J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Jul;55(7):1049-1055.
Comparison of Intraocular Pressures According to Position Using Icare Rebound Tonometer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. harry92001@naver.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate changes in intraocular pressure (IOP) according to position using a portable rebound tonometer.
METHODS
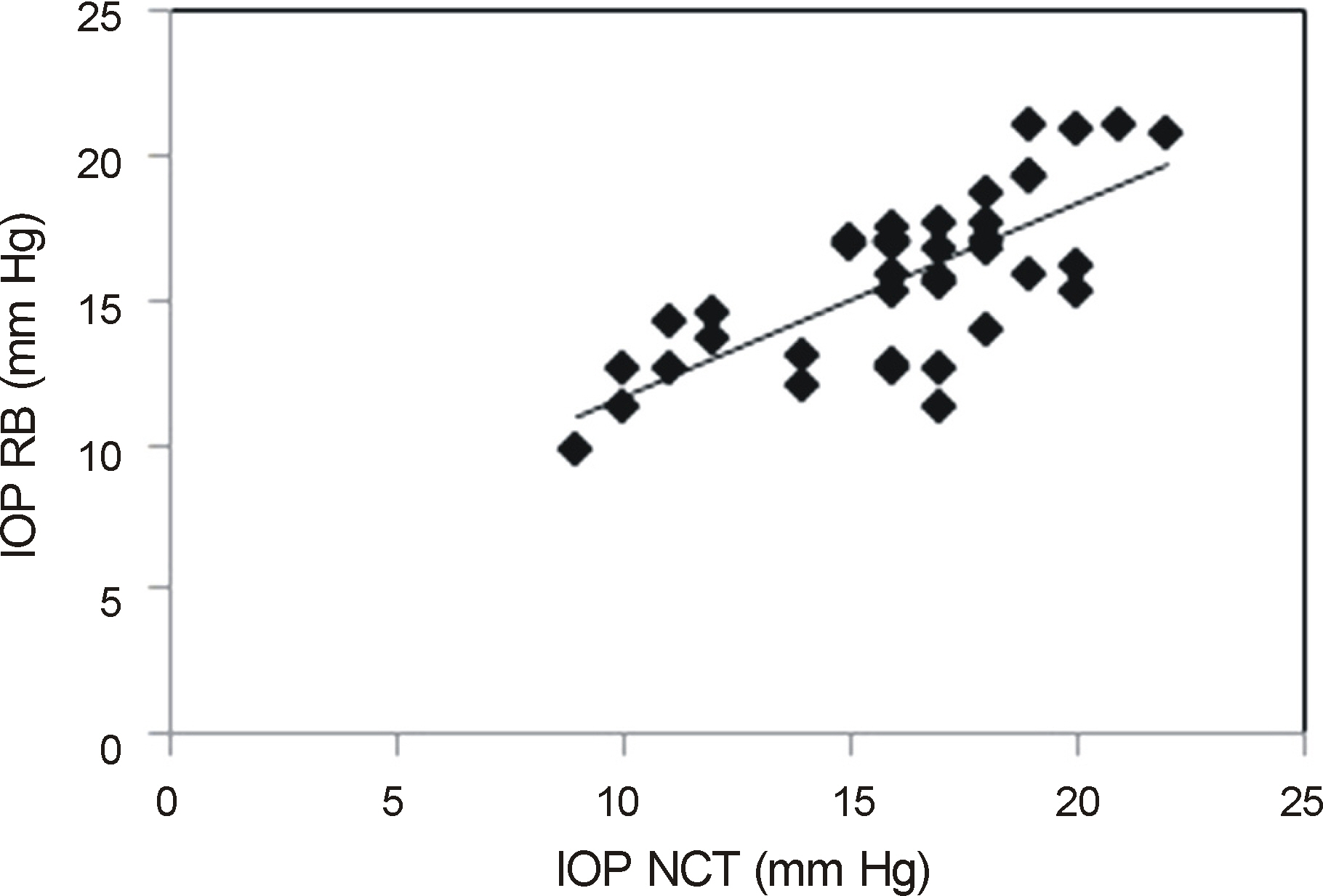
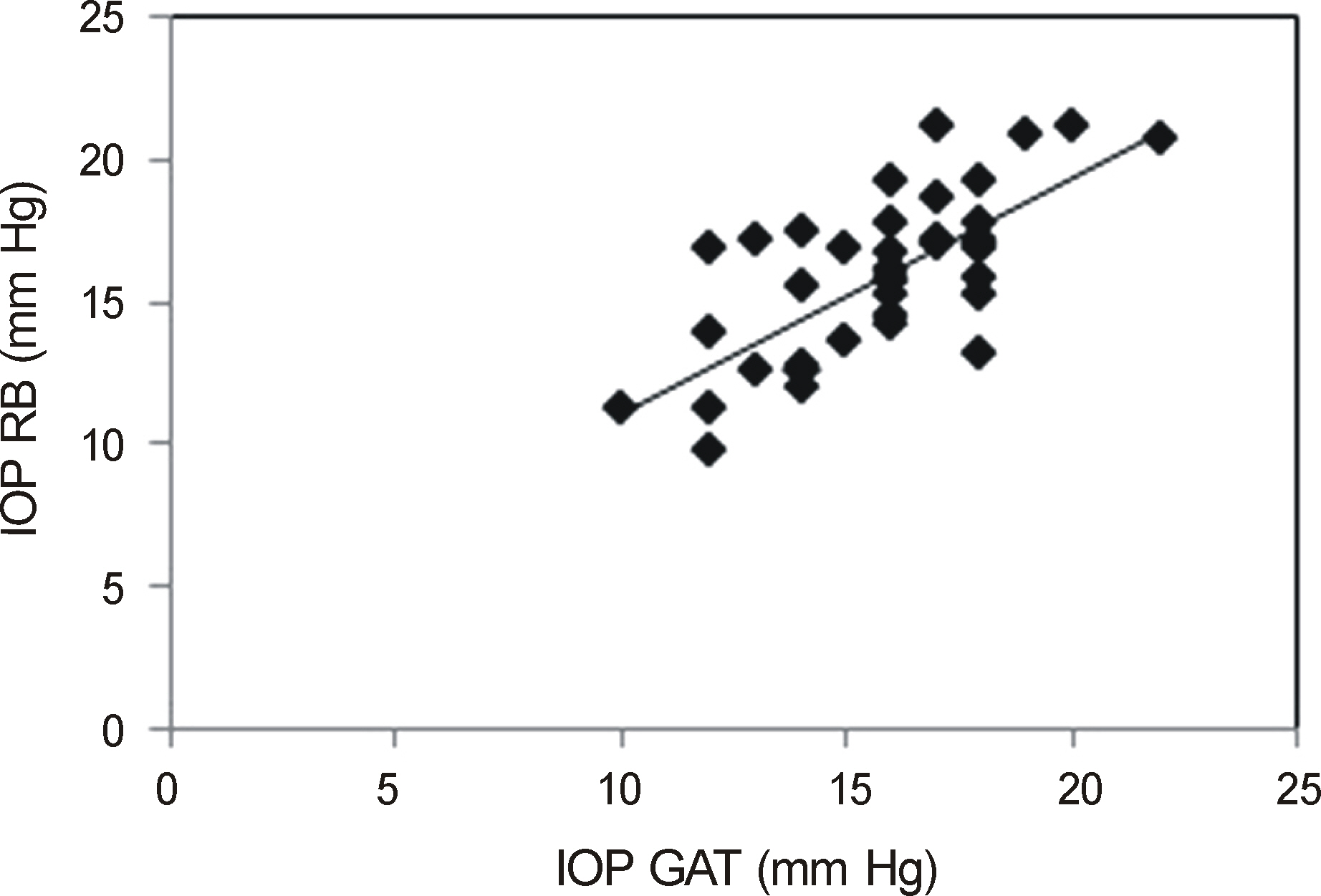
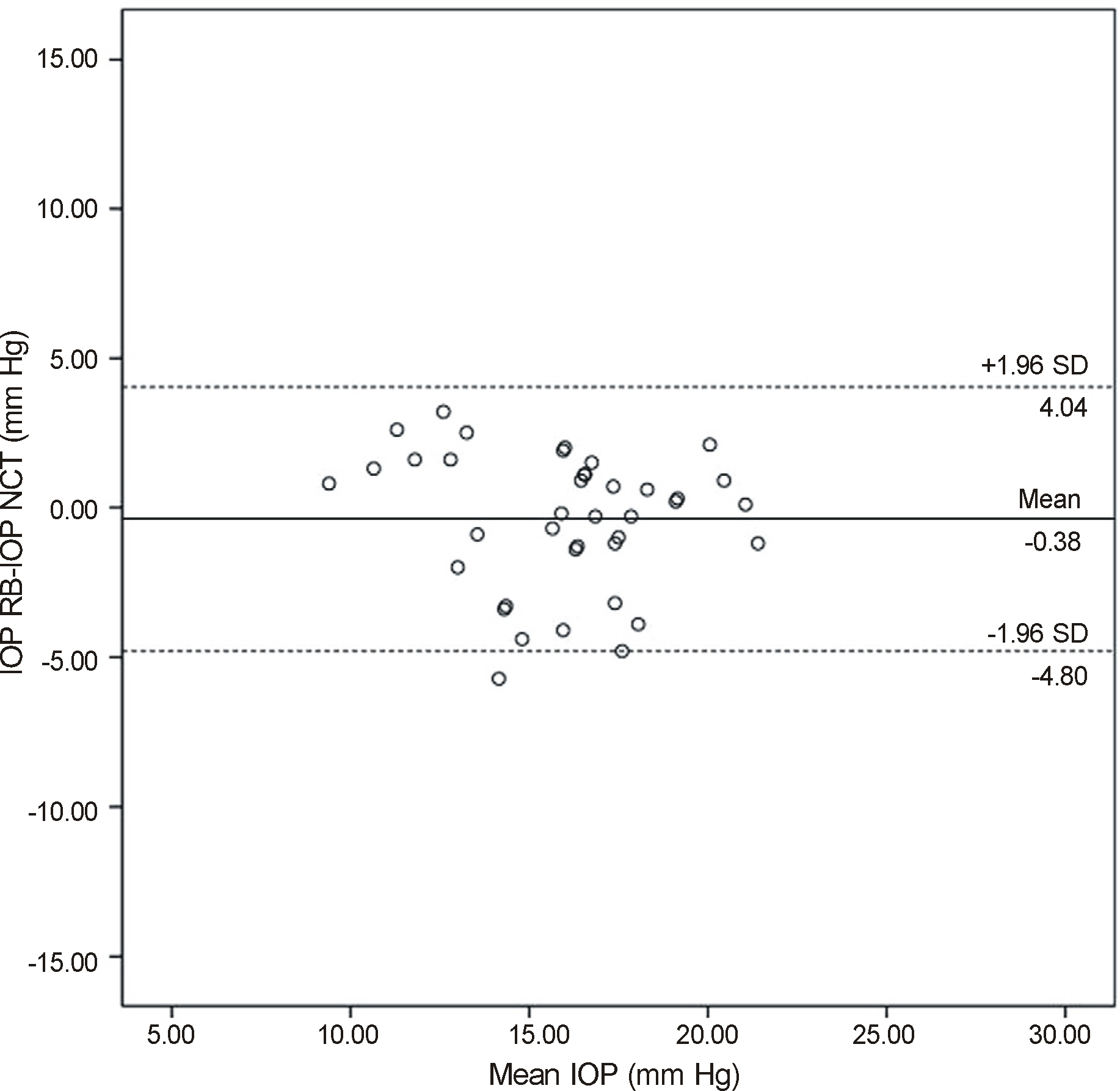
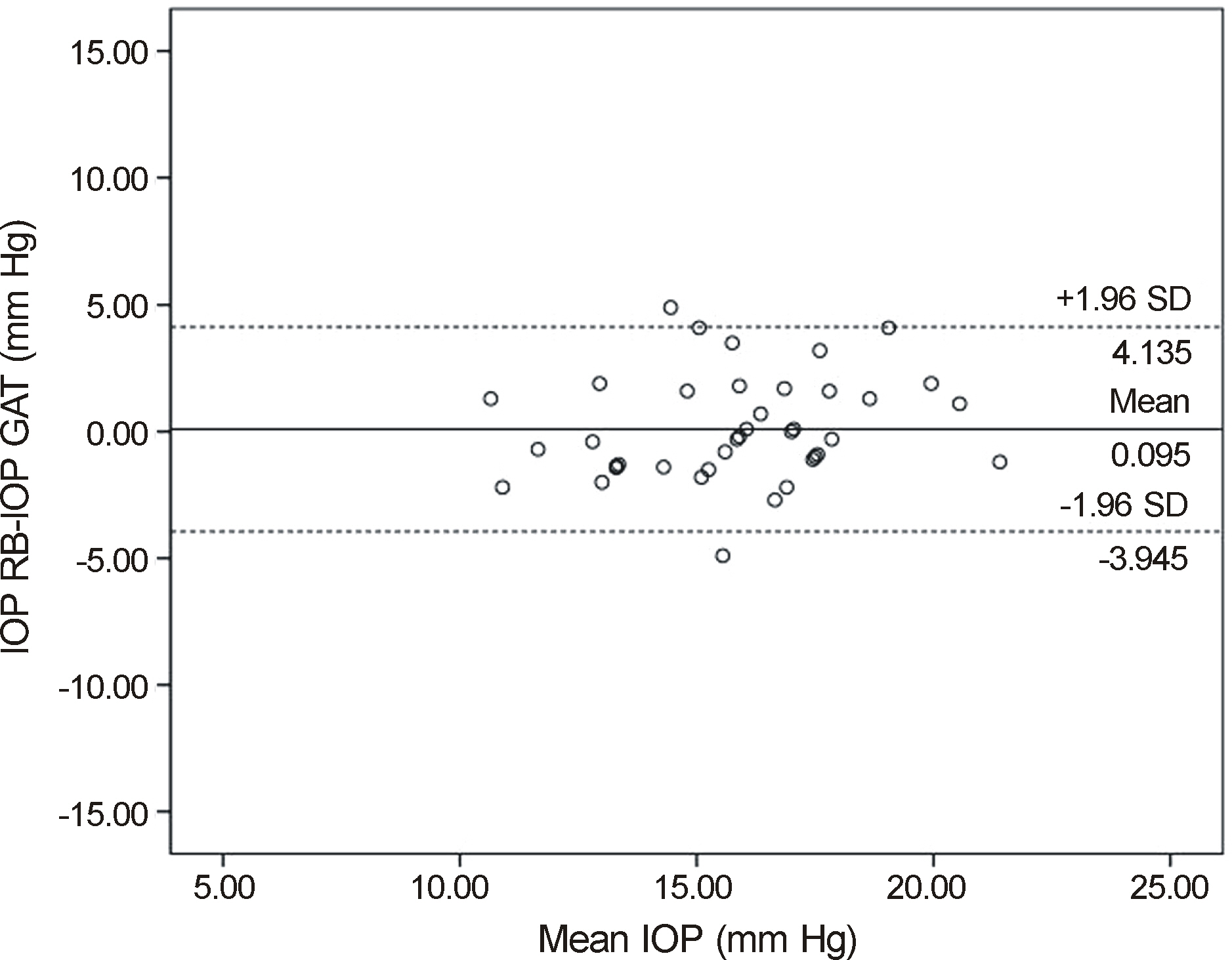
We measured the IOP values of 20 healthy volunteers (40 eyes) in the sitting, supine, right lateral decubitus and left decubitus positions with a portable rebound tonometer, and then analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed rank test. IOP in sitting position was also measured with a non-contact tonometer and a Goldmann applanation tonometer, and analyzed with Kruskal-Wallis test and Spearman correlation analysis. Agreement among the 3 tonometers was calculated using the Bland-Altman method.
RESULTS
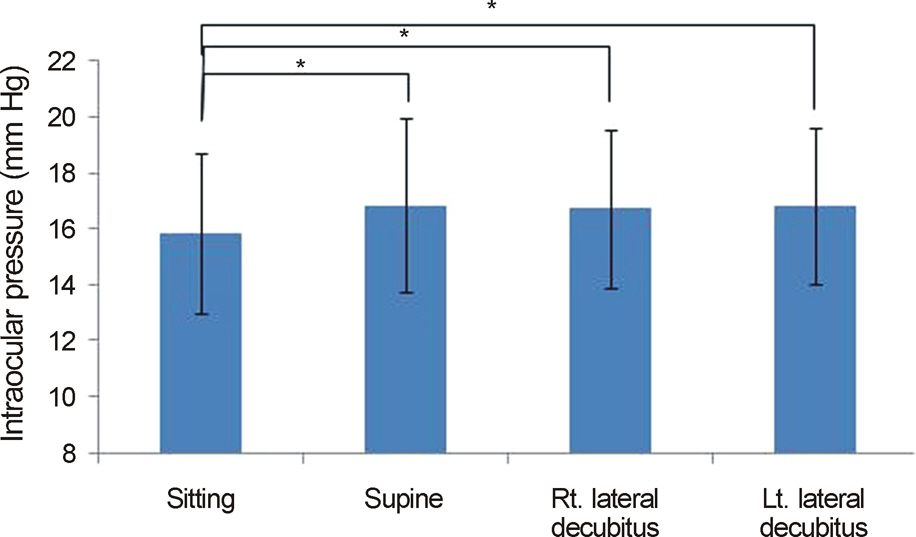
The IOP measured with rebound tonometer in the supine position was significantly higher than in the sitting position (p = 0.002). However, there was no significant difference in IOP between the supine and decubitus positions. In the decubitus position, there was no significant difference in IOP between the dependent and non-dependent eyes. IOP measurement using the rebound tonometer showed positive correlation with that of the noncontact and Goldmann applanation tonometers.
CONCLUSIONS
In normal subjects, IOP measurement obtained with a rebound tonometer in the supine position was significantly higher than in the sitting position, but there was no significant difference in IOP between the supine and decubitus positions. A rebound tonometer may be useful for patients whose intraocular pressure measurement with Goldmann applanation tonometer or non-contact tonometer is impossible. When using a portable rebound tonometer in bed-ridden or pediatric patients, we should pay attention to the interpretation of IOP in the supine position.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Goldmann H, Schmidt T. Applanation tonometry. Ophthalmologica. 1957; 134:221–42.2. Whitacre MM, Stein R. Sources of error with use of Goldmanntype tonometers. Surv Ophthalmol. 1993; 38:1–30.
Article3. Rosentreter A, Neuburger M, Jordan JF, et al. Factors influencing applanation tonometry - a practical approach. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2011; 228:109–13.4. Lee K, Lee JY, Moon JL, Park MH. Comparison of Icare rebound tonometer with Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:296–302.
Article5. Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Castillo A, Garcia-Sanchez J. Reproducibility and clinical evaluation of rebound tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:4578–80.
Article6. Fernandes P, Diaz-Rey JA, Queiros A, et al. Comparison of the ICare rebound tonometer with the Goldmann tonometer in a normal population. Ophthal Physiol Opt. 2005; 25:436–40.7. Garcia-Resua C, Gonzalez-Meijome JM, Gilino J, Yebra-Pimentel E. Accuracy of the new ICare rebound tonometer vs. other portable tonometers in healthy eyes. Optom Vis Sci. 2006; 83:102–7.8. Vincent SJ, Vincent RA, Shields D, Lee GA. Comparison of intraocular pressure measurement between rebound, noncontact and Goldmann applanation tonometry in treated glaucoma patients. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2012; 40:e163–70.
Article9. Takenaka J, Mochizuki H, Kunihara E, et al. Intraocular pressure measurement using rebound tonometer for deviated angels and positions in human eyes. Curr Eye Res. 2012; 37:109–14.10. Jablonski KS, Rosentreter A, Gaki S, et al. Clinical use of a new position-independent rebound tonometer. J Glaucoma. 2013; 22:763–7.
Article11. Anderson DR, Grant WM. The influence of position on intraocular pressure. Invest Ophthalmol. 1973; 12:204–12.12. Kontiola AI. A new induction-based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2000; 78:142–5.
Article13. Kontiola AI, Goldblum D, Mittag T, Danias J. The induction/impact tonometer: a new instrument to measure intraocular pressure in the rat. Exp Eye Res. 2001; 73:781–5.
Article14. Krieglstein GK, Waller WK. Goldmann applanation versus hand-applanation and schiötz indentation tonometry. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1975; 194:11–6.
Article15. Baskett JS, Goen TM, Terry JE. A comparison of Perkins and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Am Optom Assoc. 1986; 57:832–4.16. Lee JY, Yoo C, Jung JH, et al. The effect of lateral decubitus position on intraocular pressure in healthy young subjects. Acta Ophthalmologica. 2012; 90:e68–72.
Article17. Kim HS, Park KH, Jeoung JW. Can we measure the intraocular pressure when the eyeball is against the pillow in the lateral decubitus position. Acta Ophthalmol. 2013; 91:e502–5.
Article18. Lee TE, Yoo C, Kim YY. Effects of different sleeping postures on intraocular pressure and ocular perfusion pressure in healthy young subjects. Ophthalmology. 2013; 120:1565–70.
Article19. Almubrad TM, Ogbuehi KC. On repeated corneal applanation with the Goldmann and two non-contact tonometers. Clin Exp Optom. 2010; 93:77–82.
Article20. Gaton DD, Ehrenberg M, Lusky M, et al. Effect of repeated applanation tonometry on the accuracy of intraocular pressure measurements. Curr Eye Res. 2010; 35:475–9.
Article21. Smith TJ, Lewis J. Effect of inverted body position intraocular pressure. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985; 99:617–8.22. Malihi M, Sit AJ. Effect of head and body position on intraocular pressure. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:987–91.
Article23. Blondeau P, Tétrault JP, Papamarkakis C. Diurnal variation of episcleral venous pressure in healthy patients: a pilot study. J Glaucoma. 2001; 10:18–24.
Article24. Miyamoto S, Tambara K, Tamaki S, et al. Effects of right lateral decubitus position on plasma norepinephrine and plasma atrial natriuretic peptide levels in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2002; 89:240–2.
Article25. Miyamoto S, Fujita M, Sekiguchi H, et al. Effects of posture on cardiac autonomic nervous activity in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001; 37:1788–93.
Article26. Parsley J, Powell RG, Keightley SJ, Elkington AR. Postural response of intraocular pressure in chronic open-angle glaucoma following trabeculectomy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1987; 71:494–6.
Article27. Williams BI, Peart WS, Letley E. Abnormal intraocular pressure control in systemic hypertension and diabetic mellitus. Br J Ophthalmol. 1980; 64:845–51.
Article28. Kim KN, Jeoung JW, Park KH, et al. Effect of lateral decubitus position on intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients with asymmetric visual field loss. Ophthalmology. 2013; 120:731–5.
Article29. Lee CM, Yu YC. Intraocular pressure measurement with the noncontact tonometer and rebound tonometer through plano soft contact lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:662–7.
Article30. Rosentreter A, Athanasopoulos A, Schild AM, et al. Rebound, applanation, and dynamic contour tonometry in pathologic corneas. Cornea. 2013; 32:313–8.
Article31. Suman S, Agrawal A, Pal VK, Pratap VB. Rebound tonomter: Ideal tonometer for measurement of accurate intraocular pressure. J Glaucoma. 2013; [E-pub ahead of print].32. Lee JH, Seong MC, Kang MH, et al. Comparison of rebound tonometer, non-contact tonometer, goldmann applanation tonometer and the relationship to central corneal thickness. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:988–95.
Article33. Lee K, Lee JY, Moon JI, Park MH. Comparison of Icare rebound tonometer with Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:296–302.
Article34. Cook JA, Botello AP, Elders A, et al. Systemic review ofthe agreement of tonometers with Goldmann applanation tonometry. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:1552–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Portable Tonometers and Goldmann Applanation Tonometer for Intraocular Pressure Measurement
- Reliability Comparison of Rebound Tonometer at the Upright and Supine Position
- Usefulness of the Icare ic200 Rebound Tonometer in Korean
- Clinical Comparision of the ProTon and the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer
- Postural Intraocular Pressure Change at Trendelenberg Position Measured by Rebound Tonometer