Gram-Negative Bacterial Keratitis: A 15-Year Review of Clinical Aspects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. sbummlee@ynu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2214405
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.10.1479
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In this study we investigated pathogenic organisms, antibiotic susceptibility, and clinical characteristics of patients with Gram-negative bacterial keratitis and elucidated risk factors for poor visual outcomes.
METHODS
The authors performed a retrospective chart review of 161 eyes (169 isolates) with Gram-negative bacterial keratitis between January 1998 and December 2012 at Yeungnam University Hospital. The study was divided into 5 periods for analysis of the bacteriological profiles and in vitro antibiotic sensitivity. The epidemiological and clinical characteristics were compared according to 3 groups (Pseudomonas species, Enterobacter species, and Serratia marcescens). Additionally, logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the risk factors.
RESULTS
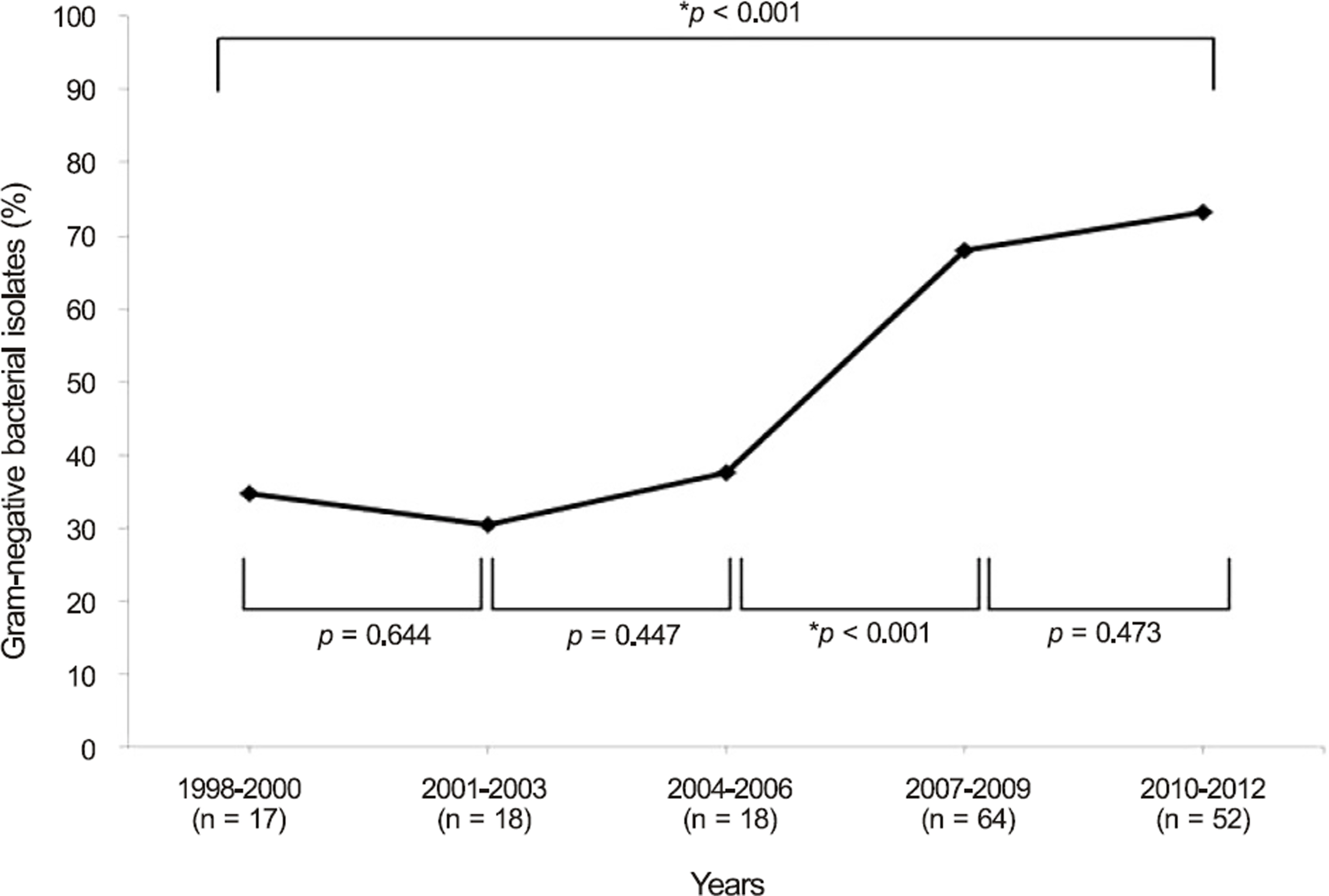
The prevalence of Gram-negative organisms increased from 34.7 to 73.2% between the 1st and 5th periods (p < 0.001). Pseudomonas spp. was the most commonly isolated organism (55 eyes, 32.5%) over the total period, followed by Enterobacter spp. (41 eyes, 24.3%) and Serratia marcescens (33 eyes, 19.5%). The effective antibiotics against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens isolated from culture were cefepime (94.5%), levofloxacin (93.4%), ciprofloxacin (93.0%), and amikacin (92.3%). The incidence was higher in the elderly over 60 years of age and in early adulthood patients in their 20s and 30s. The frequent predisposing factors were contact lens wearing and corneal trauma. S. marcescens had the shortest corneal epithelium healing time (p = 0.012) and the most favorable visual outcome after treatment (p = 0.004) compared with the other species. Risk factors for poor visual outcomes included a best corrected visual acuity less than 0.1 at initial evaluation (p < 0.001) and central corneal lesion (p = 0.027).
CONCLUSIONS
Gram-negative bacterial keratitis tended to increase and Pseudomonas spp. was the most common isolate. The clinical prognosis was most favorable in S. marcescens. Early diagnosis of Gram-negative bacterial keratitis and appropriate antibiotic selection including cefepime, quinolone, or amikacin are recommended.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Clinical Analysis of Bacterial Keratitis According to Culture Positivity
Doyeon Kim, Chan Ho Cho, Sang-Bumm Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2019;60(11):1027-1036. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.11.1027.Clinical Aspects of Infectious Keratitis in Western Gyeongsangnamdo, Republic of Korea
Mi-Hwa Park, Woong-Sun Yoo, Gyu-Nam Kim, Yong-Wun Cho, Seong-Wook Seo, Seong-Jae Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2019;60(8):731-739. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.8.731.Clinical Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Keratitis according to Methicillin-resistance
Jang Hwan Ahn, Sang-Bumm Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2017;58(8):885-895. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.8.885.Clinical Aspects and Treatment Outcomes of Moraxella keratitis
Yong Yeon Song, Sora Bang, Tae Eun Lee, Wan Seok Kang, In Cheon You
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(3):209-216. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.3.209.
Reference
-
References
1. Lichtinger A, Yeung SN, Kim P. . Shifting trends in bacterial keratitis in Toronto: an 11-year review. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:1785–90.2. Asbell P, Stenson S. Ulcerative keratitis. Survey of 30 years' labo-ratory experience. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982; 100:77–80.3. Orlans HO, Hornby SJ, Bowler IC. In vitro antibiotic susceptibility patterns of bacterial keratitis isolates in Oxford, UK: a 10-year review. Eye (Lond). 2011; 25:489–93.
Article4. Hahn YH, Lee SJ, Hahn TW. . Antibiotic susceptibilities of ocular isolates from patients with bacterial ke ratitis: a Multi-center Study. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2401–10.5. Lim SH, Lee SB. Analysis of inpatients with bacterial keratitis over a 12-year period: pathogenic organisms and antibiotic resistance. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:372–84.
Article6. Kim WJ, Kweon EY, Lee DW. . Prognostic factor and anti-biotic susceptibility in bacterial keratitis: results of an eight-year period. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1495–504.
Article7. Sun HJ, Lee JY, Kim SY, Jung MS. Clinical features of infectious keratitis in west coast area of Chungcheongnam-do, Korea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:658–63.
Article8. Tuft SJ, Matheson M. In vitro antibiotic resistance in bacterial keratitis in London. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000; 84:687–91.
Article9. Fong CF, Hu FR, Tseng CH. . Antibiotic susceptibility of bacterial isolates from bacterial keratitis cases in a university hospital in Taiwan. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 144:682–9.
Article10. Toshida H, Kogure N, Inoue N, Murakami A. Trends in microbial keratitis in Japan. Eye Contact Lens. 2007; 33:70–3.
Article11. Park JH, Lee SB. Analysis on inpatients with infectious keratitis: causative organisms, clinical aspects and risk factors. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1152–66.
Article12. Kim SJ, Lee SB. Analysis on elderly inpatients with infectious keratitis: causative organisms, clinical aspects, and risk factors. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:1554–67.
Article13. Kim JY, Yoon KC, Park YG. . Age-related clinical analysis of infectious keratitis in two tertiary centers. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:927–34.
Article14. Yoon JH, Jung JW, Moon HS. . Antibiotics susceptibility in bacterial keratitis and proper initial treatment. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:38–45.
Article15. Shin SY, Koo SH, Kwon KC. . Evaluation of the Vitek 2 Korean antimicrobial susceptibility testing cards AST N056 and AST N055. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2008; 11:23–8.
Article16. Mukerji N, Vajpayee RB, Sharma N. Technique of area measure-ment of epithelial defects. Cornea. 2003; 22:549–51.
Article17. Biemer JJ. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing by the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1973; 3:135–40.18. Jorgensen JH, Hindler JF. New consensus guidelines from the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute for antimicrobial sus-ceptibility testing of infrequently isolated or fastidious bacteria. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 44:280–6.
Article19. Green MD, Apel AJ, Naduvilath T, Stapleton FJ. Clinical out-comes of keratitis. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2007; 35:421–6.
Article20. Kim MR, Lee SB. Clinical and microbiological analysis of Gram- positive bacterial keratitis, a 15-year review. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:1432–44.21. Zhang C, Liang Y, Deng S. . Distribution of bacterial keratitis and emerging resistance to antibiotics in China from 2001 to 2004. Clin Ophthalmol. 2008; 2:575.22. Hahn YH, Hahn TW, Tchah H. . Epidemiology of infectious keratitis(II): a Multi-center Study. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:247–65.23. Cho CH, Lee SB. Analysis of inpatients with contact lens related bacterial keratitis: causative microorganisms, clinical aspects, and prognostic factors. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1327–38.
Article24. Green M, Apel A, Stapleton F. A longitudinal study of trends in keratitis in Australia. Cornea. 2008; 27:33–9.
Article25. Afshari NA, Ma JJ, Duncan SM. . Trends in resistance to cipro-floxacin, cefazolin, and gentamicin in the treatment of bacterial keratitis. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 24:217–23.
Article26. Yeh DL, Stinnett SS, Afshari NA. Analysis of bacterial cultures in infectious keratitis, 1997 to 2004. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:1066–8.
Article27. Mantadakis E, Maraki S, Michailidis L. . Antimicrobial sus-ceptibility of Gram-positive cocci isolated from patients with con-junctivitis and keratitis in Crete, Greece. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2013; 46:41–7.
Article28. Ahn G, Hahn YH, Lee HB. Serratia marcescens keratitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:658–64.29. Hahn YH, Lee SJ, Hahn YW. . Epidemiology of Pseudomonas keratitis: a multi center study. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2411–22.30. Tchah H, Kim JC, Hahn TW, Hahn YH. Epidemiology of contact lens related infectious keratitis(1995.4~1997.9): Multi-center Study. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:1417–26.31. Potron A, Poirel L, Bernabeu S. . Nosocomial spread of ESBL-positive Enterobacter cloacae co-expressing plasmid-medi-ated quinolone resistance Qnr determinants in one hospital in France. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 64:653–4.
Article32. Bourcier T, Thomas F, Borderie V. . Bacterial keratitis: predis-posing factors, clinical and microbiological review of 300 cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:834–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of Inpatients with Bacterial Keratitis Over a 12-Year Period: Pathogenic Organisms and Antibiotic Resistance
- Analysis on Inpatients With Infectious Keratitis: Causative Organisms, Clinical Aspects and Risk Factors
- Clinical and Microbiological Analysis of Gram-Positive Bacterial Keratitis, a 15-Year Review
- Analysis on Elderly Inpatients with Infectious Keratitis: Causative Organisms, Clinical Aspects, and Risk Factors
- Metallo-beta-lactamase Producing Gram-negative Bacilli