Korean Circ J.
2014 Mar;44(2):122-124. 10.4070/kcj.2014.44.2.122.
A Case of Sudden Cardiac Death due to Pilsicainide-Induced Torsades de Pointes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Osaka Rosai Hospital, Osaka, Japan. mnishino@orh.go.jp
- KMID: 2223902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2014.44.2.122
Abstract
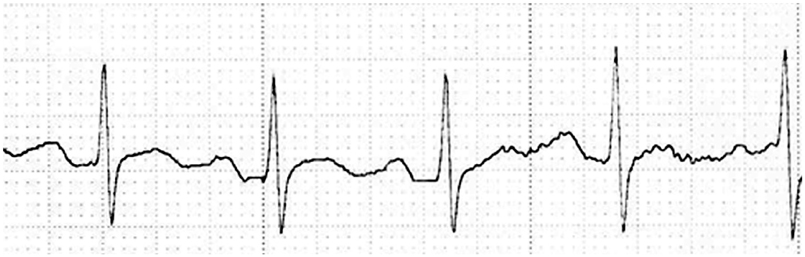
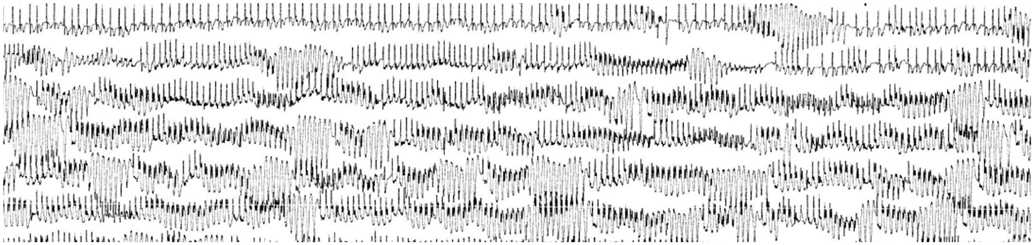
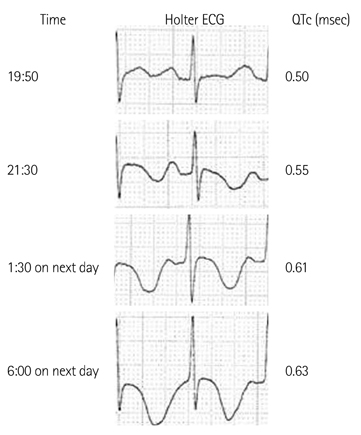
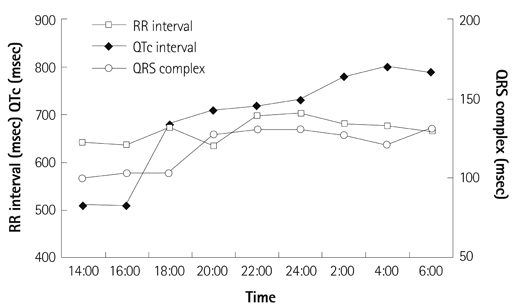
- An 84-year-old male received oral pilsicainide, a pure sodium channel blocker with slow recovery kinetics, to convert his paroxysmal atrial fibrillation to a sinus rhythm; the patient developed sudden cardiac death two days later. The Holter electrocardiogram, which was worn by chance, revealed torsade de pointes with gradually prolonged QT intervals. This drug is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and most of it is excreted from the kidney. Although the patient's renal function was not highly impaired and the dose of pilsicainide was low, the plasma concentration of pilsicainide may have been high, which can produce torsades de pointes in the octogenarian. Although the oral administration of class IC drugs, including pilsicainide, is effective to terminate atrial fibrillation, careful consideration must be taken before giving these drugs to octogenarians.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alboni P, Botto GL, Baldi N, et al. Outpatient treatment of recent-onset atrial fibrillation with the "pill-in-the-pocket" approach. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:2384–2391.2. Atarashi H, Inoue H, Hiejima K, Hayakawa H. The PSTAF Investigators. Conversion of recent-onset Atrial Fibrillation by a single oral dose of Pilsicainide (Pilsicainide Suppression Trial on atrial fibrillation). Am J Cardiol. 1996; 78:694–697.3. Kaneko Y, Nakajima T, Kato T, Kurabayashi M. Pilsicainide-induced polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Intern Med. 2012; 51:443–444.4. The Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST) Investigators. Preliminary report: effect of encainide and flecainide on mortality in a randomized trial of arrhythmia suppression after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1989; 321:406–412.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Torsades de Pointes Induced by Cisapride
- Male Pseudohermaphroditism Presented with Sudden Cardiac Arrest
- A Case of Hydroxyzine Induced Torsades de Pointes
- Initiation of Torsades de pointes by head-up tilt test in congenital long QT syndrome patient
- Cardiac Arrest Related to Torsades de Pointes in a Patient Recovering from Diabetic Ketoacidosis