frequently coexists with diabetes, so it is important to consider the relationship between diabetes and natriuretic peptide levels. We evaluated the influence of diabetes on the correlation of BNP and BMI. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: We examined 933 patients with chest pain and/or dyspnea undergoing cardiac catheterization between Feb. 2006 and Nov. 2007 in the Maryknoll cardiac center who had creatinine levels <2.0 mg/dL and normal systolic heart function. BMI was checked, transthoracic echocardiography was performed, and aminoterminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) was sampled at the start of each case. RESULTS: In 733 non-diabetic patients, mean plasma NT-proBNP levels of non obese individuals (BMI <23 kg/m2), overweight individuals (23< or = BMI <25 kg/m2), and obese individuals (BMI > or =25 kg/m2) showed a significant negative correlation with increasing BMI (856.39+/-237.3 pg/mL, 601.69+/-159.6 pg/mL, 289.62+/-164.9 pg/mL, respectively, p<0.0001). However, in 200 diabetic patients, the correlation between BMI and NT-proBNP was not significant (r=-0.21, p=0.19), and NT-proBNP did not correlate with mitral E/Ea in obese diabetic patients (r=0.14, p=0.56). NT-proBNP was significantly correlated with mitral E/Ea in the non-obese (r=0.24, p=0.008) and non diabetic (r=0.32, p=0.003) groups. Left ventricular (LV) mass index was significantly correlated with NT-proBNP in all BMI groups (r=0.61, p<0.001), and patients with concentric cardiac hypertrophy showed the highest NT-proBNP levels. CONCLUSION: The present study demonstrates that obese patients have reduced concentrations of NT-proBNP compared to non obese patients despite having higher LV filling pressures. However, NT-proBNP is not suppressed in obese patients with diabetes. This suggests that factors other than cardiac status affect NT-proBNP concentrations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Maisel AS, Krishnaswami P, Nowak RM, et al. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:161–167.2. Maeda K, Tsutamoto T, Wada A, et al. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide as a biochemical marker of high left ventricular end diastolic pressure in patients with symptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. Am Heart J. 1998. 135:825–832.3. Friedl W, Mair J, Thomas S, Pichler M, Puschendorf B. Natriuretic peptides and cyclic guanosine 3', 5'-monophosphate in asymptomatic and symptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. Heart. 1996. 76:129–136.4. Maisel AS, Clopton P, Krishnaswamy P, et al. Impact of age, race, and sex on the ability of B-type natriuretic peptide to aid in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure: results from the Breathing Not Properly (BNP) multinational study. Am Heart J. 2004. 147:1078–1084.5. Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, et al. Impact of obesity on plasma natriuretic peptide levels. Circulation. 2004. 109:594–600.6. Tang WH, Girod JP, Lee MJ, et al. Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide levels in ambulatory patients with established chronic symptomatic systolic heart failure. Circulation. 2003. 108:2964–2966.7. Krauss RM, Winston M, Fletcher BJ, Grundy SM. Obesity: impact on cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 1998. 98:1472–1476.8. de Divitiis O, Fazio S, Petitto M, Maddalena G, Contaldo F, Mancini M. Obesity and cardiac function. Circulation. 1981. 64:477–482.9. Alpert MA, Lambert CR, Terry BE, et al. Influence of left ventricular mass on left ventricular diastolic filling in normotensive morbid obesity. Am Heart J. 1995. 130:1068–1073.10. Rivera M, Cortés R, Salvador A, et al. Obese subjects with heart failure have lower N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide plasma levels irrespective of etiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2005. 7:1168–1170.11. Taylor JA, Christenson RH, Rao K, Jorge M, Gottlieb SS. B-type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide are depressed in obesity despite higher left ventricular end diastolic pressures. Am Heart J. 2006. 152:1071–1076.12. Ganau A, Devereux RB, Roman MJ, et al. Patterns of left ventricular hypertrophy and geometric remodeling in essential hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992. 19:1550–1558.13. Tei C, Nishimura RA, Seward JB, Tajik AJ. Noninvasive Doppler-derived myocardial performance index: correlation with simultaneous measurements of cardiac catheterization measurements. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1997. 10:169–178.14. Hall C. Essential biochemistry and physiology of (NT-pro) BNP. Eur J Heart Fail. 2004. 6:257–260.15. Maeda K, Tsutamoto T, Wada A, Hisanaga T, Kinoshita M. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide as a biochemical marker of high left ventricular end-diastolic pressure in patients with symptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. Am Heart J. 1998. 135:825–832.16. Kang DH, Kim MJ, Kang SJ, et al. Role of B-type natriuretic peptide in diagnosis and follow-up of diastolic heart failure. Korean Circ J. 2006. 36:359–365.17. Kim SH, Kim JS, Baek KK, et al. Role of NT-proPNP in evaluation of functional status in congestive heart failure. Korean Circ J. 2004. 34:894–899.18. Dao Q, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, et al. Utility of B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure in an urgentcare setting. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001. 37:379–385.19. Choi JY. The role of Brain natriuretic peptide in the patients with acute dyspnea in the emergency department. Korean Circ J. 2007. 37:464–469.20. McCord J, Mundy BJ, Hudson MP, et al. Relationship between obesity and B-type natriuretic peptide levels. Arch Intern Med. 2004. 164:2247–2252.21. Horwich TB, Fonarow GC, Hamilton MA, MacLellan WR, Woo MA, Tillisch JH. The relationship between obesity and mortality in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001. 38:789–795.22. Levine B, Kalman J, Mayer L, Fillit HM, Packer M. Elevated circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1990. 323:236–241.23. Sarzani R, Dessi-Fulgheri P, Paci VM, Espinosa E, Rappelli A. Expression of natriuretic peptide receptors in human adipose and other tissues. J Endocrinol Invest. 1996. 19:581–585.24. Ommen SR, Nishimura RA, Appleton CP, et al. Clinical utility of Doppler echocardiography and tissue Doppler imaging in the estimation of left ventricular filling pressures: a comparative simultaneous Doppler-catheterisation study. Circulation. 2000. 102:1788–1794.25. Sengenes C. Increased lipolysis in adipose tissue and lipid mobilization to natriuretic peptides during low-calorie diet in obes women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002. 26:24–32.26. Kalra PR, Tigas S. Regulation of lipolysis: natriuretic peptides and the development of cachexia. Int J Cardiol. 2002. 85:125–132.27. Bhalla MA, Chiang A, Epshteyn VA, et al. Prognostic role of B-type natriuretic peptide levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. 44:1047–1052.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation of N-Terminal Pro-Brain Type Natriuretic Peptide Level and Echocardiographic Parameters
- Bradyarrhythmia Can Increase the Plasma Level of N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide
- Relationship between Serum N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Level and Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Extracellular Water in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients
- Changes in N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in a neonate with symptomatic isolated left ventricular noncompaction
- Biomarkers in Heart Failure: Focus on B-type Natriuretic Peptide