J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Feb;56(2):228-233. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.2.228.
Accuracy and Reliability of the Icare PRO in Enucleated Porcine Eyes - Upright and Horizontal Positions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. demian7435@gmail.com
- KMID: 2216006
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.2.228
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the accuracy and reliability of intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements in enucleated porcine eyes using the Icare PRO in the upright and horizontal positions.
METHODS
We designed an enucleated porcine eye model whose anterior chamber was cannulated with a 30-gauge needle, connected in parallel to a pneumatic pressure device. The reference pressure was manipulated by changing the air pressure from 70 to 10 mm Hg at 10 mm Hg intervals, and the IOP of porcine eyes was measured with the Icare PRO at each pressure. Correlation analysis, comparison using the Bland-Altman plot and Wilcoxon signed rank test, was performed to assess the accuracy of IOP measurements. Intraclass correlation coefficients were calculated to assess the intra-observer variability in the upright and horizontal positions, respectively.
RESULTS
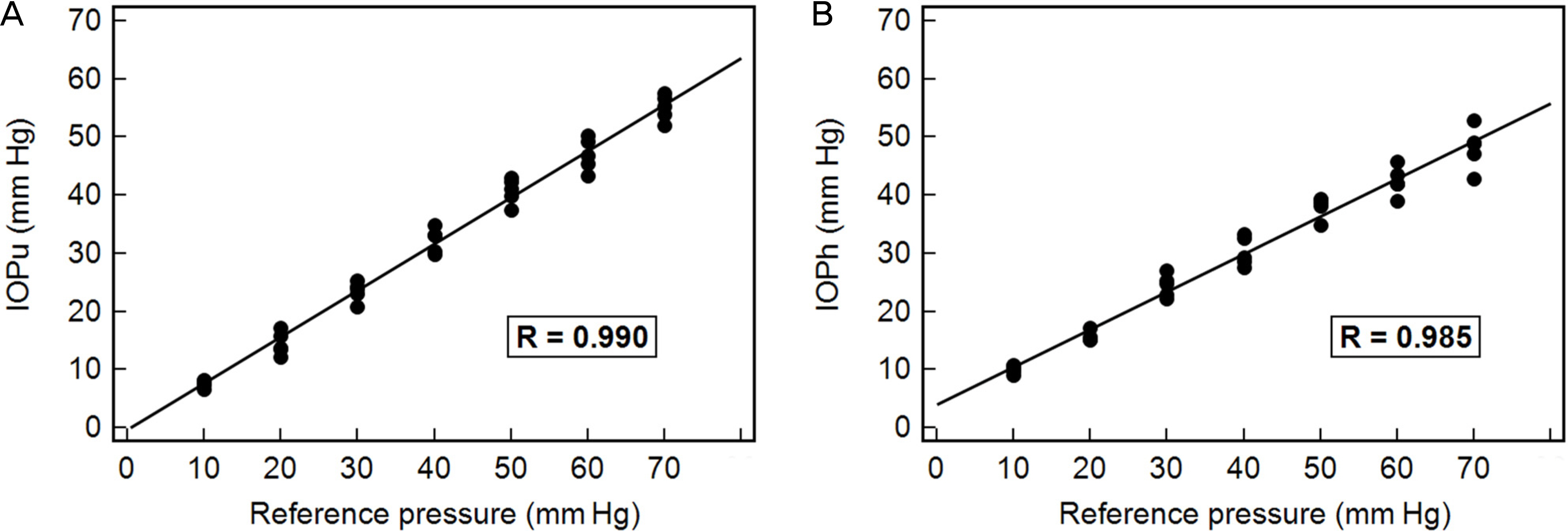
The IOP value in both upright and horizontal positions was well correlated with the reference pressure (r = 0.992 and 0.985, respectively). The Bland-Altman plot showed good agreement between the two positions. However, all IOP values in both positions were lower than the reference pressures. The IOP values in the horizontal position were significantly lower than those in the upright position at the a reference pressure of 50 mm Hg or greater. Values of intraclass correlation coefficient ranged from 0.911 to 0.984 when measured in the upright position and from 0.707 to 0.914 in the horizontal position.
CONCLUSIONS
IOP measurements of Icare PRO in porcine eyes were remarkably lower than reference pressures controlled by the pneumatic method even though they showed a good correlation with reference values. The higher was the reference pressure, the greater was the degree of underestimation of IOP measurement in both positions. This trend was more pronounced in the horizontal position, and the reliability of IOP measurements was also lower than that in the upright position.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kass MA, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ. . The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002; 120:701–13. discussion 829-30.2. Landers J, Goldberg I, Graham SL. Analysis of risk factors that may be associated with progression from ocular hypertension to primary open angle glaucoma. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2002; 30:242–7.
Article3. Davies LN, Bartlett H, Mallen EA, Wolffsohn JS. Clinical evaluation of rebound tonometer. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2006; 84:206–9.
Article4. Kontiola AI. A new induction-based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2000; 78:142–5.
Article5. Muttuvelu DV, Baggesen K, Ehlers N. Precision and accuracy of the ICare tonometer - Peripheral and central IOP measurements by rebound tonometry. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012; 90:322–6.
Article6. Brusini P, Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M. . Comparison of ICare tonometer with Goldmann applanation tonometer in glaucoma patients. J Glaucoma. 2006; 15:213–7.
Article7. Fernandes P, Díaz-Rey JA, Queirós A. . Comparison of the ICare rebound tonometer with the Goldmann tonometer in a normal population. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2005; 25:436–40.8. López-Caballero C, Contreras I, Muñoz-Negrete FJ. . [Rebound tonometry in a clinical setting. Comparison with applanation ton-ometry]. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2007; 82:273–8.9. Nakamura M, Darhad U, Tatsumi Y. . Agreement of rebound tonometer in measuring intraocular pressure with three types of applanation tonometers. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:332–4.
Article10. Jablonski KS, Rosentreter A, Gaki S. . Clinical use of a new po-sition-independent rebound tonometer. J Glaucoma. 2013; 22:763–7.
Article11. Chiquet C, Custaud MA, Le Traon AP. . Changes in intraocular pressure during prolonged (7-day) headdown tilt bedrest. J Glaucoma. 2003; 12:204–8.
Article12. Prata TS, De Moraes CG, Kanadani FN. . Posture-induced in-traocular pressure changes: considerations regarding body position in glaucoma patients. Surv Ophthalmol. 2010; 55:445–53.
Article13. Tsukahara S, Sasaki T. Postural change of IOP in normal persons and in patients with primary wide open-angle glaucoma and low-tension glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984; 68:389–92.
Article14. Feke GT, Pasquale LR. Retinal blood flow response to posture change in glaucoma patients compared with healthy subjects. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115:246–52.
Article15. Munkwitz S, Elkarmouty A, Hoffmann EM. . Comparison of the iCare rebound tonometer and the Goldmann applanation ton-ometer over a wide IOP range. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008; 246:875–9.
Article16. Lee EJ, Park KH, Kim DM. . Assessing intraocular pressure by rebound tonometer in rats with an air-filled anterior chamber. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2008; 52:500–3.
Article17. Löbler M, Rehmer A, Guthoff R. . Suitability and calibration of a rebound tonometer to measure IOP in rabbit and pig eyes. Vet Ophthalmol. 2011; 14:66–8.
Article18. Wang X, Dong J, Wu Q. Twenty-four-hour measurement of IOP in rabbits using rebound tonometer. Vet Ophthalmol. 2013; 16:423–8.
Article19. Chihara E. Assessment of true intraocular pressure: the gap between theory and practical data. Surv Ophthalmol. 2008; 53:203–18.
Article20. Hallberg P, Santala K, Lindén C. . Comparison of Goldmann applanation and applanation resonance tonometry in a biomicro-scope-based in vitro porcine eye model. J Med Eng Technol. 2006; 30:345–52.21. Reuter A, Müller K, Arndt G, Eule JC. Accuracy and reproduci-bility of the TonoVet rebound tonometer in birds of prey. Vet Ophthalmol. 2010; 13(Suppl):80–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reliability Comparison of Rebound Tonometer at the Upright and Supine Position
- Comparison of Portable Tonometers and Goldmann Applanation Tonometer for Intraocular Pressure Measurement
- Postural Intraocular Pressure Change at Trendelenberg Position Measured by Rebound Tonometer
- Comparison of Intraocular Pressures According to Position Using Icare Rebound Tonometer
- Change in Intraocular Pressure of Normal Healthy Eyes During Sit-up With Various Postures