J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Dec;52(12):1440-1447. 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.12.1440.
A Randomized, Prospective Clinical Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Topical Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in Ophthalmologic Microsurgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. okeye@hanmir.com
- 2Department of Molecular Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine and Clinical Trial Center of Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2215147
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2011.52.12.1440
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report the results of a clinical comparison study of a prophylactic new generation fluoroquinolone (FQs; levofloxacin 0.5%, gatifloxacin 0.3% and moxifloxacin 0.5%) topical antibiotic regimen administered prior to intraocular microsurgery.
METHODS
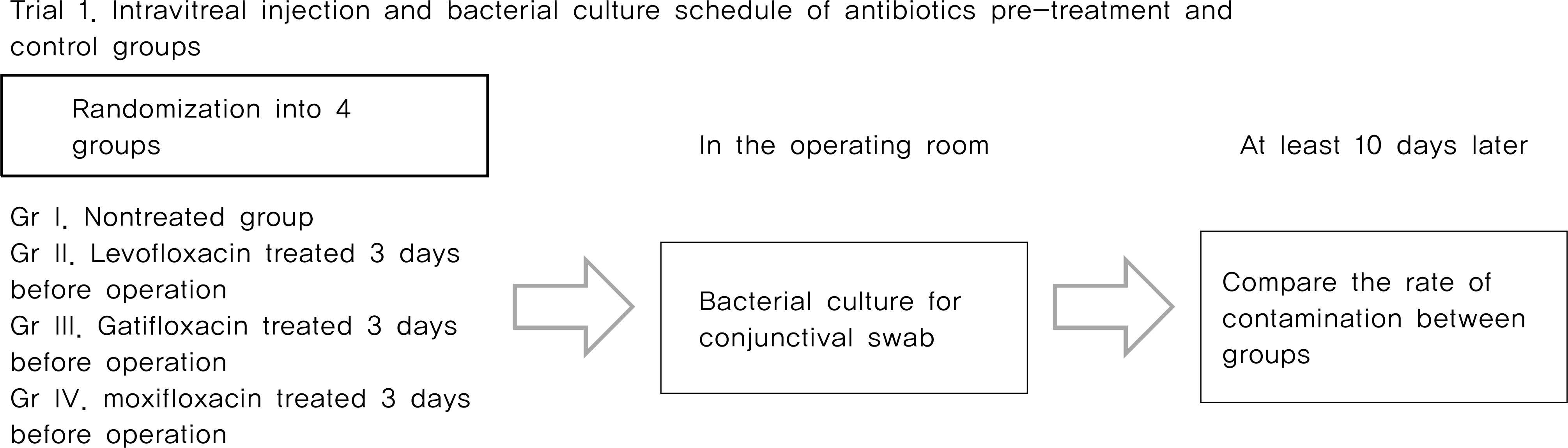
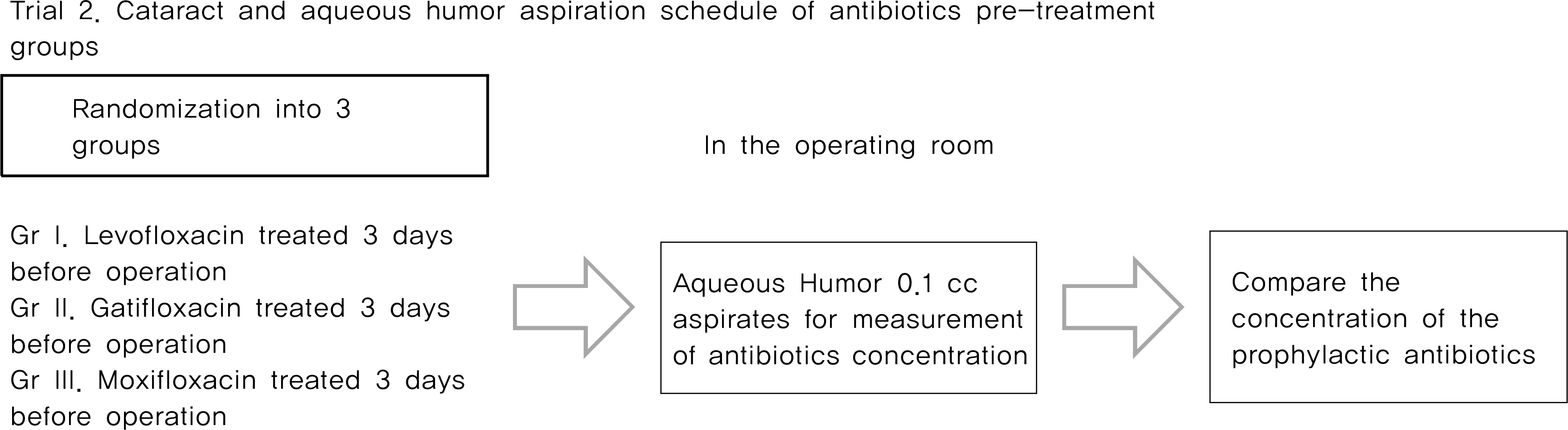
From May 2007 to April 2010, Trial 1, 214 eyes of 211 patients scheduled for intravitreal injection were randomized into one of three FQ-treated groups or the control (non-treated) group. Patients who were randomized into FQ-treated groups were treated with eye drops containing one of three FQ antibiotics (levofloxacin 0.5%, gatifloxacin 0.3% and moxifloxacin 0.5%) preoperatively four times a day for three days before surgery. The rate of positive bacterial cultures from conjunctival scrapings were assessed and compared. Trial 2, 159 eyes of 159 patients scheduled for cataract surgery were randomized into one of three FQ-treated groups, and treated with eye drops as same method in trial 1. The concentration of antibiotics in the anterior chamber of the eye were measured and compared.
RESULTS
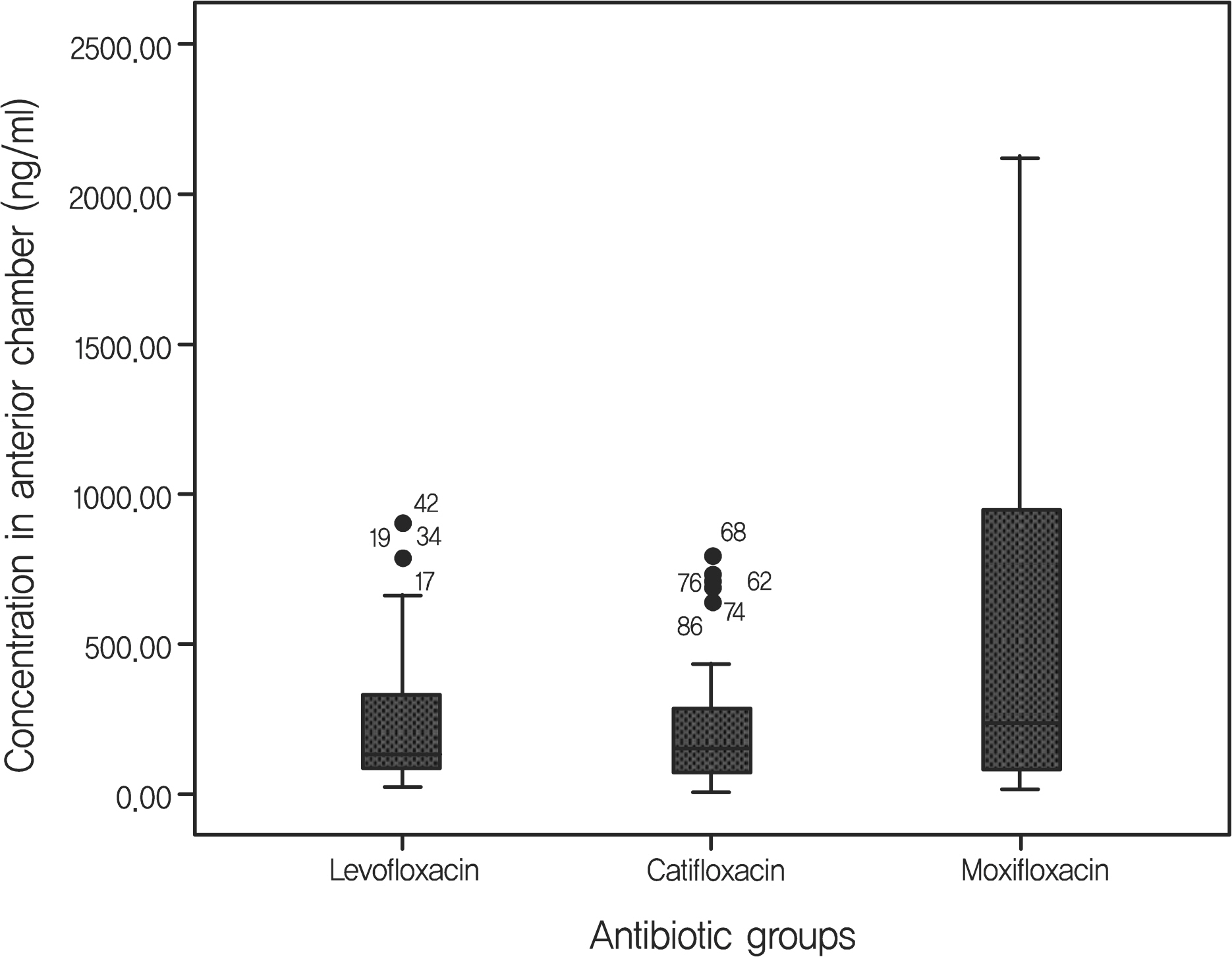
The positive bacterial culture rates of trial 1 were 48.9%, 38.3%, 23.4% in the levofloxacin-treated group, the gatifloxacin- group, and the moxifloxacin-treated group, respectively. These rates were all significantly lower than the 70.2% positivity rate observed in the control group. Average antibiotic residue concentrations in the aqueous humor measured in trial 2 were 0.37 +/- 0.49 microg/ml in the levofloxacin-treated group, 0.31 +/- 0.37 microg/ml in the gatifloxacin-treated group and 0.59 +/- 0.72 microg/ml in the moxifloxacin-treated group. These concentrations were not significantly different. There were no reported side effects during the study period.
CONCLUSIONS
Eye drops containing new generation FQ antibiotics instilled three days before microscopic ophthalmic surgery can be used safely and effectively for the prevention of postoperative endophthalmitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Analysis of the 0.3% Tosufloxacin Ophthalmic Solution Effect on Conjunctival Normal Flora
Young Ki Kwon, Kun Wook Kang, Hong Kyun Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(2):199-204. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.2.199.
Reference
-
References
1. Speaker MG, Milch FA, Shah MK, et al. Role of external bacterial flora in the pathogenesis of acute postoperative endophthalmitis. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:639–49.
Article2. Inoue Y, Usui M, Ohashi Y, et al. Preoperative disinfection of the conjunctival sac with antibiotics and iodine compounds: a prospective randomized multicenter study. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2008; 52:151–61.
Article3. Ng JQ, Morlet N, Bulsara MK, Semmens JB. Reducing the risk for endophthalmitis after cataract surgery: population-based nested case-control study: endophthalmitis population study of Western Australia sixth report. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:269–80.4. Gills JP. Filters and antibiotics in irrigating solution for cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1991; 17:385.
Article5. Peyman GA, Sathar ML, May DR. Intraocular gentamicin as intraoperative prophylaxis in South India eye camps. Br J Ophthalmol. 1977; 61:260–2.
Article6. Garat M, Moser CL, Martin-Baranera M, et al. Prophylactic intra-cameral cefazolin after cataract surgery: endophthalmitis risk reduction and safety results in a 6-year study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:637–42.7. Barza M, Doft B, Lynch E. Ocular penetration of ceftriaxone, cef-tazidime, and vancomycin after subconjunctival injection in humans. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:492–4.
Article8. Iyer MN, Han DP, Yun HJ, et al. Subconjunctival antibiotics for acute postcataract extraction endophthalmitis–is it necessary? Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:1120–1.
Article9. Seal DV, Barry P, Gettinby G, et al. ESCRS study of prophylaxis of postoperative endophthalmitis after cataract surgery: Case for a European multicenter study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:396–406.10. Barry P, Seal DV, Gettinby G, et al. ESCRS study of prophylaxis of postoperative endophthalmitis after cataract surgery: Preliminary report of principal results from a European multicenter study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:407–10.11. Hara J, Yasuda F, Higashitsutsumi M. Preoperative disinfection of the conjunctival sac in cataract surgery. Ophthalmologica. 1997; 211:62–7.
Article12. Snyder-Perlmutter LS, Katz HR, Melia M. Effect of topical ciprofloxacin 0.3% and ofloxacin 0.3% on the reduction of bacterial flora on the human conjunctiva. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:1620–5.
Article13. Barkana Y, Almer Z, Segal O, et al. Reduction of conjunctival bacterial flora by povidone-iodine, ofloxacin and chlorhexidine in an outpatient setting. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005; 83:360–3.
Article14. De Kaspar HM, Chang RT, Shriver EM, et al. Three-day application of topical ofloxacin reduced the contamination rate of micro-surgical knives in cataract surgery: a prospective randomized study. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:1352–5.15. Wilhelmus KR, Penland RL. Emerging resistance among ocular isolates of gram-positive cocci [abstract]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996; 37:S877.16. Goldstein MH, Kowalski RP, Gordon YJ. Emerging fluoroquinolone resistance in bacterial keratitis: a 5 year review. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:1313–8.17. Pinna A, Zanetti S, Sotgui M, et al. Identification and antibiotic susceptibility of coagulase negative staphylococci isolated in cor-nea/external infections. Br J Ophthalmol. 1999; 83:771–3.18. Marangon FB, Miller D, Muallem MS, et al. Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin resistance among methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus isolates from keratitis and conjunctivitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:453–8.
Article19. Taban M, Behrens A, Newcomb RL, et al. Acute endophthalmitis following cataract surgery: a systematic review of the literature. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005; 123:613–20.20. Han DP, Wisniewski SR, Wilson LA, et al. Spectrum and suscepti-bilities of microbiologic isolates in the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996; 122:1–17.
Article21. Chung SE, Ham DI. Visual prognosis of culture-proven bacterial endophthalmitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1292–7.22. Levine JM, Noecker RJ, Lane LC, et al. Comparative penetration of moxiflocacin and gatifloxacin in rabbit aqueous humor after topical dosing. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:2177–82.23. Kim DH, Stark WJ, O'Brien TP, Dick JD. Aqueous penetration and biological activity of moxifloxacin 0.5% ophthalmic solution and gatifloxacin 0.3% solution in cataract surgery patents. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1992–6.24. Kowalski RP, Yates KA, Romanowski EG, et al. An ophthalmologist's guide to understanding antibiotic susceptibility and minimum inhibitory concentration data. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1987.
Article25. Hori Y, Nakazawa T, Maeda N, et al. Susceptibility comparisons of normal preoperative conjunctival bacteria to fluoroquinolones. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:475–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Preoperative Topical Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in Intraocular Surgery
- A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials of Antibiotic Use in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Infections: Focus on Clinical Cure
- Do we need topical antibiotics for simple excision or the dressing after a skin wound?
- The use of fluoroquinolone in children
- Risk Factors for Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Ocular Cultures