J Rheum Dis.
2015 Dec;22(6):387-390. 10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.387.
Cavitary Lung Lesion in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Unusual Manifestation of Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. mdjin922@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2222814
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.387
Abstract
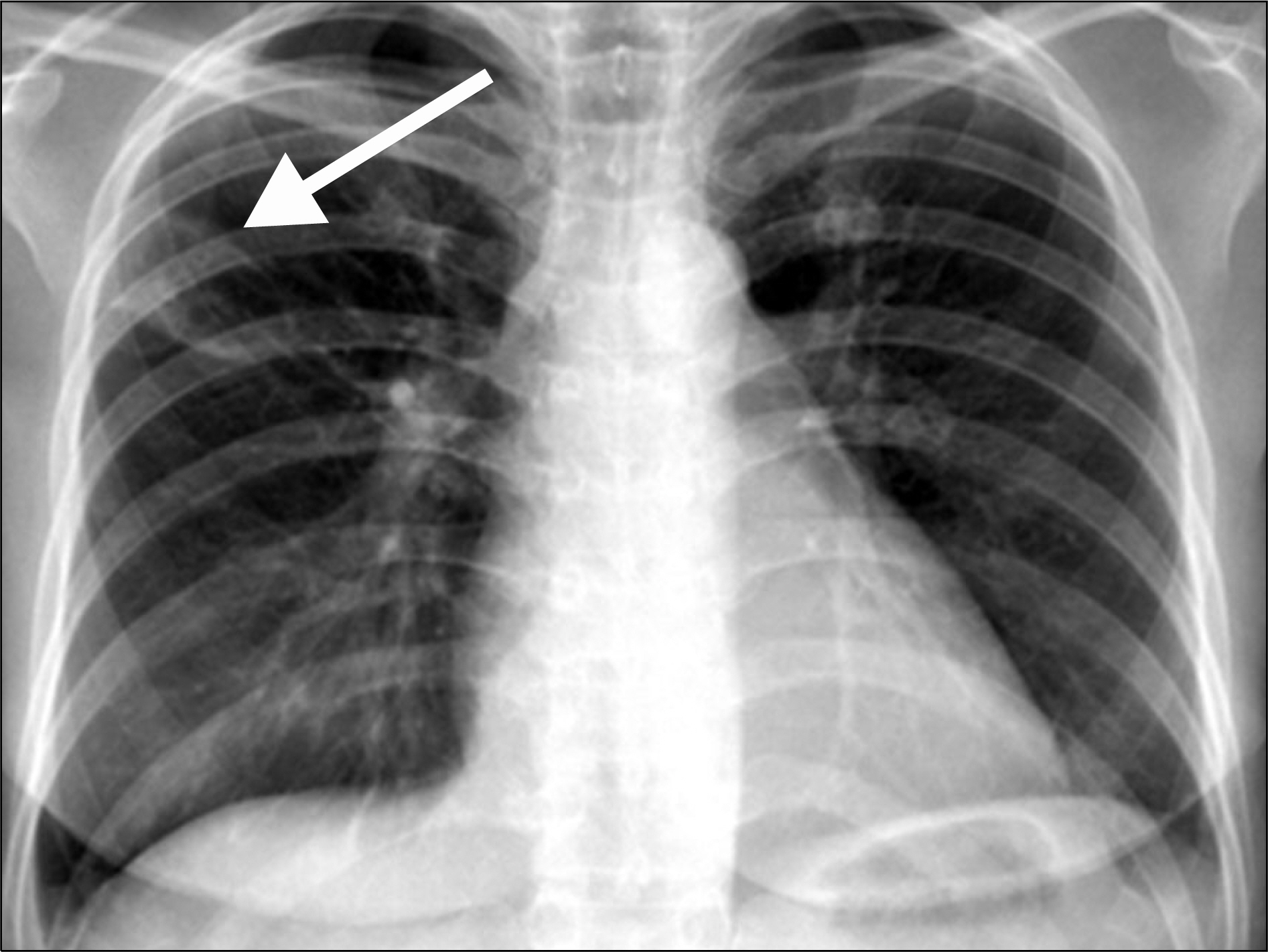
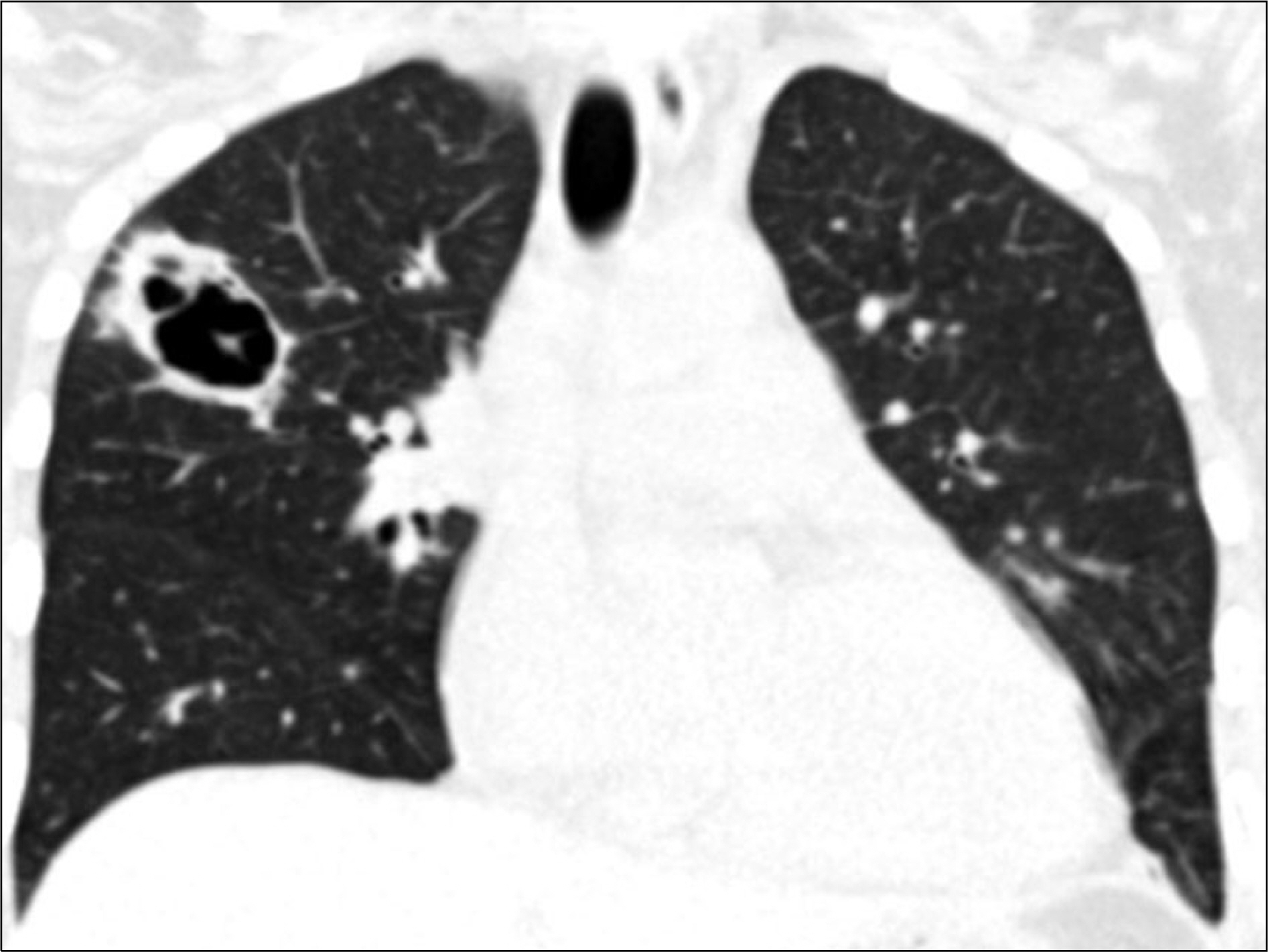
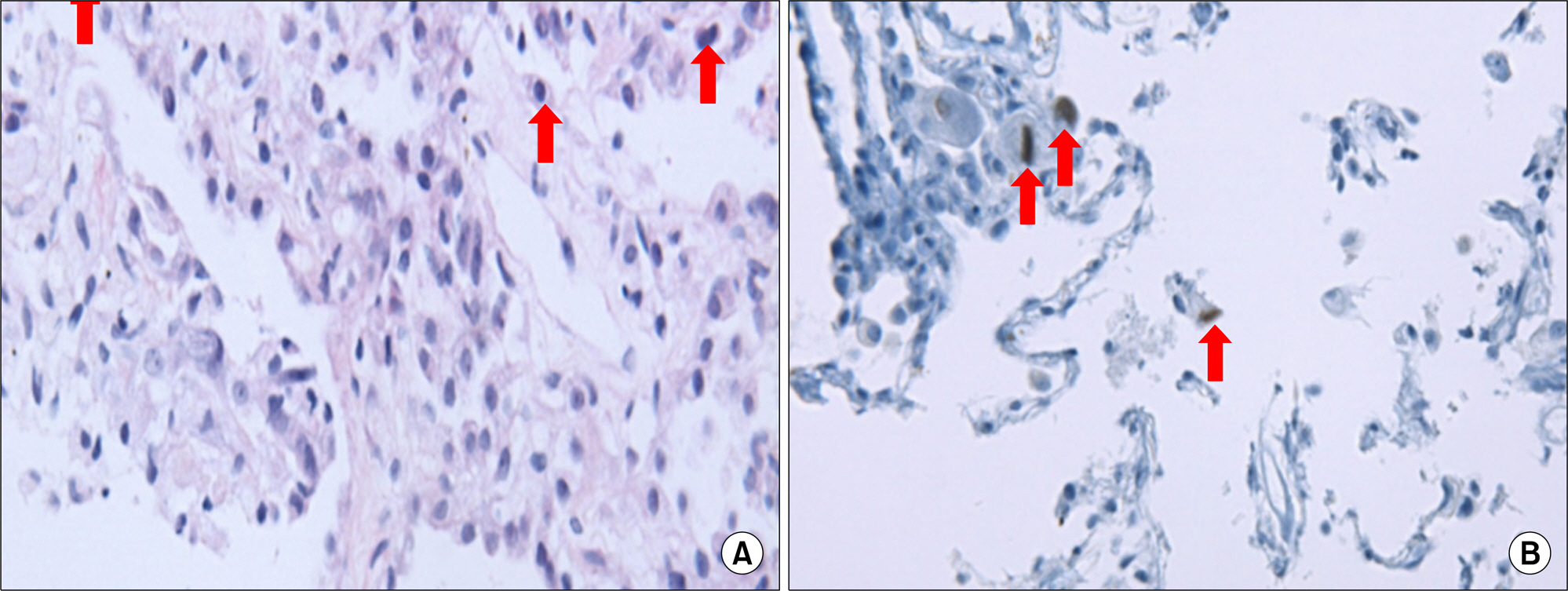
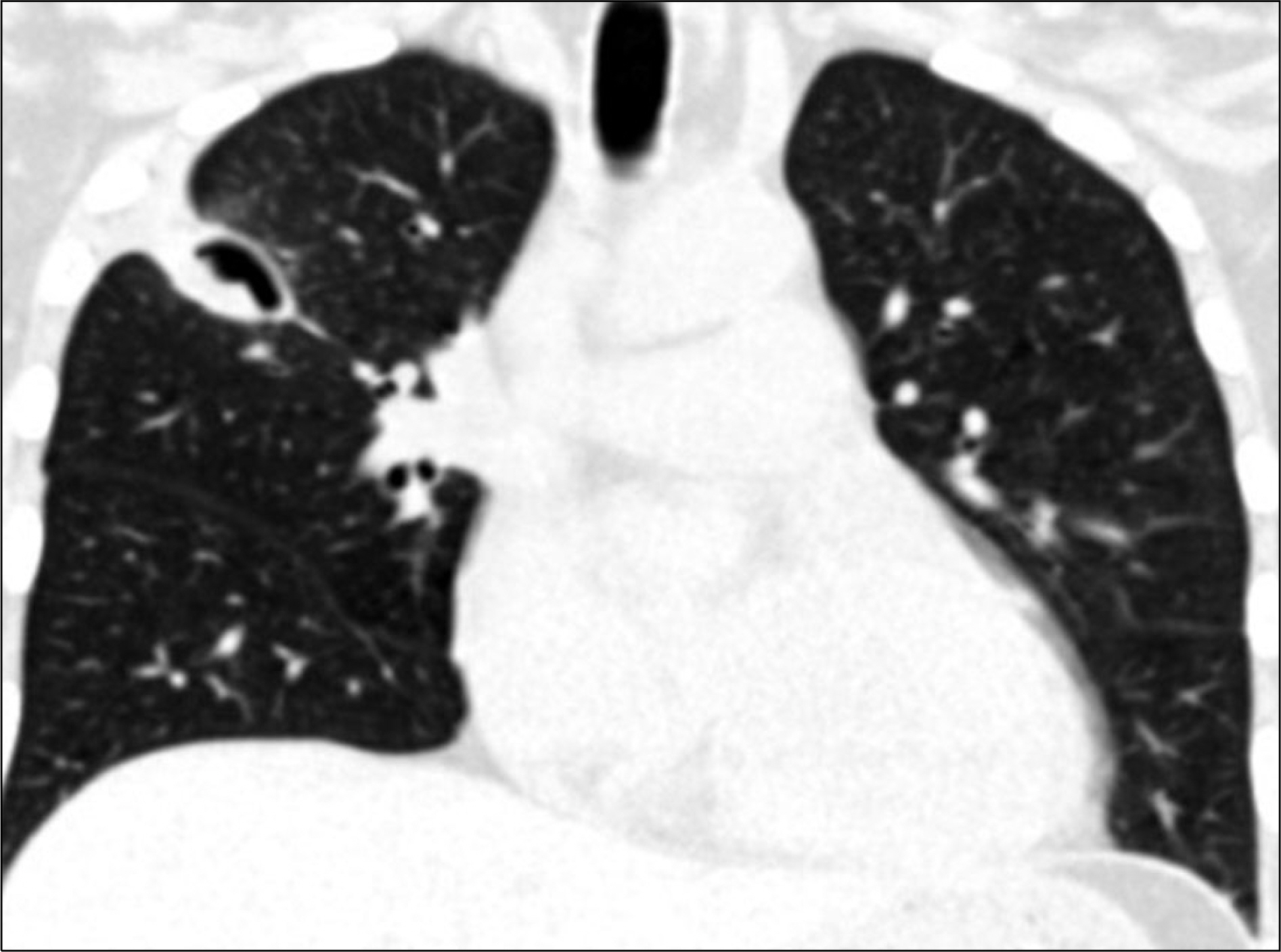
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV), a member of the human herpesvirus group, causes severe disease in immunocompromised patients. In particular, CMV pneumonia can be a life-threatening disease to patients taking immunosuppressive drugs. The radiographic manifestations of CMV are variable and may consist of reticular or reticulonodular patterns, ground-glass opacities, air-space consolidations, or mixed patterns. A cavitary lesion in pneumonia associated with CMV infection is extremely rare. Herein we report on a case of CMV pneumonia which presented with a cavitary lesion and was treated successfully in a systemic lupus erythematosus patient who was taking immunosuppressive drugs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Juárez M, Misischia R, Alarcón GS. Infections in systemic connective tissue diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2003; 29:163–84.
Article2. Leland DS, Emanuel D. Laboratory diagnosis of viral infections of the lung. Semin Respir Infect. 1995; 10:189–98.3. Kang EY, Patz EF Jr, Müller NL. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia in transplant patients: CT findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1996; 20:295–9.
Article4. Gadkowski LB, Stout JE. Cavitary pulmonary disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008; 21:305–33.
Article5. Najjar M, Siddiqui AK, Rossoff L, Cohen RI. Cavitary lung masses in SLE patients: an unusual manifestation of CMV infection. Eur Respir J. 2004; 24:182–4.
Article6. Karakelides H, Aubry MC, Ryu JH. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia mimicking lung cancer in an immunocompetent host. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003; 78:488–90.
Article7. Katagiri A, Ando T, Kon T, Yamada M, Iida N, Takasaki Y. Cavitary lung lesion in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: an unusual manifestation of cytomegalovirus pneumonitis. Mod Rheumatol. 2008; 18:285–9.
Article8. Azuma N, Hashimoto N, Yasumitsu A, Fukuoka K, Yokoya-ma K, Sawada H, et al. CMV infection presenting as a cavitary lung lesion in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Intern Med. 2009; 48:2145–9.
Article9. Lee DH, Kim JW, Shin DH, Oh MD, Song YW, Choi KW, et al. A case of cytomegalovirus pneumonitis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Korean J Med. 1999; 56:103–7.10. Han SH, Sohn YJ, Park MA, Lee S, Ryu SH, Lim TH, et al. A case of cytomegalovirus pneumonia and retinitis in a patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2003; 10:456–61.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Transverse Myelitis as a First Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A case of cytomegalovirus pneumonitis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus
- Two Cases of Pulmonary Problems as Initial Clinical Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Cardiac tamponade as an initial manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus--single case report
- A Case of Cytomegalovirus Infection Presenting as Pericarditis and Lupus Nephritis Flare-up