J Rheum Dis.
2011 Dec;18(4):306-310. 10.4078/jrd.2011.18.4.306.
A Case of Steroid and Methotrexate-Resistant Eosinophilic Fasciitis Treated with Adalimumab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. goldgu@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2223136
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2011.18.4.306
Abstract
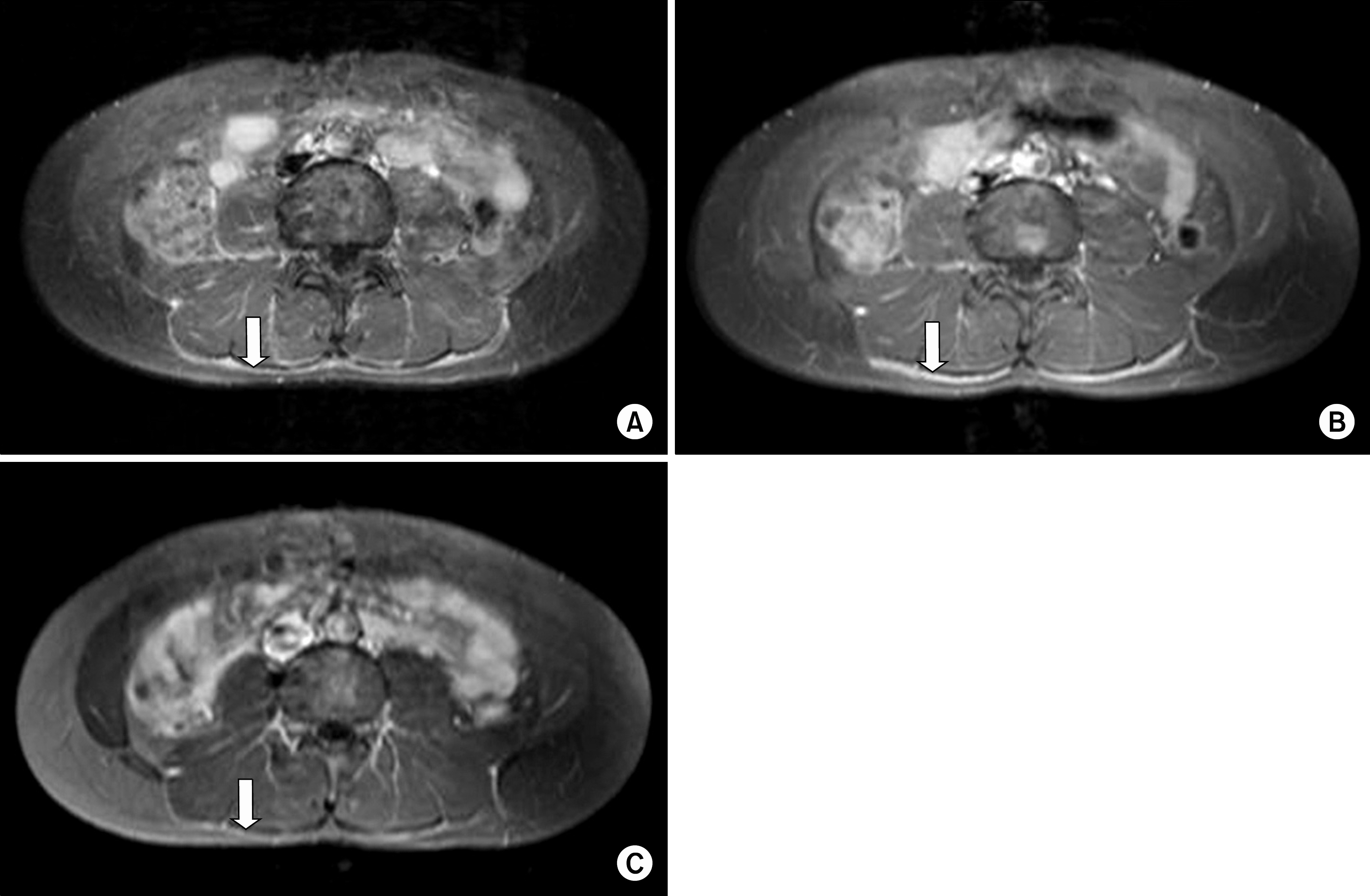
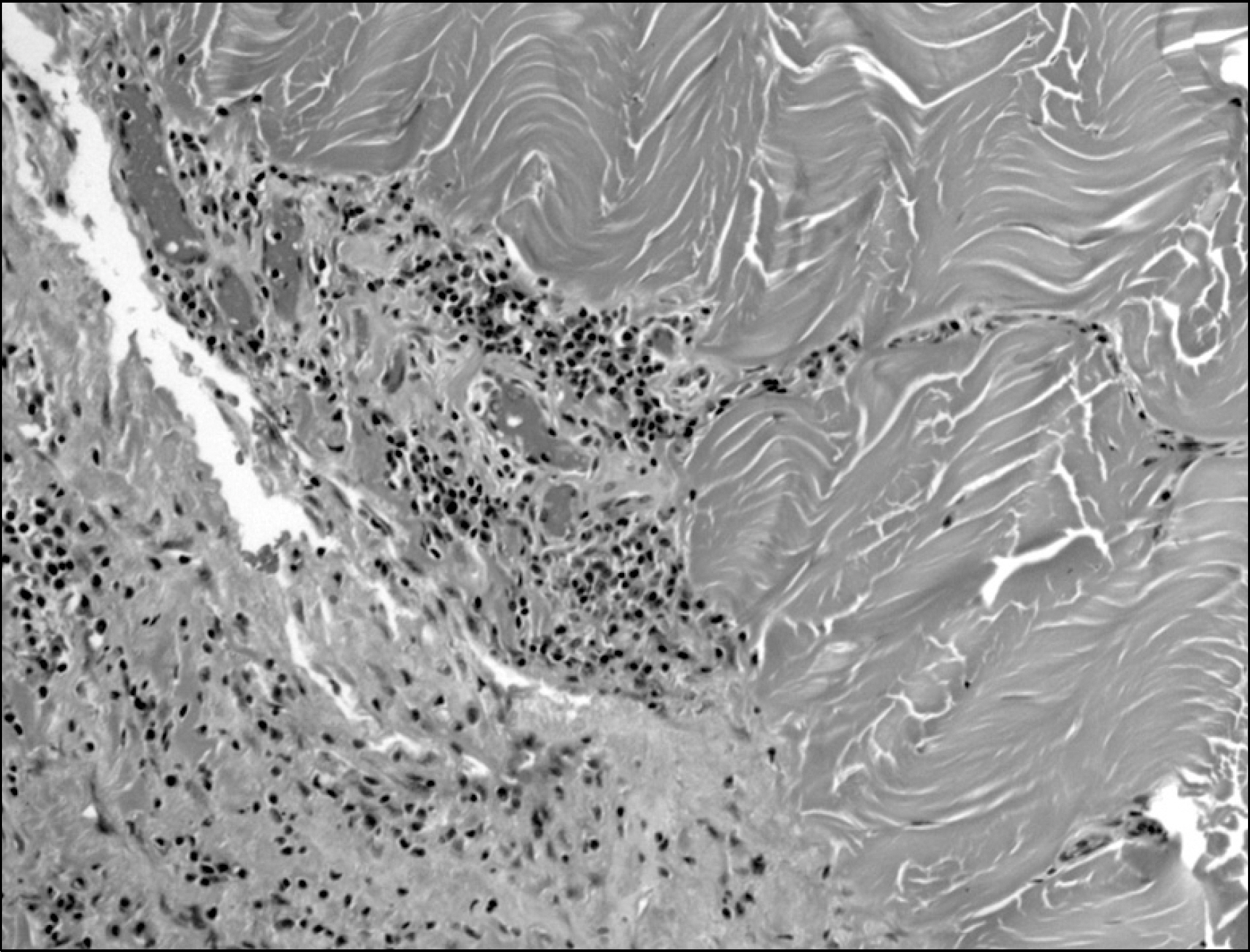
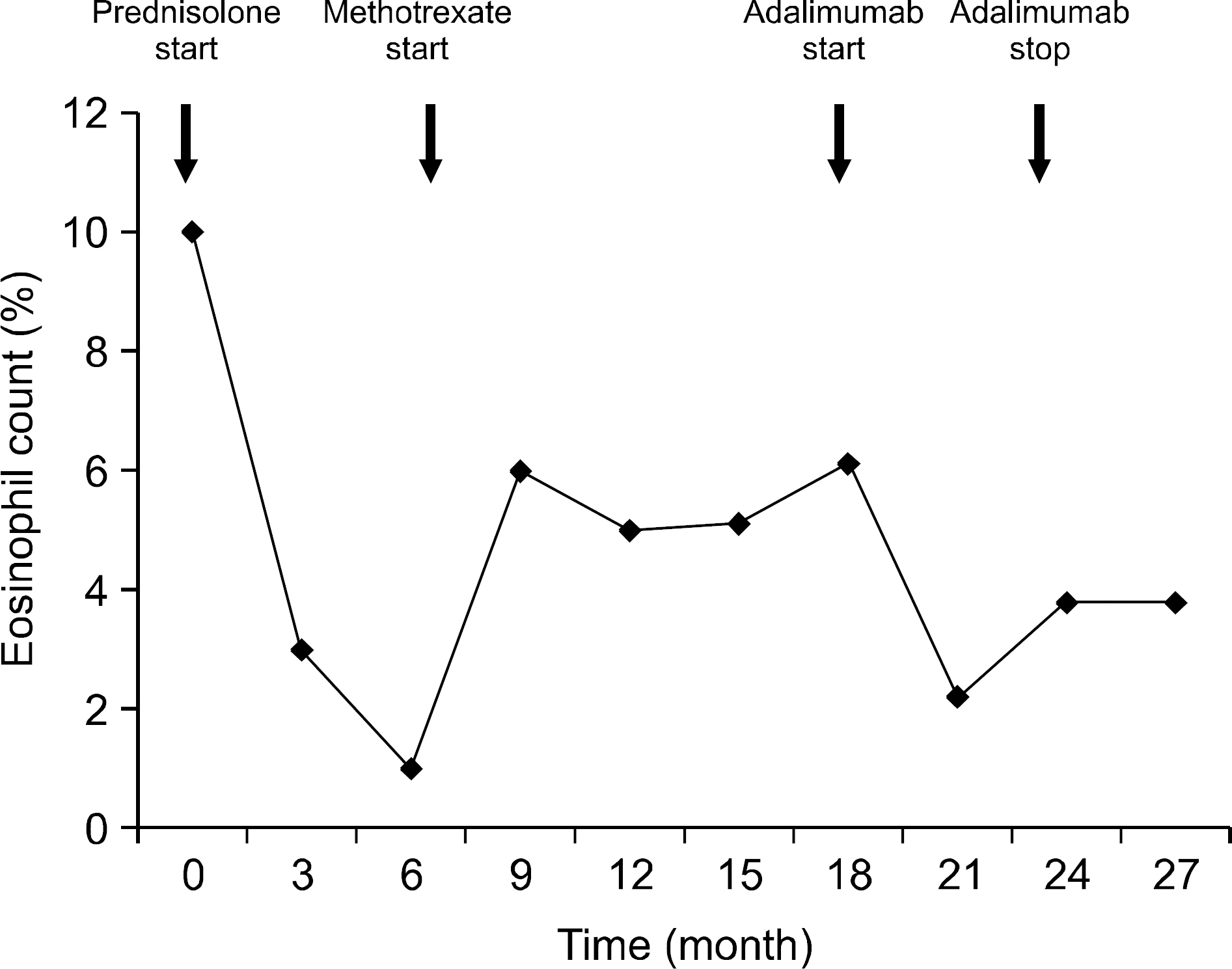
- Eosinophilic fasciitis (EF) is a rare fibrosing disorder characterized by painful swelling and induration of the limbs and trunk, characteristic histology with sclerosis and lymphocytic inflammation affecting the fascia. The cause and pathogenesis of EF are still unknown and current therapies include glucocorticoids with or without use of immunosuppressive agents. Recently, there have been several case reports documenting the efficacy of a TNF alpha inEosinophilic fasciitis (EF) is a rare fibrosing disorder characterized by painful swelling and induration of the limbs and trunk, characteristic histology with sclerosis and lymphocytic inflammation affecting the fascia. The cause and pathogenesis of EF are still unknown and current therapies include glucocorticoids with or without use of immunosuppressive agents. Recently, there have been several case reports documenting the efficacy of a TNF alpha inhibitor in EF following a steroid-resistant disease course. However, there has been no report on the experience in treatment of EF with a TNF alpha inhibitor in Korea. Hence, we report a case of steroid and methotrexate-resistant EF which was successfully treated with adalimumab, along with a review of the relevant articles.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Shulman LE. Diffuse fasciitis with eosinophilia: a new syndrome? Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1975; 88:70–86.2. Lakhanpal S, Ginsburg WW, Michet CJ, Doyle JA, Moore SB. Eosinophilic fasciitis: clinical spectrum and therapeutic response in 52 cases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 17:221–31.
Article3. Helfman T, Falanga V. Eosinophilic fasciitis. Clin Dermatol. 1994; 12:449–55.
Article4. Baumann F, Brühlmann P, Andreisek G, Michel BA, Marincek B, Weishaupt D. MRI for diagnosis and monitoring of patients with eosinophilic fasciitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:169–74.
Article5. Barnes L, Rodnan GP, Medsger TA, Short D. Eosinophilic fasciitis. A pathologic study of twenty cases. Am J Pathol. 1979; 96:493–518.6. Pouplin S, Daragon A, Le Loët X. Treatment of eosinophilic fasciitis with methotrexate. J Rheumatol. 1998; 25:606–7.7. Bukiej A, Dropiński J, Dyduch G, Szczeklik A. Eosinophilic fasciitis successfully treated with cyclosporine. Clin Rheumatol. 2005; 24:634–6.
Article8. Whang YJ, Kim KM, Oh SJ, Jang KY, Lee SI, Yoo WH, et al. Diagnostic availability of ultrasonography and the effects of methotrexate therapy in patients with eosinophilic fasciitis: report of two cases. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2006; 13:56–63.9. Khanna D, Agrawal H, Clements PJ. Infliximab may be effective in the treatment of steroid-resistant eosinophilic fasciitis: report of three cases. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49:1184–8.
Article10. Liou CH, Huang GS, Taylor JA, Juan CJ, Gao HW, Chen CY. Eosinophilic fasciitis in a military recruit: MRI evaluation with clinical correlation. Skeletal Radiol. 2003; 32:52–7.
Article11. Barnes L, Rodnan GP, Medsger TA, Short D. Eosinophilic fasciitis. A pathologic study of twenty cases. Am J Pathol. 1979; 96:493–518.12. Bischoff L, Derk CT. Eosinophilic fasciitis: demographics, disease pattern and response to treatment: report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008; 47:29–35.
Article13. Tzaribachev N, Holzer U, Schedel J, Maier V, Klein R, Kuemmerle-Deschner J. Infliximab effective in ste-roid-dependent juvenile eosinophilic fasciitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47:930–2.
Article14. Lam GK, Hummers LK, Woods A, Wigley FM. Efficacy and safety of etanercept in the treatment of scleroderma- associated joint disease. J Rheumatol. 2007; 34:1636–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Eosinophilic Fasciitis and Musculoskeletal Complication in a Child : A case report
- Diagnostic Availability of Ultrasonography and the Effects of Methotrexate Therapy in Patients with Eosinophilic Fasciitis: Report of Two Cases
- Eosinophilic Fasciitis Associated with Overlying Intraepidermal Blister Formation: A Case Report
- A Case of Eosinophilic Fasciitis
- Successful Treatment of Refractory Cutaneous Polyarteritis Nodosa with Adalimumab