J Rheum Dis.
2018 Oct;25(4):302-305. 10.4078/jrd.2018.25.4.302.
Successful Treatment of Refractory Cutaneous Polyarteritis Nodosa with Adalimumab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. thalsdnrso@naver.com
- KMID: 2429715
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2018.25.4.302
Abstract
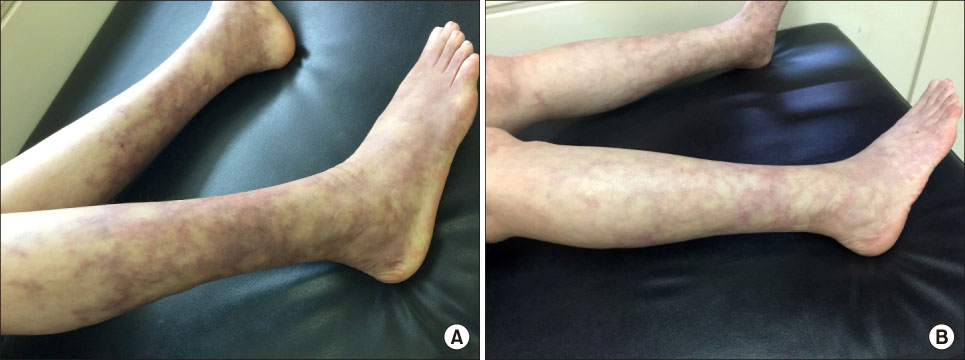
- Cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa (CPAN) is a form of necrotizing vasculitis of the medium and small-sized arteries. The condition is limited to the skin and there is a lack of visceral involvement. Treatment with systemic glucocorticoids alone or in combination with azathioprine, methotrexate or cyclophosphamide, depending on the disease severity, has been shown to be effective. This paper reports the clinical case of a 53-year-old female patient with CPAN refractory to treatment with high dose glucocorticoid, methotrexate, azathioprine, and cyclophosphamide, who was treated successfully with anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy (adalimumab).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. De Virgilio A, Greco A, Magliulo G, Gallo A, Ruoppolo G, Conte M, et al. Polyarteritis nodosa: A contemporary overview. Autoimmun Rev. 2016; 15:564–570.
Article2. Stanton M, Bhimji SS. Polyarteritis nodosa. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls;2018.3. Daoud MS, Hutton KP, Gibson LE. Cutaneous periarteritis nodosa: a clinicopathological study of 79 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1997; 136:706–713.
Article4. Nakamura T, Kanazawa N, Ikeda T, Yamamoto Y, Nakabayashi K, Ozaki S, et al. Cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa: revisiting its definition and diagnostic criteria. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009; 301:117–121.
Article5. Ishiguro N, Kawashima M. Cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa: a report of 16 cases with clinical and histopathological analysis and a review of the published work. J Dermatol. 2010; 37:85–93.
Article6. Morgan AJ, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa: a comprehensive review. Int J Dermatol. 2010; 49:750–756.
Article7. Vega Gutierrez J, Rodriguez Prieto MA, Garcia Ruiz JM. Successful treatment of childhood cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa with infliximab. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007; 21:570–571.
Article8. Zoshima T, Matsumura M, Suzuki Y, Kakuchi Y, Mizushima I, Fujii H, et al. A case of refractory cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa in a patient with hepatitis B carrier status successfully treated with tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade. Mod Rheumatol. 2013; 23:1029–1033.
Article9. Campanilho-Marques R, Ramos F, Canhão H, Fonseca JE. Remission induced by infliximab in a childhood polyarteritis nodosa refractory to conventional immunosuppression and rituximab. Joint Bone Spine. 2014; 81:277–278.
Article10. Valor L, Monteagudo I, de la Torre I, Fernández CG, Montoro M, Longo JL, et al. Young male patient diagnosed with cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa successfully treated with etanercept. Mod Rheumatol. 2014; 24:688–689.
Article11. Keystone EC. The utility of tumour necrosis factor blockade in orphan diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004; 63:Suppl 2. ii79–ii83.
Article12. Mackay F, Loetscher H, Stueber D, Gehr G, Lesslauer W. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced cell adhesion to human endothelial cells is under dominant control of one TNF receptor type, TNF-R55. J Exp Med. 1993; 177:1277–1286.
Article13. Aringer M, Smolen JS. SLE - Complex cytokine effects in a complex autoimmune disease: tumor necrosis factor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003; 5:172–177.14. Radford DJ, Lord JM, Savage CO. The activation of the neutrophil respiratory burst by anti-neutrophil cytoplasm autoantibody (ANCA) from patients with systemic vasculitis requires tyrosine kinases and protein kinase C activation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999; 118:171–179.
Article