J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Jan;55(1):102-109.
Comparison of Portable Tonometers and Goldmann Applanation Tonometer for Intraocular Pressure Measurement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwang, Korea. exo70@naver.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
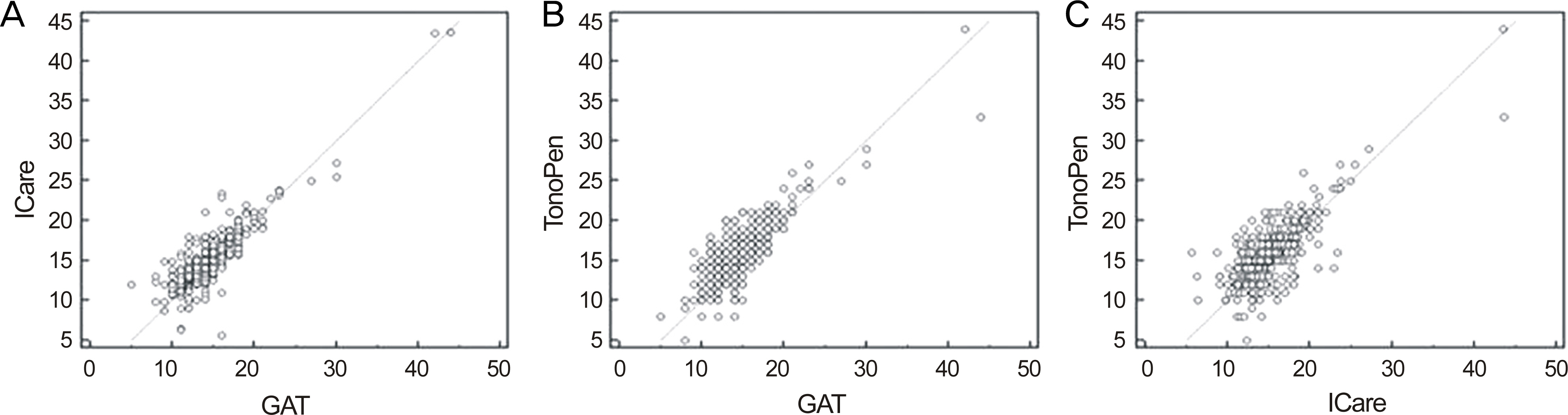
To compare the intraocular pressure (IOP) measured by portable rebound tonometer and TonoPen applanation tonometer with pressure measured by Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT) and analyze the factors affecting IOP disagreement between tonometers.
METHODS
In a prospective study of 463 eyes, IOP was measured with Icare Pro(R) rebound tonometer, TonoPen AVIA(R) applanation tonometer, and GAT. Bland-Altman plot, intraclass correlation coefficient, Pearson's correlation analysis, and multiple regression analysis were performed to evaluate the agreement of IOP measured by each tonometer and the factors affecting the measurements.
RESULTS
The IOP values measured by Icare Pro(R) and TonoPen AVIA(R) were consistently higher than those measured by GAT, but showed no significant differences with those measured by GAT (p = 0.307 and 0.114, respectively). In Bland-Altman plot, the IOP values measured by Icare Pro(R) and TonoPen AVIA(R) exhibited excellent agreement with those measured by GAT. Both Icare Pro(R)/GAT and TonoPen AVIA(R)/GAT differences increased with younger age (p = 0.041 and 0.049, respectively) and higher central corneal thickness (p = 0.019 and 0.035, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
IOPs measured by portable Icare Pro(R) rebound tonometer and TonoPen AVIA(R) applanation tonometer were significantly correlated with IOP measured by GAT. Therefore, such instruments can be useful when measuring IOP with GAT is difficult. However, central corneal thickness and age should be considered when measuring IOP with portable tonometers.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Comparison of glaucomatous progression between untreated pa-tients with normal-tension glaucoma and patients with therapeuti-cally reduced intraocular pressures. Collaborative Normal-Tension Glaucoma Study Group. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:487–97.2. The Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS): 7. The rela-tionship between control of intraocular pressure and visual field deterioration. The AGIS Investigators. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:429–40.3. Kass MA, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ. . The Ocular Hyper- tension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that top-ical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002; 120:701–13. discussion 829-30.4. Leske MC, Heijl A, Hyman L. . EMGT Group. Predictors of long-term progression in the early manifest glaucoma trial. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:1965–72.
Article5. Kontiola A.A new electromechanical method for measuring intra-ocular pressure. Doc Ophthalmol. 1996-1997; 93:265–76.
Article6. Kanngiesser HE, Kniestedt C, Robert YC.Dynamic contour ton-ometry: presentation of a new tonometer. J Glaucoma. 2005; 14:344–50.7. Luce DA.Determining in vivo biomechanical properties of the cornea with an ocular response analyzer. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:156–62.
Article8. Iliev ME, Goldblum D, Katsoulis K. . Comparison of rebound tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry and correlation with central corneal thickness. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006; 90:833–5.
Article9. Cook JA, Botello AP, Elders A. et al. Surveillance of Ocular Hypertension Study Group. Systematic review of the agreement of tonometers with Goldmann applanation tonometry. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:1552–7.10. Kotecha A, White ET, Shewry JM, Garway-Heath DF. The relative effects of corneal thickness and age on Goldmann applanation ton-ometry and dynamic contour tonometry. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005; 89:1572–5.
Article11. Broman AT, Congdon NG, Bandeen-Roche K, Quigley HA.Influence of corneal structure, corneal responsiveness, and other ocular parameters on tonometric measurement of intraocular pressure. J Glaucoma. 2007; 16:581–8.
Article12. Frenkel RE, Hong YJ, Shin DH.Comparison of the Tono-Pen to the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988; 106:750–3.
Article13. Iester M, Mermoud A, Achache F, Roy S.New Tonopen XL: com-parison with the Goldmann tonometer. Eye (Lond). 2001; 15(Pt 1):52–8.
Article14. Brusini P, Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M. . Comparison of ICare ton-ometer with Goldmann applanation tonometer in glaucoma patients. J Glaucoma. 2006; 15:213–7.
Article15. Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Castillo A, Garcia- Sanchez J.Reproducibility and clinical evaluation of rebound tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:4578–80.
Article16. Danias J, Kontiola AI, Filippopoulos T, Mittag T.Method for the noninvasive measurement of intraocular pressure in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:1138–41.
Article17. Jablonski KS, Rosentreter A, Gaki S. . Clinical use of a new position-independent rebound tonometer. J Glaucoma. 2013; 22:763–7.
Article18. Ehlers N, Hansen FK, Aasved H.Biometric correlations of corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1975; 53:652–9.
Article19. Whitacre MM, Stein R.Sources of error with use of Goldmann-type tonometers. Surv Ophthalmol. 1993; 38:1–30.
Article20. Chihara E.Assessment of true intraocular pressure: the gap be-tween theory and practical data. Surv Ophthalmol. 2008; 53:203–18.
Article21. Pakrou N, Gray T, Mills R. . Clinical comparison of the Icare tonometer and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Glaucoma. 2008; 17:43–7.
Article22. Poostchi A, Mitchell R, Nicholas S. . The iCare rebound ton-ometer: comparisons with Goldmann tonometry, and influence of central corneal thickness. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2009; 37:687–91.
Article23. Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Vico E. . Effect of corneal thickness on dynamic contour, rebound, and goldmann tonometry. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:2156–62.
Article24. Halkiadakis I, Stratos A, Stergiopoulos G. . Evaluation of the Icare-ONE rebound tonometer as a self-measuring intraocular pressure device in normal subjects. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:1207–11.
Article25. Bhartiya S, Bali SJ, Sharma R. . Comparative evaluation of TonoPen AVIA, Goldmann applanation tonometry and non-contact tonometry. Int Ophthalmol. 2011; 31:297–302.
Article26. Rosentreter A, Jablonski KS, Mellein AC. . A new rebound tonometer for home monitoring of intraocular pressure. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011; 249:1713–9.
Article27. Sakamoto M, Kanamori A, Fujihara M. . Assessment of IcareONE rebound tonometer for self-measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol. 2013.
Article28. Kim KN, Jeoung JW, Park KH. . Comparison of the new re-bound tonometer with Goldmann applanation tonometer in a clin-ical setting. Acta Ophthalmol. 2013; 91:e392–6.
Article29. Hessemer V, Rössler R, Jacobi KW.Tono-pen, a new position-in-dependent tonometer. Comparison with the Goldmann tonometer by applanation measurement]. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1988; 193:420–6.30. Rao A, Kumar M, B P, Varshney G. Relationship of central corneal thickness and intraocular pressure by iCare rebound tonometer. J Glaucoma. 2012.
Article31. Dohadwala AA, Munger R, Damji KF.Positive correlation be-tween Tono-Pen intraocular pressure and central corneal thickness. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:1849–54.
Article32. Mok KH, Wong CS, Lee VW.Tono-Pen tonometer and corneal thickness. Eye (Lond). 1999; 13(Pt 1):35–7.
Article33. Bhan A, Browning AC, Shah S. . Effect of corneal thickness on intraocular pressure measurements with the pneumotonometer, Goldmann applanation tonometer, and Tono-Pen. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002; 43:1389–92.34. Kim NR, Kim CY, Kim H. . Comparison of goldmann applana-tion tonometer, noncontact tonometer, and TonoPen XL for intra-ocular pressure measurement in different types of glaucomatous, ocular hypertensive, and normal eyes. Curr Eye Res. 2011; 36:295–300.
Article35. Jorge JM, González-Méijome JM, Queirós A. . Correlations between corneal biomechanical properties measured with the ocu-lar response analyzer and ICare rebound tonometry. J Glaucoma. 2008; 17:442–8.
Article36. Chui WS, Lam A, Chen D, Chiu R.The influence of corneal prop-erties on rebound tonometry. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115:80–4.
Article37. Weinreb RN, Toris CB, Gabelt BT. . Effects of prostaglandins on the aqueous humor outflow pathways. Surv Ophthalmol. 2002; 47(Suppl 1):S53–64.
Article38. Harasymowycz PJ, Papamatheakis DG, Ennis M. et al. Travoprost Central Corneal Thickness Study Group. Relationship between travoprost and central corneal thickness in ocular hypertension and open-angle glaucoma. Cornea. 2007; 26:34–41.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Intraocular Pressures According to Position Using Icare Rebound Tonometer
- Clinical Comparision of the ProTon and the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer
- The Influence of Central Corneal Thickness on Intraocular Pressures Measured with Goldmann Applanation Tonometer and Non-contact Tonometer
- Comparison of the Noncontact Tonometer with Goldmann Tonometer
- Clinical Evaluation of A Noncontact Applanation Tonometer