J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Jan;54(1):60-64. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.1.60.
The Effects of Conjunctival Shield on Pain Alleviation During Cataract Surgery in Conjunctivochalasis Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Ilsan, Korea. jhk0924@hanmail.net
- 2Chungju St. Mary Eye Center, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2216450
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.1.60
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the effect of conjunctival shield on pain alleviation during cataract surgery in conjunctivochalasis patients for conjunctiva drawn into speculum suction holes during cataract surgery.
METHODS
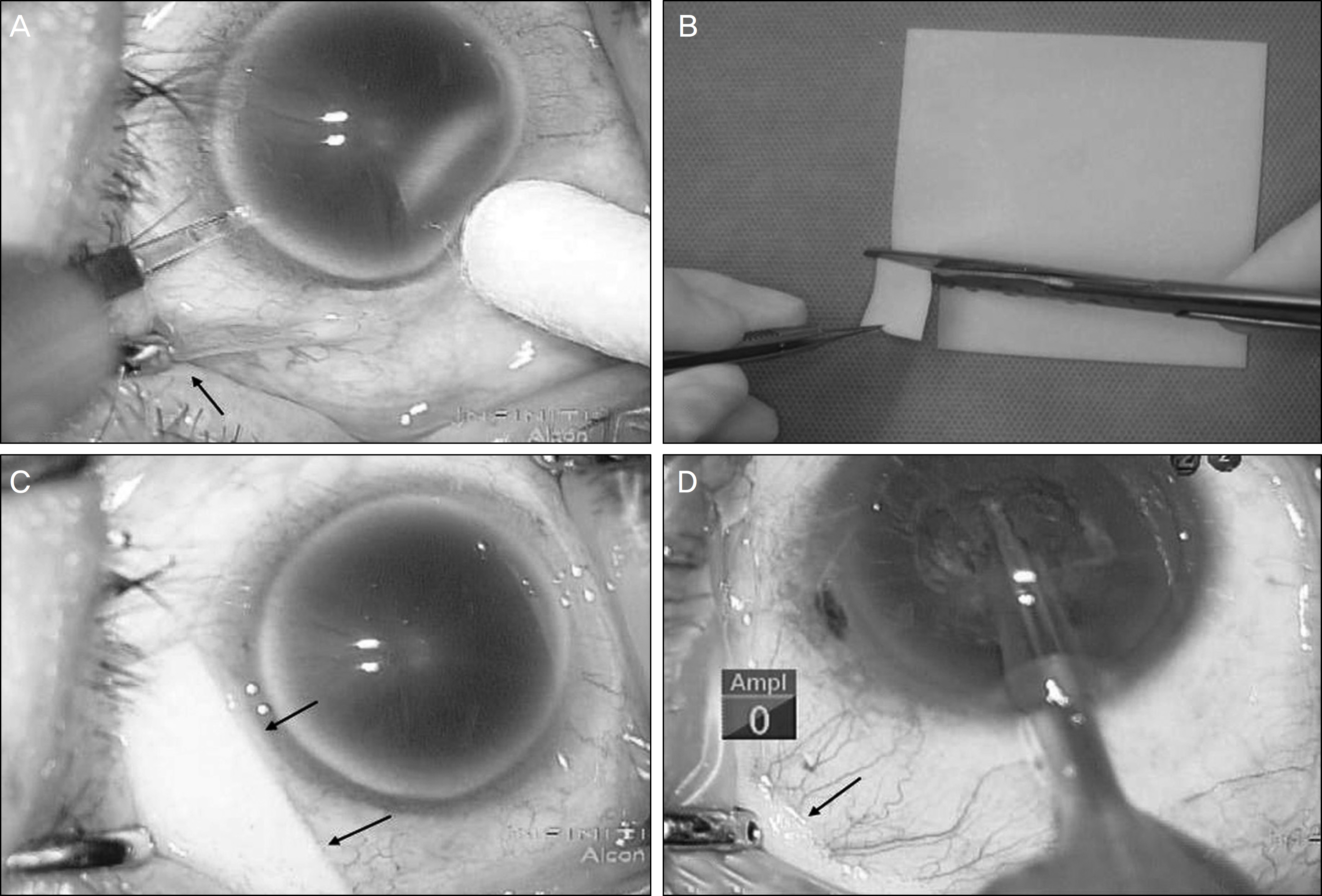
Forty patients with conjunctivochalasis undergoing cataract surgery using un aspirating speculum were evaluated in the present study. A thin piece of surgical wipe (conjunctival shield) was inserted between the lid and bulbar conjunctiva to shield the conjunctiva from the suction hole and thereby prevent it from being sucked into the hole. Additionally, patients were asked to rank pain following speculum placement both before and after conjunctiva shield insertion by visual analogue scale.
RESULTS
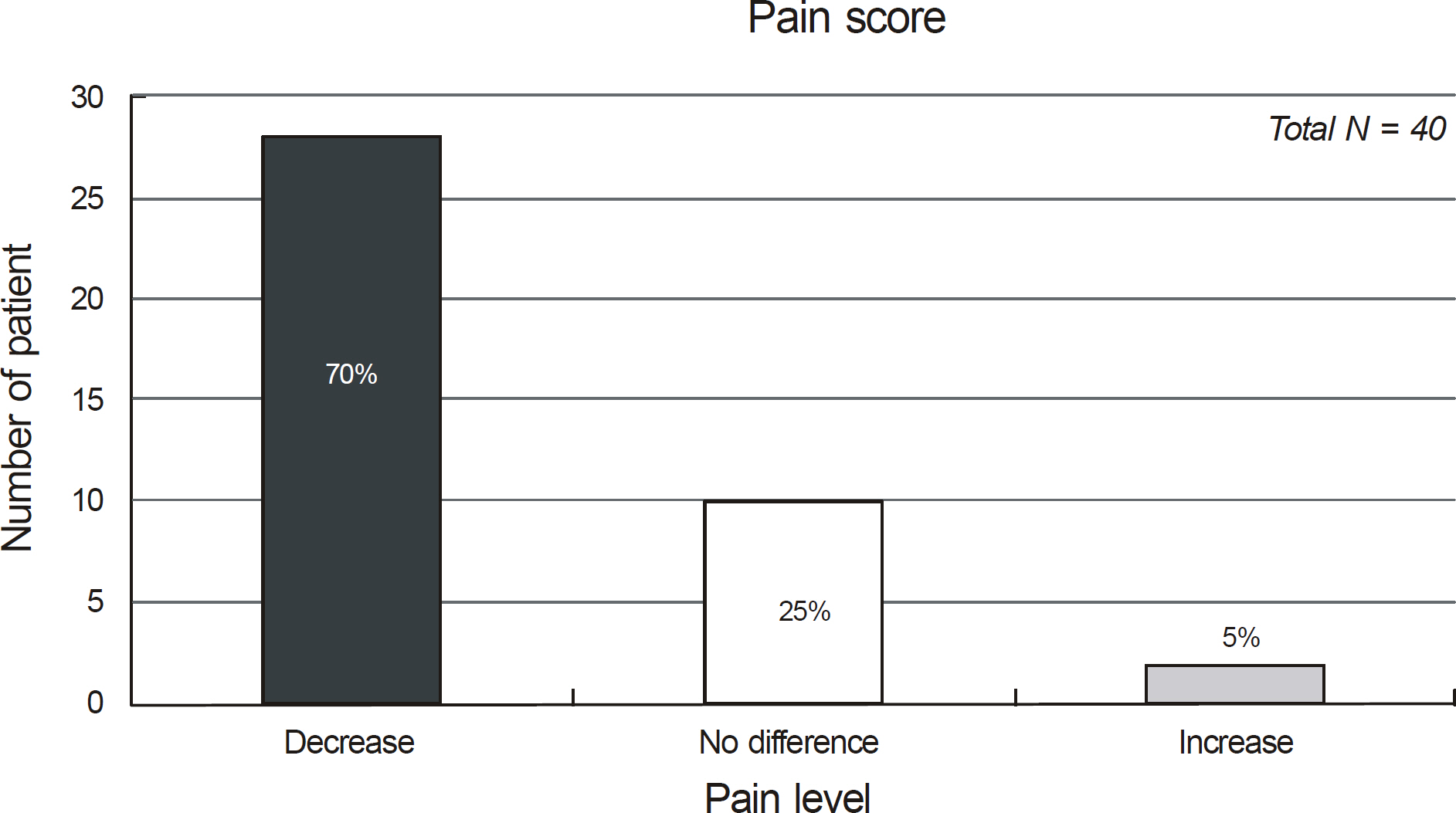
The pain scores were 2.50 +/- 0.78 points before conjunctival shield insertion, and 1.25 +/- 0.66 points after conjunctival shield insertion, which was a significant decrease (p = 0.01). In addition, the results showed a 70% reduction in pain following shield insertion.
CONCLUSIONS
Conjunctivochalasis causes pain during cataract surgery when using an aspirating speculum. The conjunctival shield insertion is a safe and simple method for pain-free cataract surgery in conjunctivochalasis patients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hughes WL. Conjunctivochalasis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1942; 25:48–51.
Article2. Liu D. Conjunctivochalasis. A cause of tearing and its management. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986; 2:25–8.3. Douvas NG. Aspirating fine wire speculum. Arch Ophthalmol. 1968; 80:643–4.
Article4. Fodor E, Barabino S, Montaldo E, et al. Quantitative evaluation of ocular surface inflammation in patients with different grade of conjunctivochalasis. Curr Eye Res. 2010; 35:665–9.
Article5. Bardocci A, Ciucci F, Lofoco G, et al. Pain during second eye cataract surgery under topical anesthesia: an intraindividual study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011; 249:1511–4.
Article6. Tseng SH, Chen FK. A randomized clinical trial of combined abdominal-intracameral anesthesia in cataract surgery. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:2007–11.7. Erdurmus M, Aydin B, Usta B, et al. Patient comfort and surgeon satisfaction during cataract surgery using topical anesthesia with or without dexmedetomidine sedation. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2008; 18:361–7.
Article8. Meller D, Tseng SC. Conjunctivochalasis: literature review and possible pathophysiology. Surv Ophthalmol. 1998; 43:225–32.9. Lim HJ, Lee JK, Park DJ. Conjunctivochalasis surgery: amniotic membrane transplantation with fibrin glue. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:195–204.
Article10. Otaka I, Kyu N. A new surgical technique for management of conjunctivochalasis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 129:385–7.
Article11. Di Pascuale MA, Espana EM, Kawakita T, Tseng SC. Clinical characteristics of conjunctivochalasis with or without aqueous tear deficiency. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:388–92.
Article12. Kim YS, Jang JW, Byun YJ. Comparison of ocular pain during abdominal surgery using a scleral pocket incision under pinpoint versus intracameral anesthesia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2152–9.13. Kim MS, Cho KS, Woo H, Kim JH. Effects of hand massage on anxiety in cataract surgery using local anesthesia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:884–90.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Epiphora in Patients with Conjunctivochalasis Using Conjunctival Fixation to the Sclera
- Comparison of Ocular Pain during Cataract Surgery Using a Scleral Pocket Incision under Pinpoint versus Intracameral Anesthesia
- Comparison of Miniflap and Rotational Conjunctival Flap Techniques of Pterygium Accompanied by Conjunctivochalasis
- The Efficacy of Fibrin Glue in Surgical Treatment of Conjunctivochalasis With Epiphora
- Histopathologic Characteristics of Conjunctivochalasis