J Rheum Dis.
2012 Feb;19(1):47-50. 10.4078/jrd.2012.19.1.47.
A Case of Secondary Gout Associated with Essential Thrombocythemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dankook University Medical College, Cheonan, Korea. avnrt@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2223120
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.1.47
Abstract
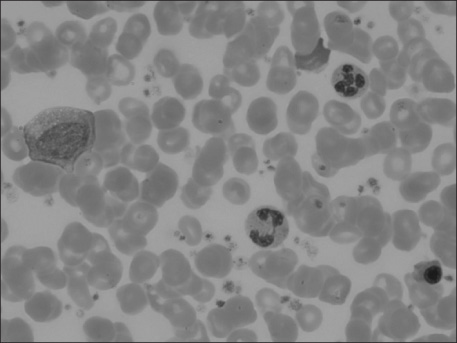
- Gouty arthritis is a metabolic disorder characterized by hyperuricemia, deposition of monosodium urate crystal in the joints, and recurrent episodes of acute inflammatory arthritis. Depending on the actual causes of hyperuricemia, gout is classified as primary or secondary gout. In myeloproliferative neoplasms, a turnover of nucleic acids is greatly augmented and therefore the blood concentration of uric acid may be markedly increased. But an acute attack of gout is extremely rare in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms. Essential thrombocythemia, one of the myeloproliferative neoplasms, is characterized by megakaryocytic hyperplasia in bone marrow and marked thrombocytosis. We report a case of secondary gout in a 66-year-old man with essential thrombocythemia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schlesinger N. Diagnosis of gout: clinical, laboratory, and radiologic findings. Am J Manag Care. 2005. 11:15 Suppl. S443–S450.2. Park MR, Im JY, Jung JS, Jung MJ, Kim TW, Hong YM, et al. A case of essential thrombocythemia in a patient with Behçet's disease. Korean J Med. 2010. 78:776–779.3. Agudelo CA, Wise CM. Gout: diagnosis, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001. 13:234–239.4. Gupta SJ. Crystal induced arthritis: an overview. J Indian Rheumatol Assoc. 2002. 10:5–13.5. Schlesinger N, Baker DG, Schumacher HR Jr. Serum urate during bouts of acute gouty arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1997. 24:2265–2266.6. Logan JA, Morrison E, McGill PE. Serum uric acid in acute gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997. 56:696–697.7. Yü TF. Secondary gout associated with myeloproliferative diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1965. 8:765–771.8. Pavithran K, Thomas M. Chronic myeloid leukemia presenting as gout. Clin Rheumatol. 2001. 20:288–289.9. Bang SM, Kim HY, Kim HJ, Kim HJ, Won JH, Kim BS, et al. Korean Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Working Party. Diagnostic and therapeutic guideline for myeloproliferative neoplasm. J Korean Med Assoc. 2011. 54:112–126.10. Tefferi A. JAK2 mutations in polycythemia vera: molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. N Engl J Med. 2007. 356:444–445.11. Kvasnicka HM, Thiele J. The impact of clinicopathological studies on staging and survival in essential thrombocythemia, chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, and polycythemia rubra vera. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006. 32:362–371.12. Thiele J, Kvasnicka HM. Chronic myeloproliferative disorders with thrombocythemia: a comparative study of two classification systems (PVSG, WHO) on 839 patients. Ann Hematol. 2003. 82:148–152.13. Thiele J, Kvasnicka HM. Clinicopathological criteria for differential diagnosis of thrombocythemias in various myeloproliferative disorders. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006. 32:219–230.14. Brousseau M, Parot-Schinkel E, Moles M-P, Boyer F, Hunault M, Rousselet M-C. Practical application and clinical impact of the WHO histopathological criteria on bone marrow biopsy for the diagnosis of essential thrombocythemia versus prefibrotic primary myelofibrosis. Histopathology. 2010. 56:758–767.